Embed presentation
Download to read offline

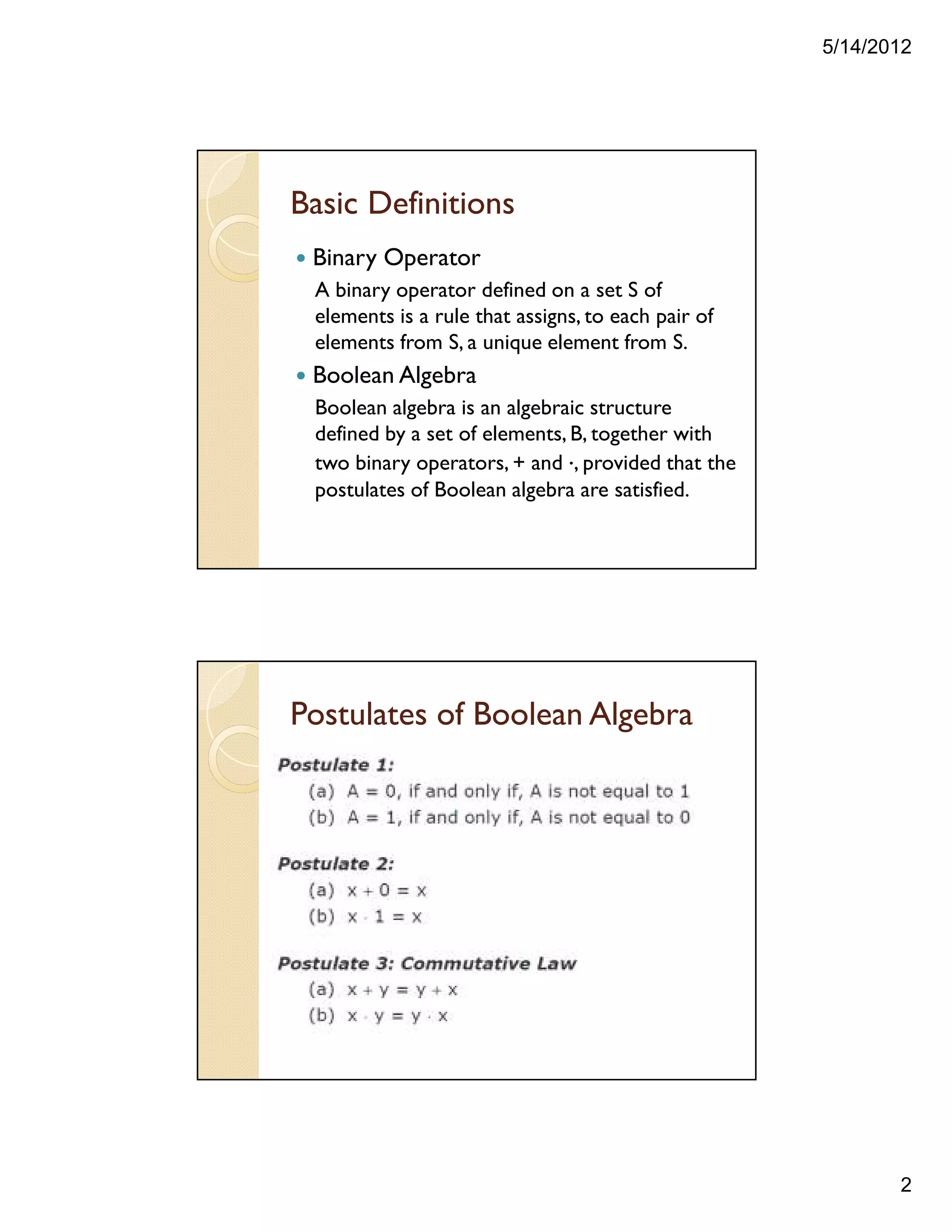
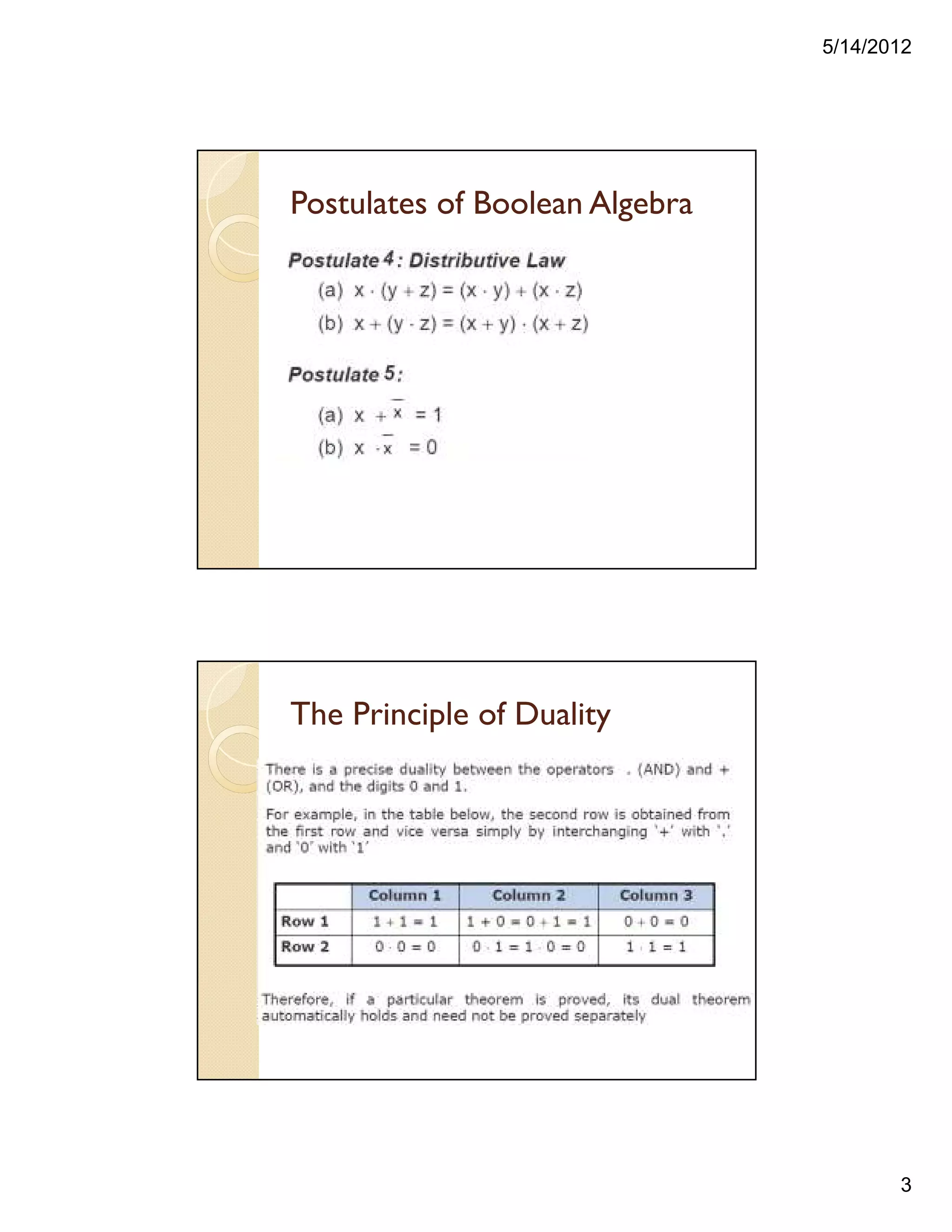
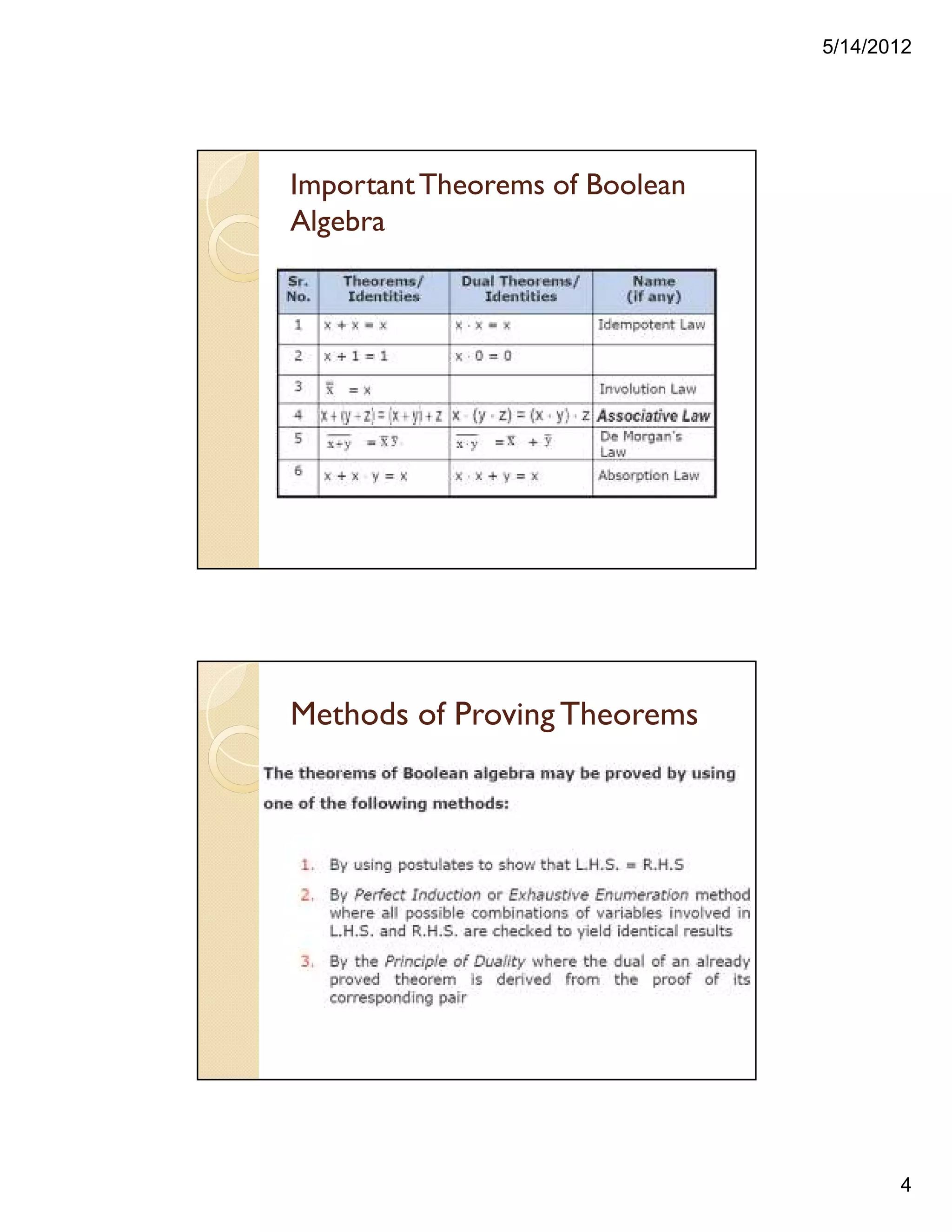
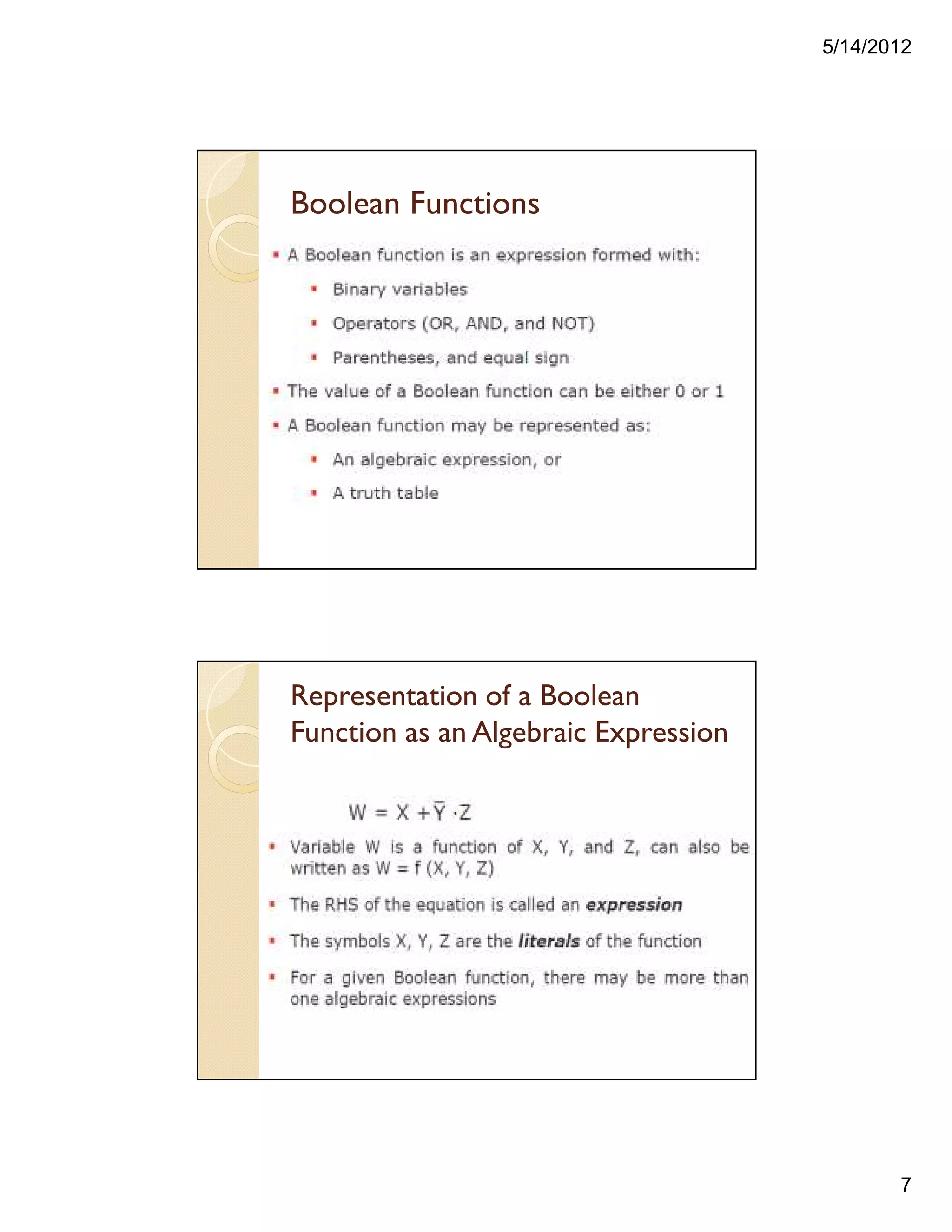
![5/14/2012
5
Proving a Theorem by using Postulates
andTheorems
[ x.1 = x ]
[ x.(y+z)=(x.y) + (x.z) ]
[ x+y=y+x ]
[ x+1=1 ]
[ x.1=x ]
Proving a Theorem by Perfect
Induction / Exhaustive Enumeration
[x + x.y = x ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dldlecturemodule05-170222200641/75/Dld-lecture-module-05-5-2048.jpg)
