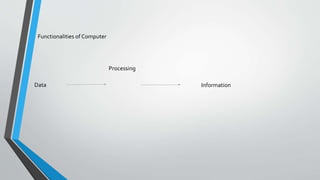
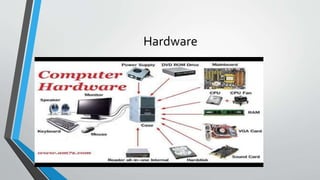
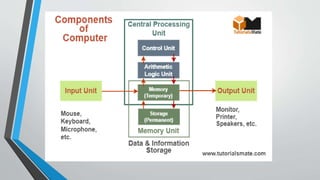
The document provides an introduction to computers. It defines a computer as an electronic device that can accept data as input, process it according to instructions, produce output, and store information. The main components of a computer are the hardware (physical parts) and software (programs). Hardware includes devices like the screen and internal components like the central processing unit (CPU) which contains the arithmetic logic unit and control unit to process data. Software allows the hardware to perform tasks and comes in types like application, system, and programming software. The document outlines the history of computers and types including personal computers, mainframes, supercomputers, and minicomputers. It describes the basic units of a computer system as the input, output, CPU,