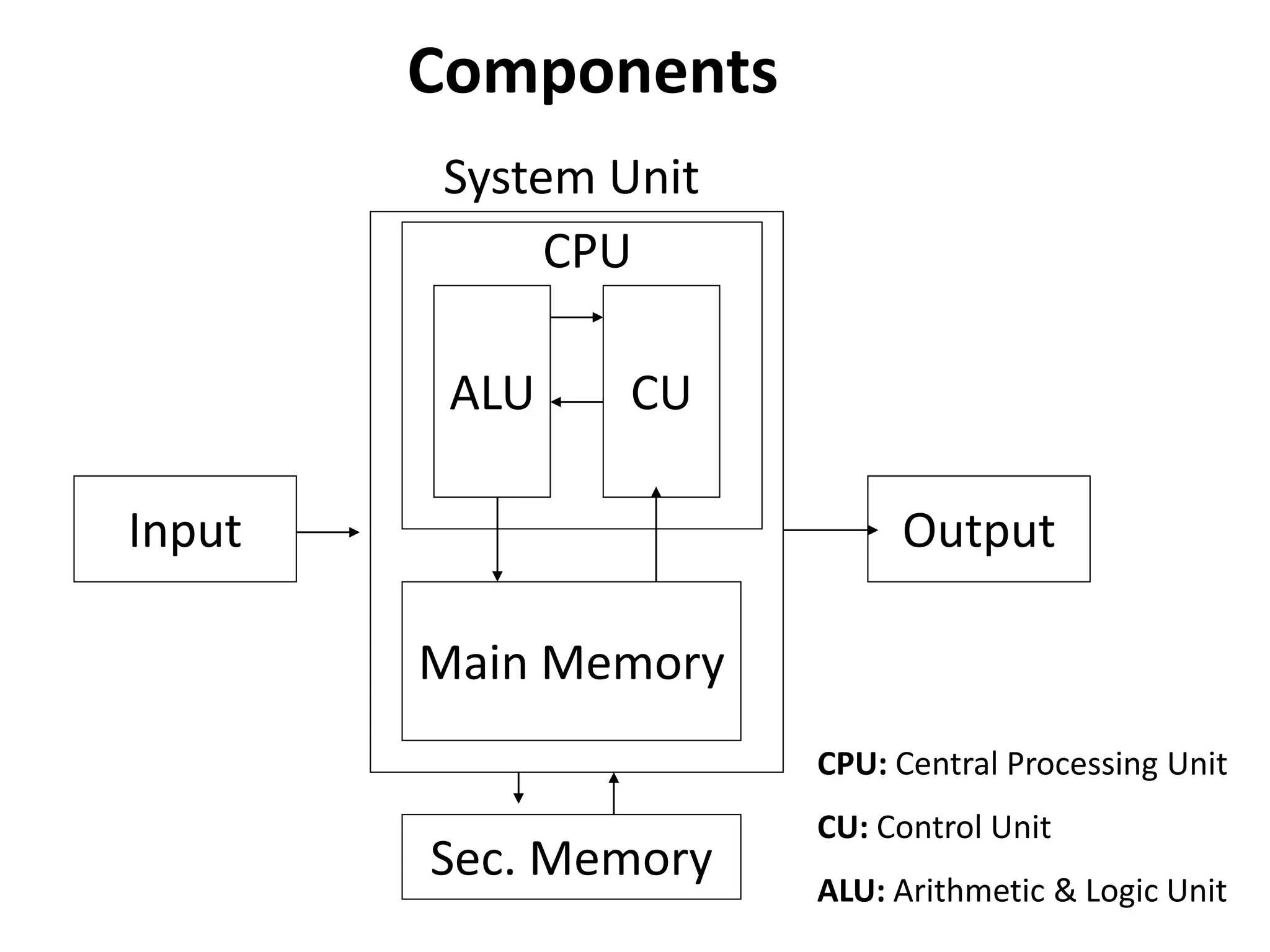
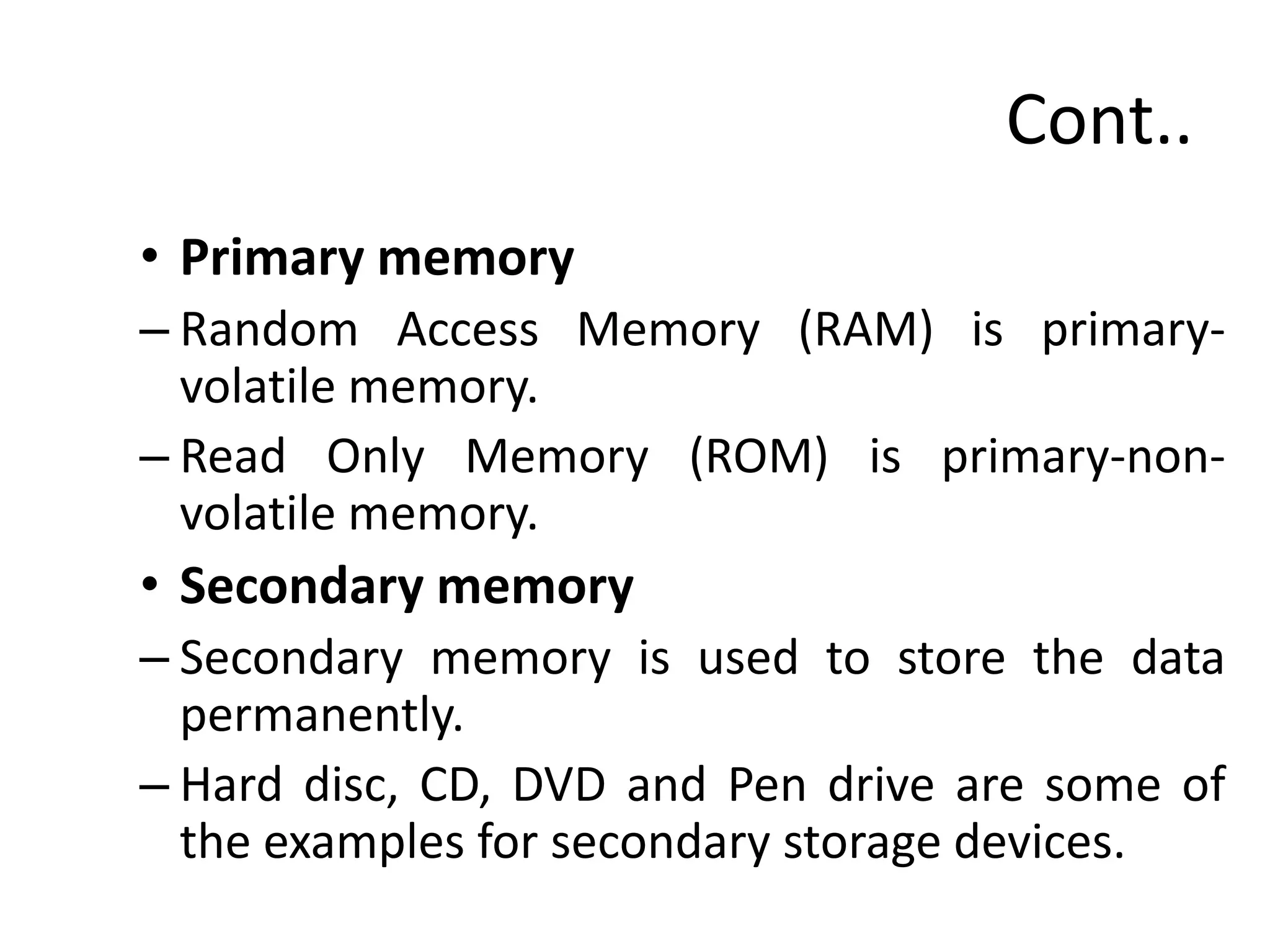
A computer is an electronic device that accepts data as input, processes that data, produces output, and stores the results. It has three main components: an input unit, an output unit, and a system unit. The system unit contains the central processing unit (CPU) and memory unit. The CPU contains the control unit and arithmetic logic unit, which perform processing and control operations. The memory unit stores data and instructions during processing and provides space for intermediate and final results. Computers are characterized by their speed, accuracy, diligence, versatility, and large storage capacity.