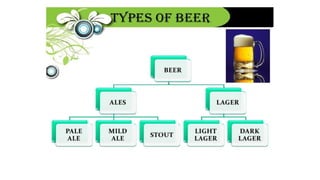
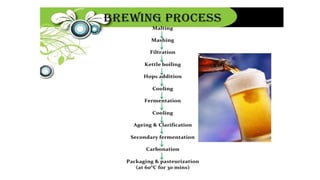
This document summarizes the beer production process, which includes malting, kilning, milling, mashing, boiling the wort, fermentation, finishing, aging, maturation, and carbonation. During malting, barley grains are soaked, germinated, and dried. Milling crushes the grains. Mashing involves mixing the grist with warm water to produce sugars and flavor components. The wort is boiled with hops added for flavor and sterilization. Fermentation converts sugars to alcohol and carbon dioxide using yeast. Finishing involves aging, clarifying, and carbonating the beer.