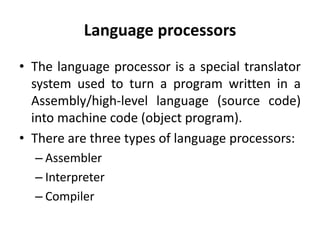
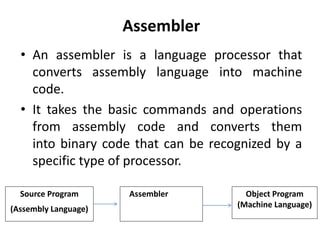
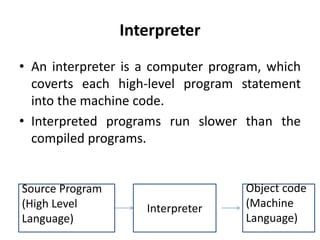
This document discusses different types of programming languages and language processors. It describes low-level languages like machine language and assembly language that are directly understood by computers. It also describes high-level languages that are easier for humans to read and write but require compilers or interpreters to be converted to machine code. Language processors like assemblers, compilers, and interpreters are used to convert programs between source and machine codes.