This document discusses biodiesel, including its history, definition, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and future potential. It provides a case study on using microalgae for biodiesel production in Iran. The key points are:
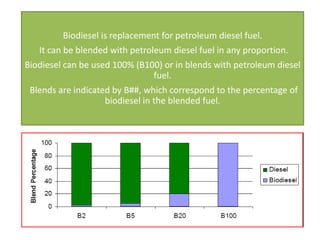
1) Biodiesel is made from vegetable oils or animal fats through a process called transesterification. It can be used in many vehicles and applications as a replacement for or blended with petroleum diesel.
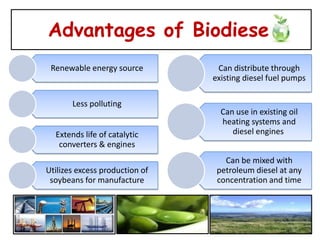
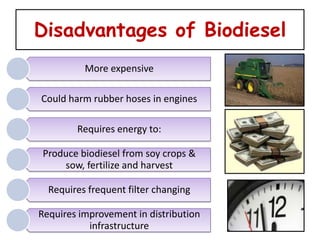
2) Advantages include being renewable and less polluting, while disadvantages include higher costs and infrastructure requirements.
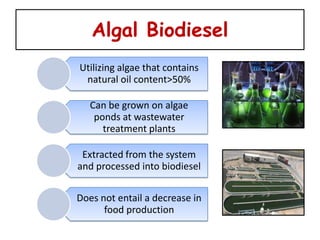
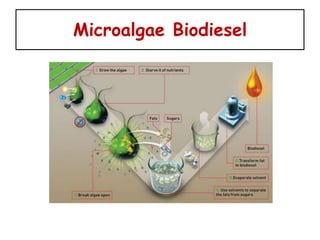
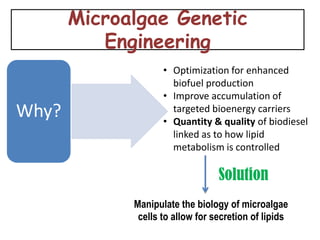
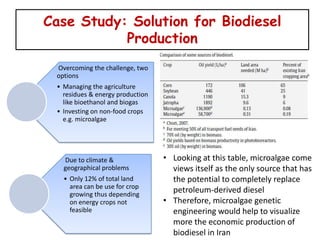
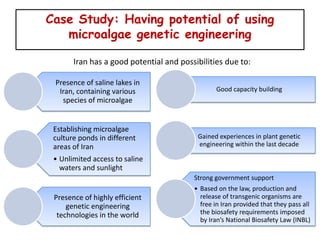
3) Future potential lies in genetically engineering microalgae which can produce high oil yields without affecting food supplies or requiring much land. A case