This document provides definitions and explanations of key concepts related to business communication. It defines business as an economic activity aimed at satisfying human wants through production and distribution of goods and services. Communication is defined as the exchange of meaning between people. Business communication is then defined as the sharing of information within and outside an organization for commercial benefit.
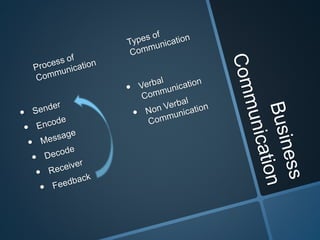
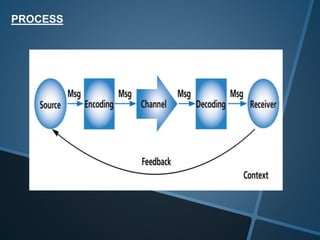
The document discusses the importance of communication as the lifeblood of any organization. It explains the basic process of communication as involving a sender encoding a message and transmitting it through a channel to a receiver who decodes and provides feedback. Verbal communication is divided into oral communication like conversations and written communication like emails. Non-verbal communication involves body language and other apparent or less obvious messages.