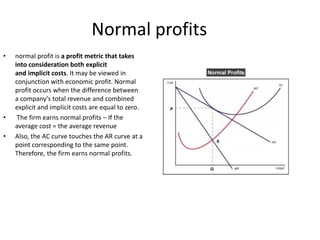
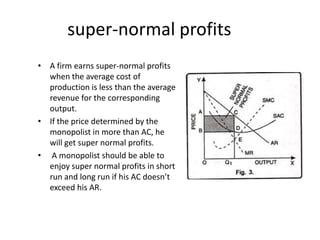
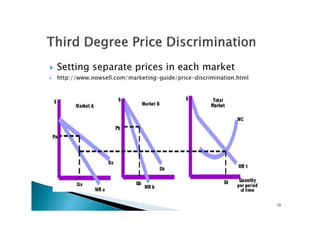
The document discusses different types of monopoly profits and pricing strategies. It defines normal profits as occurring when revenue equals costs. Super-normal profits are earned when costs are less than revenue. The monopolist aims to produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost to maximize profits, earning profits represented by the area between the average cost and demand curves. Price discrimination allows a monopolist to charge different prices to different groups to enhance profits by more closely aligning prices with what different consumers are willing to pay.