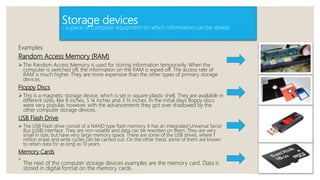
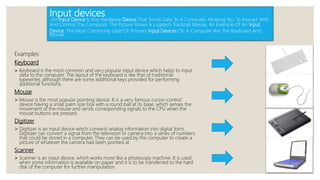
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computers, detailing their definition and core functions, including input, processing, output, and storage. It describes various input and output devices, such as keyboards, mice, printers, and scanners, as well as processor types and computer categories, from supercomputers to personal computers. Additionally, it outlines primary and secondary memory types, emphasizing key components that make up a computer system.


![Processing device
-A Processing Device Is Any Device In A Computer That Handles This Intermediate Stage.
Example, In The Diagram Below, The CPU Is The Processing Device. Some Of The Most
Common Processing Devices In A Computer Include The Following: Central Processing Unit
(CPU) Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Examples:
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
A central processing unit (CPU) is the electronic circuitry within a computer that carries out
the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control
and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
A graphics processing unit (GPU), occasionally called visual processing unit (VPU), is a
specialized electronic circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory to accelerate
the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device.
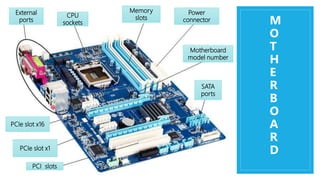
Motherboard
a printed circuit board containing the principal components of a computer or other device,
with connectors into which other circuit boards can be slotted.
Network Card
A network interface controller (NIC, also known as a network interface card, network adapter,
LAN adapter or physical network interface,[1] and by similar terms) is a computer hardware
component that connects a computer to a computer network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myresearch-170705052806/85/The-Computer-5-320.jpg)
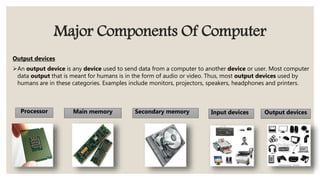
![OUTPUT DEVICES
- An Output Device Is Any Peripheral That Receives Data From A Computer, Usually For
Display, Projection, Or Physical Reproduction. ... Monitors And Printers Are Two Of The Most
Common Output Devices Used With A Computer
Examples:
3D Printer
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing (AM), refers to processes used to
create a three-dimensional object[1] in which layers of material are formed under
computer control to create an object.
Braille Embosser
A braille embosser is an impact printer that renders text as tactile braille cells. Using
braille translation software, a document can be embossed with relative ease, making
braille production efficient and cost-effective.
Braille reader
A braille reader, also called a braille display, is an electronic device that allows a blind
person to read the text displayed on a computer monitor. The computer sends the text
to the output device, where it is converted to Braille and "displayed" by raising rounded
pins through a flat surface on the machine.
Headphones
Headphones (or head-phones in the early days of telephony and radio) are a pair of
small loudspeaker drivers that are designed to be worn on or around the head over a
user's ears.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myresearch-170705052806/85/The-Computer-6-320.jpg)