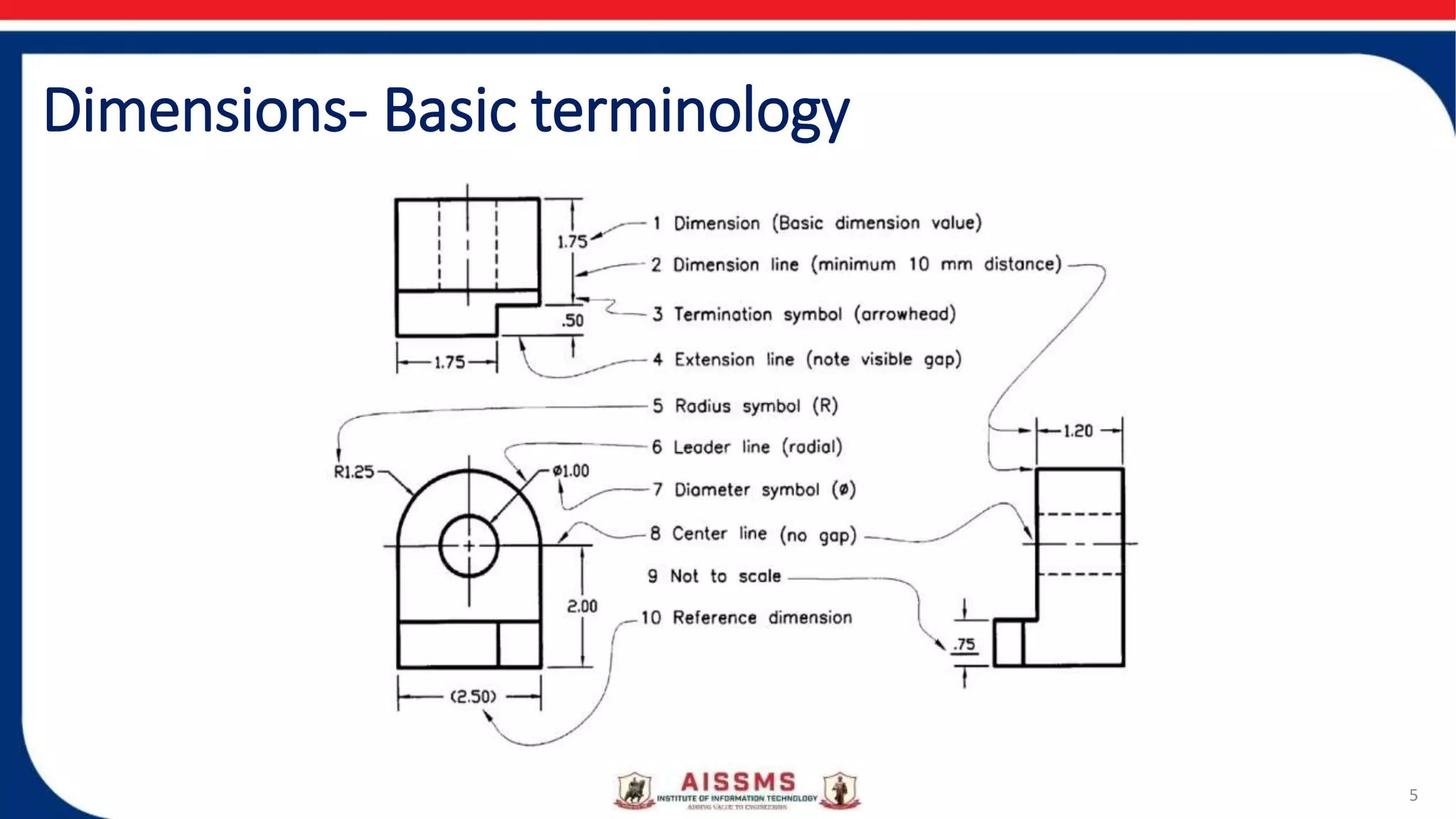
