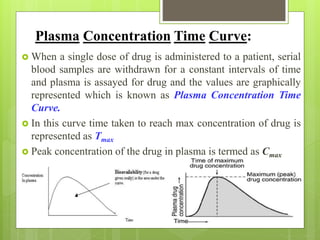
Dr. Priyanka Patil's seminar addresses the concepts of bioavailability (BA) and bioequivalence (BE) in drug administration, highlighting that oral drug absorption is often incomplete due to various factors. BA refers to the rate and extent of drug absorption, while BE compares the bioavailability of two chemically equivalent drugs to ensure therapeutic equivalence. The seminar emphasizes the importance of assessing BA and BE to ensure optimal and consistent drug absorption for safe and effective treatment.