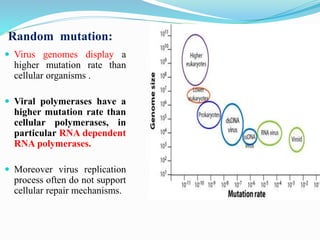
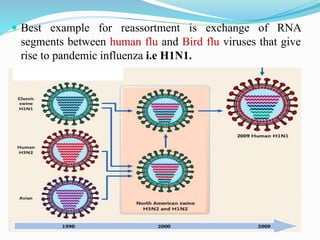
Viruses evolve rapidly through mutation and recombination. Many viruses have high mutation rates due to error-prone replication and lack of repair mechanisms. There are three hypotheses for the origins of viruses: escape from host genes, evolution before cells, and reduction of small cells into parasites. Evolution occurs through random mutation, recombination, reassortment, and antigenic drift/shift. Reassortment of influenza virus segments leads to pandemics, while antigenic drift accumulates mutations to evade antibodies. Viral evolution poses challenges for vaccines and drugs as resistant mutations often emerge.