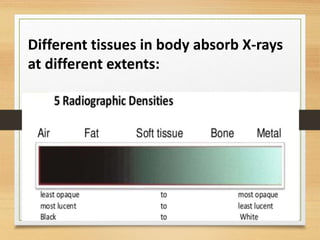
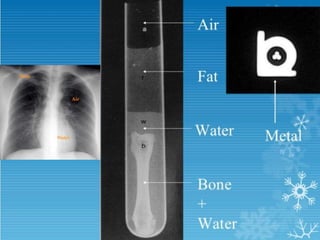
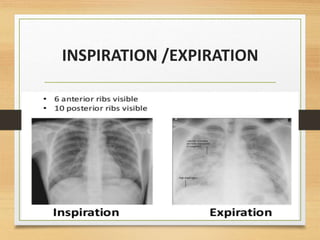
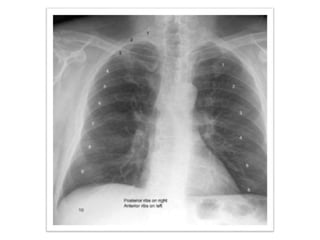
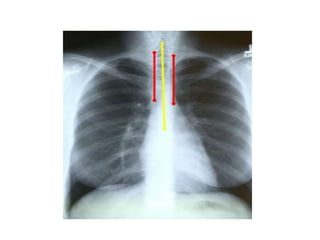
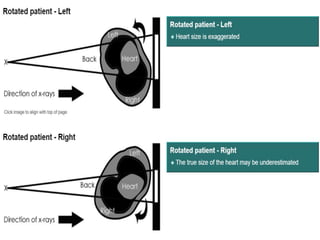
This document provides an overview of normal x-ray interpretation. It discusses technical aspects like orientation, inspiration, penetration and rotation that should be considered for all x-rays. It describes what should be looked at in an x-ray like the bony framework, soft tissues, lungs, heart and abdomen. The stages of evaluating an abnormality are outlined as identification, localization, identification of pathological process and etiology. Practice and repetition are emphasized for improving x-ray interpretation skills.