This document presents a method for finding the best polynomial approximation of degree one for a function over a given interval using the method of least parallelograms. It introduces the problem, outlines the main results which include theorems on the existence and properties of the least parallelogram and its relationship to the minimax polynomial. Examples are also provided to illustrate the method.
![Best Polynomials Approximation of Degree One at C[a, b] Space
by Method of Least Parallelogram
Dadang Amir Hamzah, S.Si., M.Si.
INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI BANDUNG
2013
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 1 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/75/Best-polynomial-approximation-1-2048.jpg)





![Introduction
Approximation of function is the technique to replace a function
with another simpler function, such as Taylor series, step function
or polynomials.
Before we pose the approximation problem we should decide
three main component, first function space F which its element
will be approximated, second the function class A which we use to
approximate, and the third the Norm which measure the
approximation error.
In this presentation we use F = C[a, b] space which is the set of
continuous function at closed interval [a, b], then the class of
approximation function A = P1 which is class of polynomial of
degree one, and the norm we use is maximum norm which is the
norm defined at C[a, b] space that is
f = f ∞ = max
x∈[a,b]
|f(x)|; (1)
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 5 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-9-320.jpg)
![Best Polynomial Approximation Problem
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b]. Find p1 ∈ P1 such that
f − p1 = min
x∈P1
f − p1 ∞
Such p1 ∈ P1 called best polynomial approximation of f ∈ C[a, b].
Because of its property that minimize for every maximum possibility
polynomial p1 above also called minimax polynomial.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 6 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-10-320.jpg)
![Best Polynomial Problem in C[a, b] Space
Theorem (Existence and Uniquenes)
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b]. There is a pn ∈ Pn such that
f − pn ∞ = minq∈Pn f − q ∞.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 7 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-11-320.jpg)
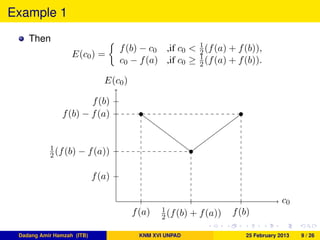
![Example 1
Suppose given increasing function f ∈ C[a, b]. Find p0 ∈ P0 for
f ∈ C[a, b].
Let p0(x) ≡ c0, we seek c0 ∈ R such that
f − p0 ∞ = maxx∈[0,1] |f(x) − c0| minimum.
Because f is increasing, f(x) − c0 minimum at x = a and
maximum at x = b, in result |f(x) − c0| maximum at one of end
point of [a, b] that is
E(c0) = max
x∈[0,1]
|f(x) − c0| = max{|f(a) − c0|, |f(b) − c0|}.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 8 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-12-320.jpg)

![Best Polynomial Problem in C[a, b] Space
How to construct minimax polynomial p1?
Before we answer this problem lets see the case for f non
monotone, that is f either increasing and decreasing at [a, b].
There will always be ξ, η ∈ [a, b] Such that f(ξ) maksimum and
f(η) minimum.
By the same argument as example 1 easily we can get minimax
polynomial for f at [a, b] that is
p0(x) ≡
1
2
(f(η) + f(ξ)), x ∈ [a, b].
Let the Error approximation
f(x) − p0(x) =
1
2
(f(x) − f(ξ)) +
1
2
(f(x) − f(η))
From this we get f(x) − p0(x) positif for x = ξ and negative for
x = η.
This gives us notion that f(x) − p0(x) has 2 opposites sign at its
maximum and minimum of f. Is this valid for every case?
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 11 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-15-320.jpg)
![Best Polynomial Problem in C[a, b] Space
Teorema (De la Vall´ee Poussin)
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b] andr ∈ Pn. Then suppose there is n + 2
point x0 < x1 < . . . < xn+1 in [a, b]. if f(xi) − r(xi) and
f(xi+1) − r(xi+1) has opposites sign, for i = 0, 1, 2, . . . , n then
min
q∈Pn
f − q ∞ ≥ min
i=0,1,...,n+1
|f(xi) − r(xi)|. (2)
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 12 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-16-320.jpg)
![Best Polynomial Problem in C[a, b] Space
Teorema (Chebyshev Oscillation)
Suppose given arbitrary f ∈ C[a, b]. A polynomial r ∈ Pn is minimax
polynomial for f if and only if there is n + 2 chronological points
xi, i = 0, 1, 2, . . . , n + 1 such that a ≤ x0 < x1 < x2 < . . . < xn+1 ≤ b
|f(xi) − r(xi)| = f − r ∞, i = 0, 1, . . . , n + 1,
dan
f(xi) − r(xi) = −[f(xi+1) − r(xi+1)], i = 0, 1, 2, . . . , n.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 13 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-17-320.jpg)
![Method of The Least Parallelogram
Definition
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b]. A parallelogram J which is bordered by
g1, g2 line and g1 > g2 is called contain f if
g1 − f ≤ g1 − g2, dan f − g2 ≤ g1 − g2.
