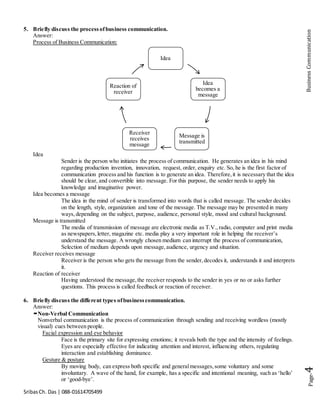
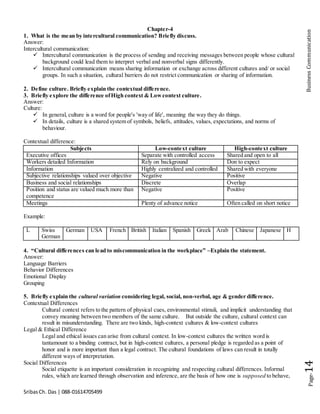
The document defines communication and business communication, emphasizing the importance of effective communication and its various benefits for organizations. It discusses common barriers to communication, such as perceptual differences and language issues, and offers strategies to overcome these barriers. Additionally, it outlines the process of business communication, types of communication, and the significance of listening in a business context.