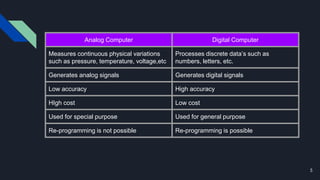
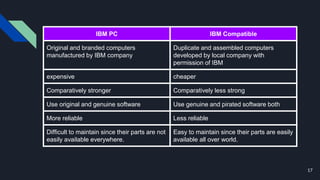
This document classifies computers based on capacity, use, size, brand, and model. It discusses analog, digital, and hybrid computers based on work. Computers are also classified as specific purpose or general purpose based on their intended use. Classification by size includes supercomputers, mainframes, mini computers, and microcomputers. Computers can also be classified based on brand as IBM PC, IBM compatible, or Apple/Macintosh. Finally, classification by model discusses XT, AT, and PS/2 computers.