Definition (The Least Parallelogram)
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b]. A parallelogram J with height tJ = g1 − g2
is called the least parallelogram for f if
1 J contain f.
2 If there is another parallelogram say J∗ with height tJ∗ which also
contain f then tJ∗ ≤ tJ .
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 16 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-20-320.jpg)
![Theorem
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b]. If J is the least parallelogram for f then
there must be one of border line of J passing through two point of f
and another border line of J passing through one point of f.
Proof.
Misalkan J adalah jajargenjang terkecil bagi f. Berdasarkan
pengamatan geometris, haruslah terdapat dua titik yang terletak
pada kurva f yang masing-masing dilewati oleh batas J.
Andaikan masing-masing batas J hanya melewati satu titik pada
kurva f.
Dengan mengubah gradien dari batas J akan didapat
jajargenjang baru J yang masih memuat f tetapi tinggi J lebih
kecil dari tinggi J.
Kontradiksi dengan J jajargenjang terkecil.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 17 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-21-320.jpg)
![Theorem
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b]. If J is the least parallelogram of f then the
median line of J is the minimax polynomial for f.
Proof.
Misalkan J adalah jajargenjang terkecil bagi f.
Perhatikan garis tengah J.
Menurut Lema sebelumnya ada tiga titik pada kurva f sedemikian
sehingga jarak garis tengah J terhadap f di tiga titik tersebut
bernilai sama, dengan selisih dari garis tengah J dan f, dua kali
berubah tanda.
Menurut teorema Osilasi Chebyshev garis tengah J adalah
polinom minimaks berderajat satu bagi f.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 18 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-22-320.jpg)
![Theorem
Suppose given f ∈ C[a, b]. if p is the minimax polynomial of f with
f − p ∞ = E then the parallelogram of J which is bordered by p + E
and p − E is the least parallelogram of f.
Proof.
Misalkan J adalah jajargenjang yang memuat f dengan garis
batas p + E dan p − E.
Misalkan J∗ = J adalah jajargenjang lain yang memuat f.
Dengan menggunakan Lema dapat ditunjukkan bahwa tinggi J∗
selalu lebih besar dari tinggi J.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 19 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-23-320.jpg)
![Theorem
Suppose given f ∈ C[a.b]. A parallelogram J which contain f is called
the least parallelogram of f if and only if there are two points at f such
that one of border line of J passing through two point of f and another
border line of J passing through one point of f.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 20 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-24-320.jpg)
![Example 2
Misal diberikan f(x) = ex dengan x ∈ [−1, 1]. Akan dicari polinom
minimaks p1 ∈ P1 untuk f pada [0, 1].
Fungsi f merupakan fungsi monoton naik cekung pada [−1, 1].
Gradien garis yang melalui (−1, f(−1)) dan (1, f(1)) adalah 1.175.
Kemudian titik d yang memenuhi f (d) = 1.175 adalah d = 0.161.
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 21 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-25-320.jpg)
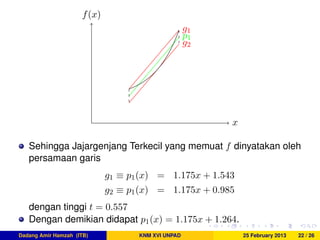
![Example 3
Misal diberikan f(x) = x3 pada selang [−1, 1]. Polinom p1 = 3
4x
adalah polinom minimaks bagi f dengan f − p1 ∞ = 1
4.
x
f(x)
g1
g2
p1
Dadang Amir Hamzah (ITB) KNM XVI UNPAD 25 February 2013 23 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presthesisenglish-130427104427-phpapp02/85/Best-polynomial-approximation-27-320.jpg)