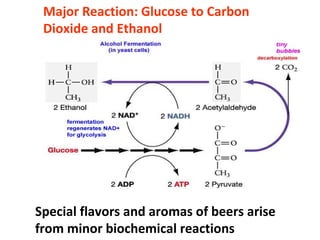
Alcoholic fermentation converts sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide through the metabolic process of yeasts. The major reaction is glucose transforming into carbon dioxide and ethanol. Beer production involves malting grains such as barley to activate enzymes, mashing to extract soluble substances, boiling with hops, fermentation using bottom- or top-fermenting yeasts, conditioning, and packaging. Factors like temperature, oxygen supply and sugar content affect fermentation.