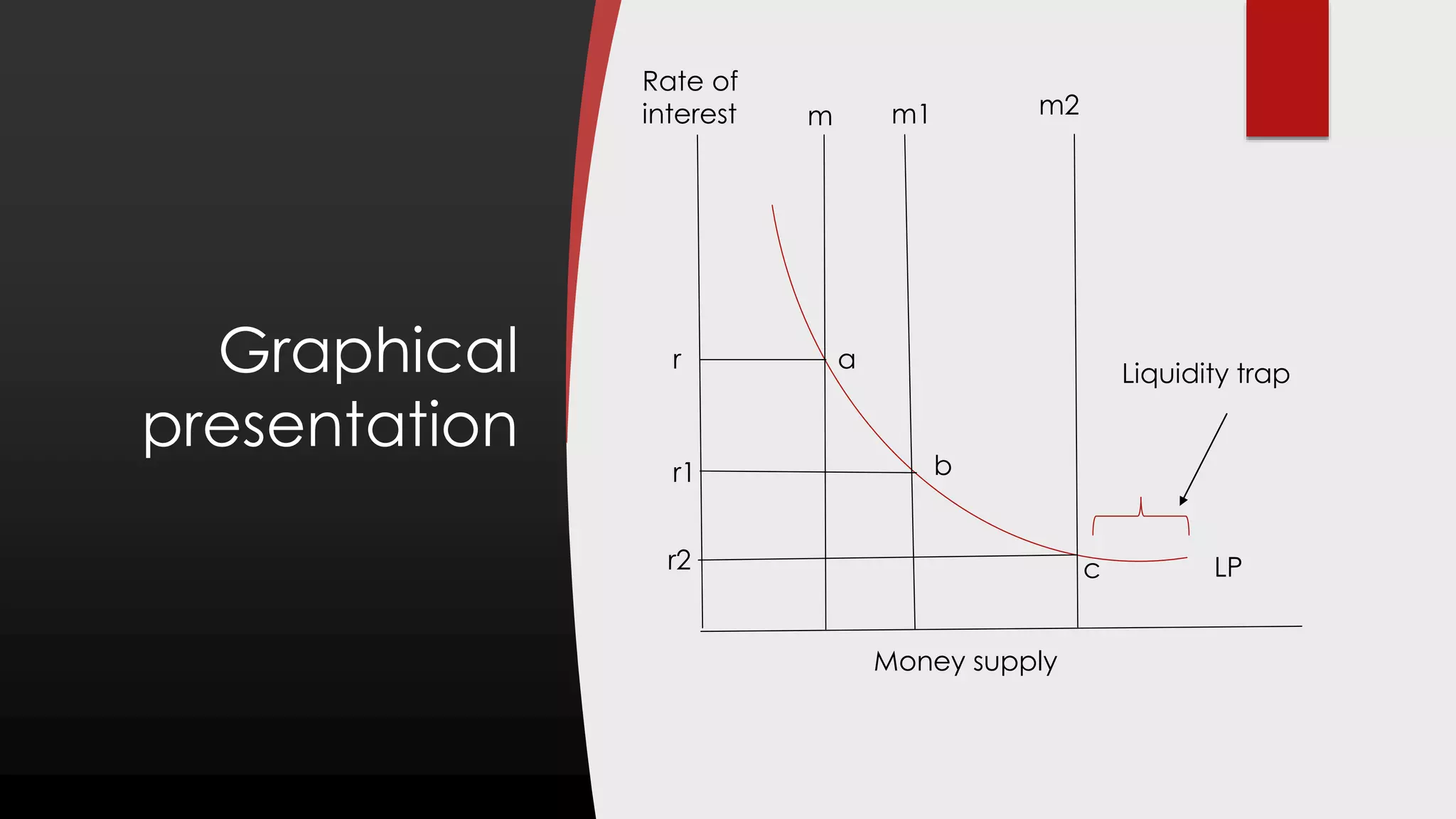
The presentation discusses liquidity preference theory as proposed by John Maynard Keynes, highlighting the concept of liquidity and its significance in investment and spending. It outlines three motives for liquidity demand: transaction, precautionary, and speculative, and explains their implications on interest rates and money supply. The theory faces criticism for being indeterminate, applicable only to advanced economies, and neglecting the productivity of capital.