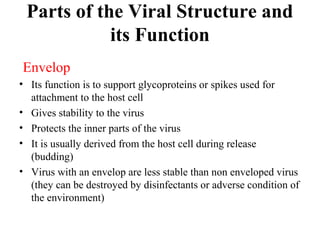
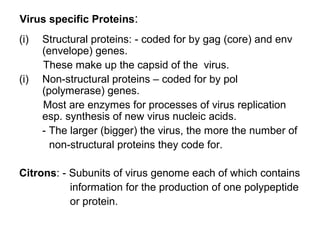
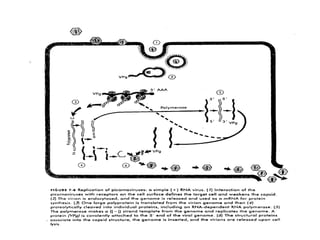
Viruses replicate by taking over the host cell's machinery. They produce mRNA using their genome as a template. This mRNA directs the production of viral proteins, including structural proteins that make up the capsid and non-structural proteins that help with replication. The virus growth cycle involves adsorption to receptors, entry, uncoating, synthesis of new viral components, assembly, and release. DNA viruses replicate in the nucleus while RNA viruses replicate in the cytoplasm, except retroviruses and influenza which enter the nucleus. New viruses are assembled and released to infect other cells.