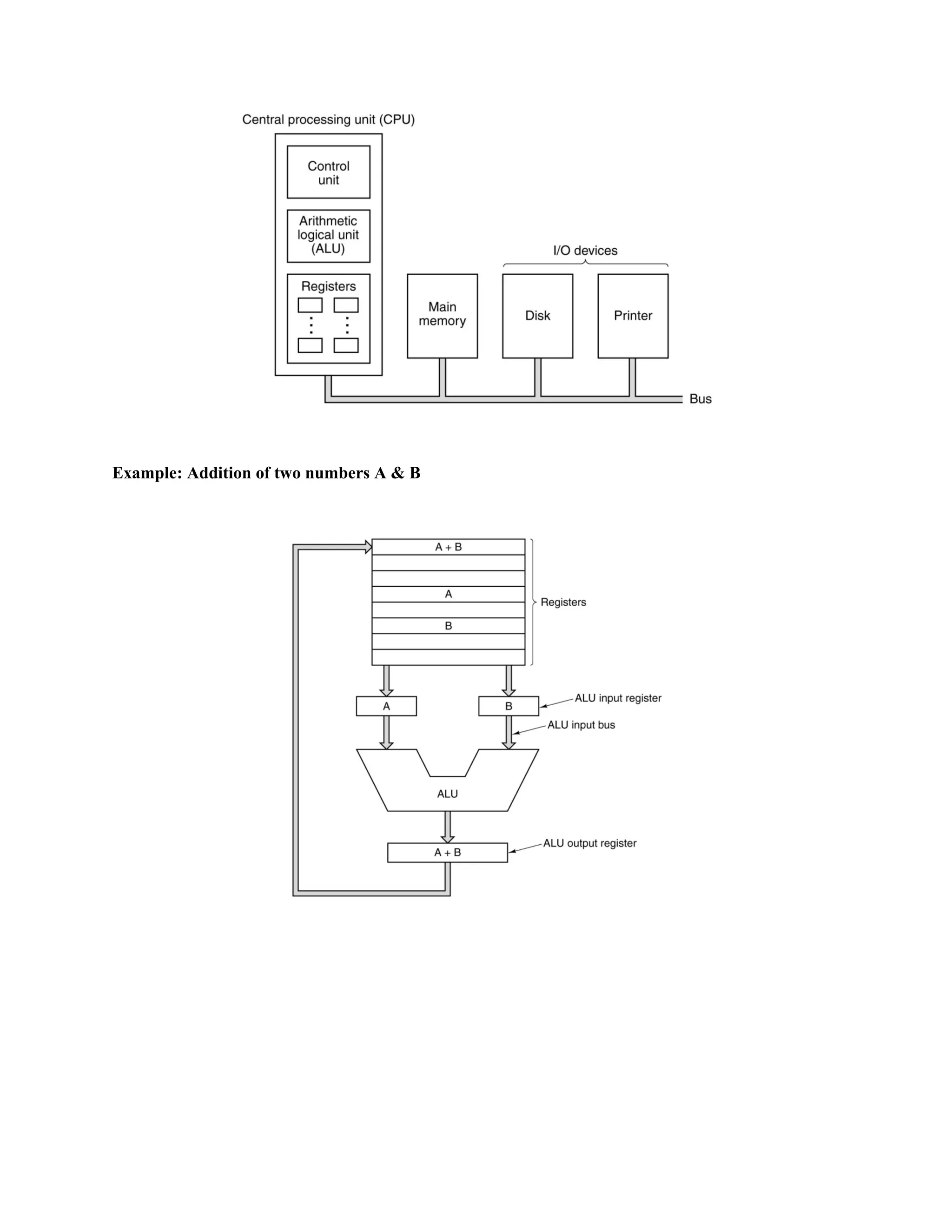
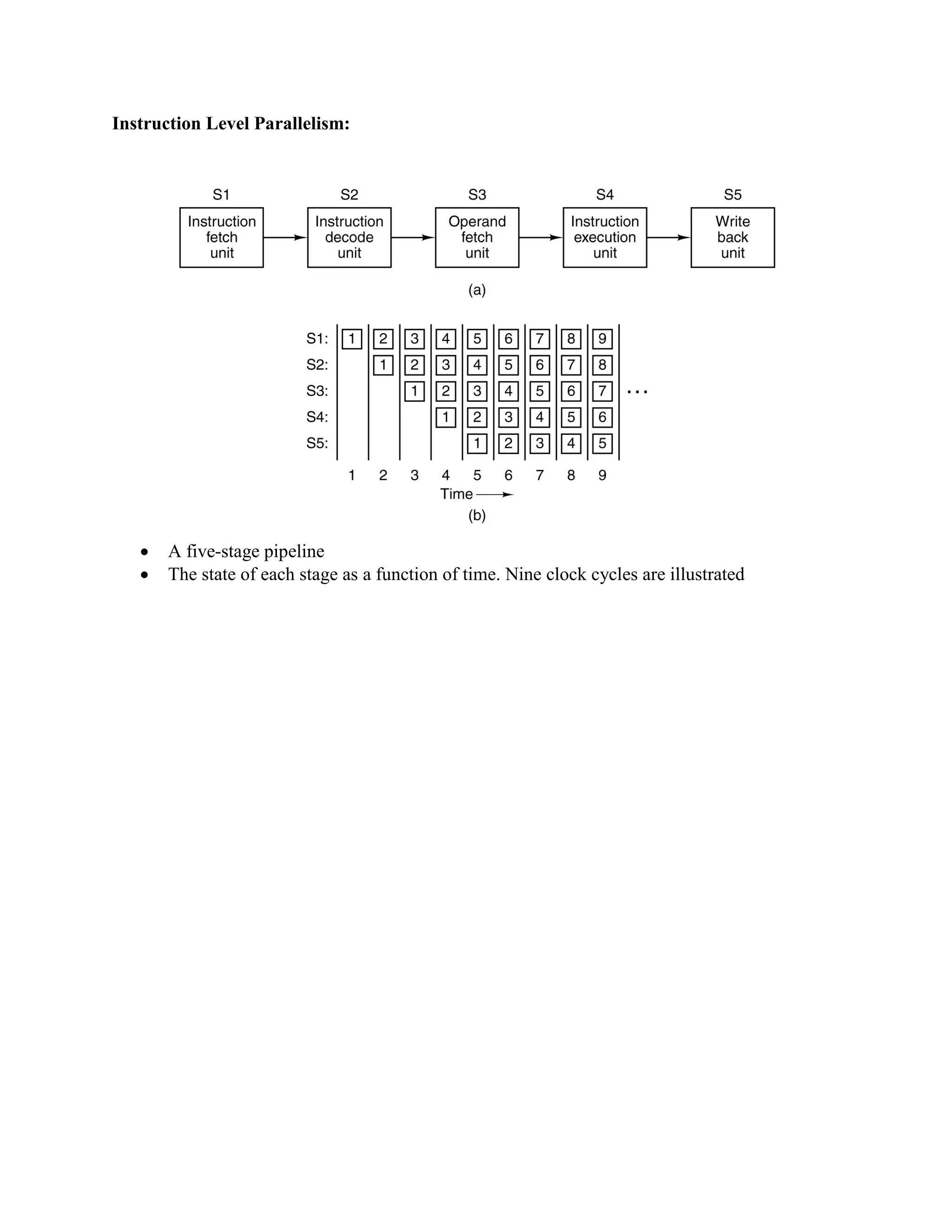
Computer architecture consists of instruction set architecture (ISA), which is software, and machine organization, which is hardware and design. The basic machine organization includes a CPU with an ALU and control unit, memory subsystem to store data, and I/O subsystem connecting to devices. These components communicate through buses - the address bus specifies memory locations, the data bus transfers data, and the control bus sends signals. The CPU follows an instruction cycle of fetching, decoding, operand fetching, executing instructions, and writing back results through the buses to memory or I/O.