![5/14/2012
6
Proving a Theorem by Duality
[ x.1=x ]
[ x +x=1 ]
[ x+(y.z)=(x+y).(x+z) ]
[x.x=0 ]
[ x+0=x ]
[ x+0=x ]
[ x . x=0 ]
[ x.(y+z)=(x.y)+(x.z) ]
[ x+x=1 ]
[ x.1=x ]
Reading Assignment:Venn Diagrams](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dldlecturemodule05-170222200641/75/Dld-lecture-module-05-6-2048.jpg)




This document contains lecture notes on basic concepts in digital logic and design. It defines key terms like binary operators and Boolean algebra. It outlines postulates of Boolean algebra including the principle of duality. It discusses methods of proving theorems like using postulates, induction, and duality. It also covers Boolean functions, how to represent them as algebraic expressions and truth tables, and how to minimize and find complements of Boolean functions.




![5/14/2012
5
Proving a Theorem by using Postulates
andTheorems
[ x.1 = x ]
[ x.(y+z)=(x.y) + (x.z) ]
[ x+y=y+x ]
[ x+1=1 ]
[ x.1=x ]
Proving a Theorem by Perfect
Induction / Exhaustive Enumeration
[x + x.y = x ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dldlecturemodule05-170222200641/75/Dld-lecture-module-05-5-2048.jpg)
![5/14/2012
6
Proving a Theorem by Duality
[ x.1=x ]
[ x +x=1 ]
[ x+(y.z)=(x+y).(x+z) ]
[x.x=0 ]
[ x+0=x ]
[ x+0=x ]
[ x . x=0 ]
[ x.(y+z)=(x.y)+(x.z) ]
[ x+x=1 ]
[ x.1=x ]
Reading Assignment:Venn Diagrams](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dldlecturemodule05-170222200641/75/Dld-lecture-module-05-6-2048.jpg)




