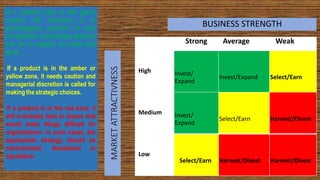
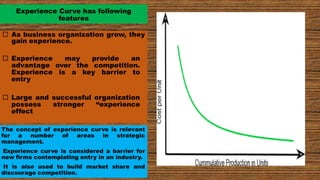
The document discusses various strategic analysis tools including the BCG matrix, GE nine cell matrix, and experience curve analysis. The BCG matrix classifies business units based on their market growth and relative market share to determine investment strategies. The GE nine cell matrix evaluates business units based on market attractiveness and business strength factors. Experience curve analysis explains that unit costs decline as a firm gains experience through increased production volumes. These tools help companies evaluate their portfolio of businesses and determine appropriate investment and strategic choices.