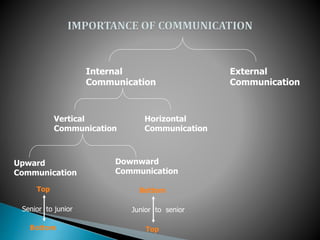
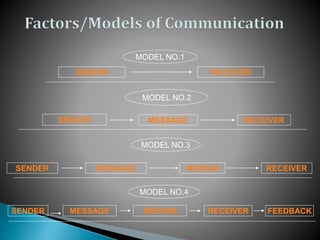
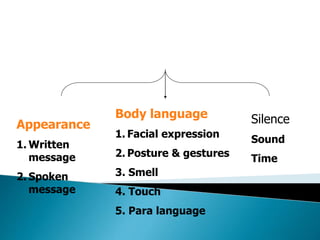
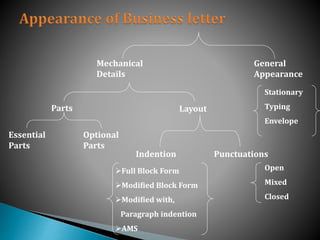
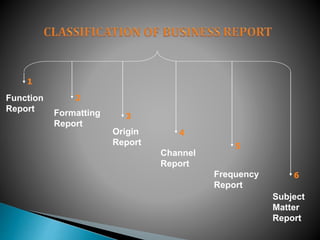
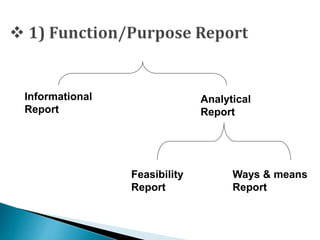
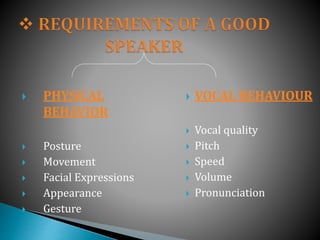
This document provides an overview of topics related to managerial communication. It discusses introducing managerial communication and planning communication. It also covers business writing principles, legal aspects of communication, and the appearance of business letters. Additionally, it addresses sales and sales promotion letters, inquiry and order letters, complaint/claim letters, job letters, collection letters, and business reports. Finally, it examines oral presentation/communication including speaking, listening, leading, participating, interviewing, and dictating. The document is authored by Hassan Samoon and is intended as an introduction to managerial communication.