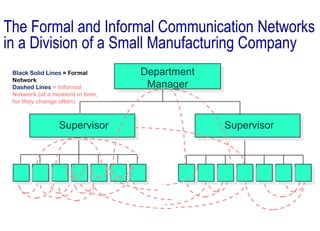
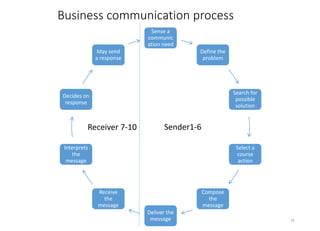
Communication is essential for businesses to function effectively. There are three main forms of communication in businesses: internal operational communication within a company, external operational communication with outside parties, and personal communication to build relationships. Both formal communication networks along operational lines and informal grapevine networks are important. The communication process involves sensing a need, defining the problem, finding solutions, taking action, composing and delivering messages, receiving and interpreting responses. Context, medium, and individual differences can impact communication effectiveness. Surveys show communication skills are highly valued for business success.