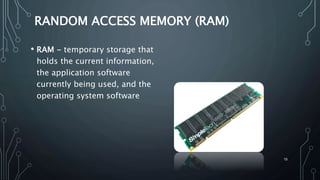
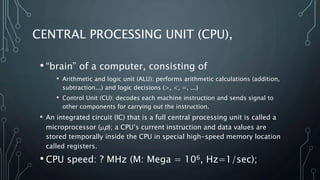
This document defines and describes computers and their components. It begins by defining a computer as a device that accepts digital data as input and processes it according to stored instructions. It then categorizes different types of computers and describes their typical uses. The rest of the document discusses the key components of a computer system, including hardware components like CPUs, memory, storage devices, and input/output devices. It also discusses software components like operating systems, applications, and system utilities. Overall, the document provides a comprehensive overview of computers and their basic anatomy and functionality.