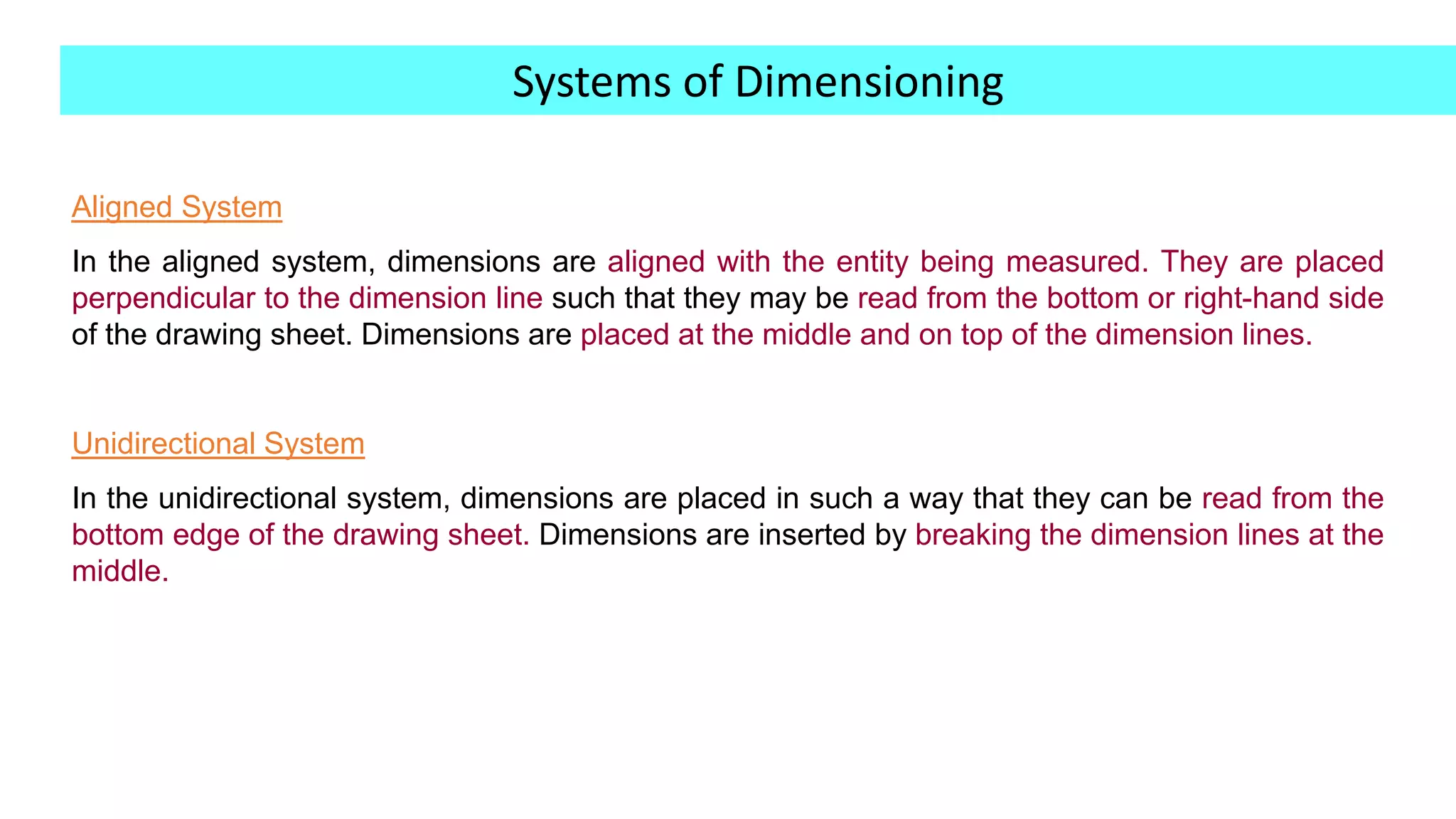
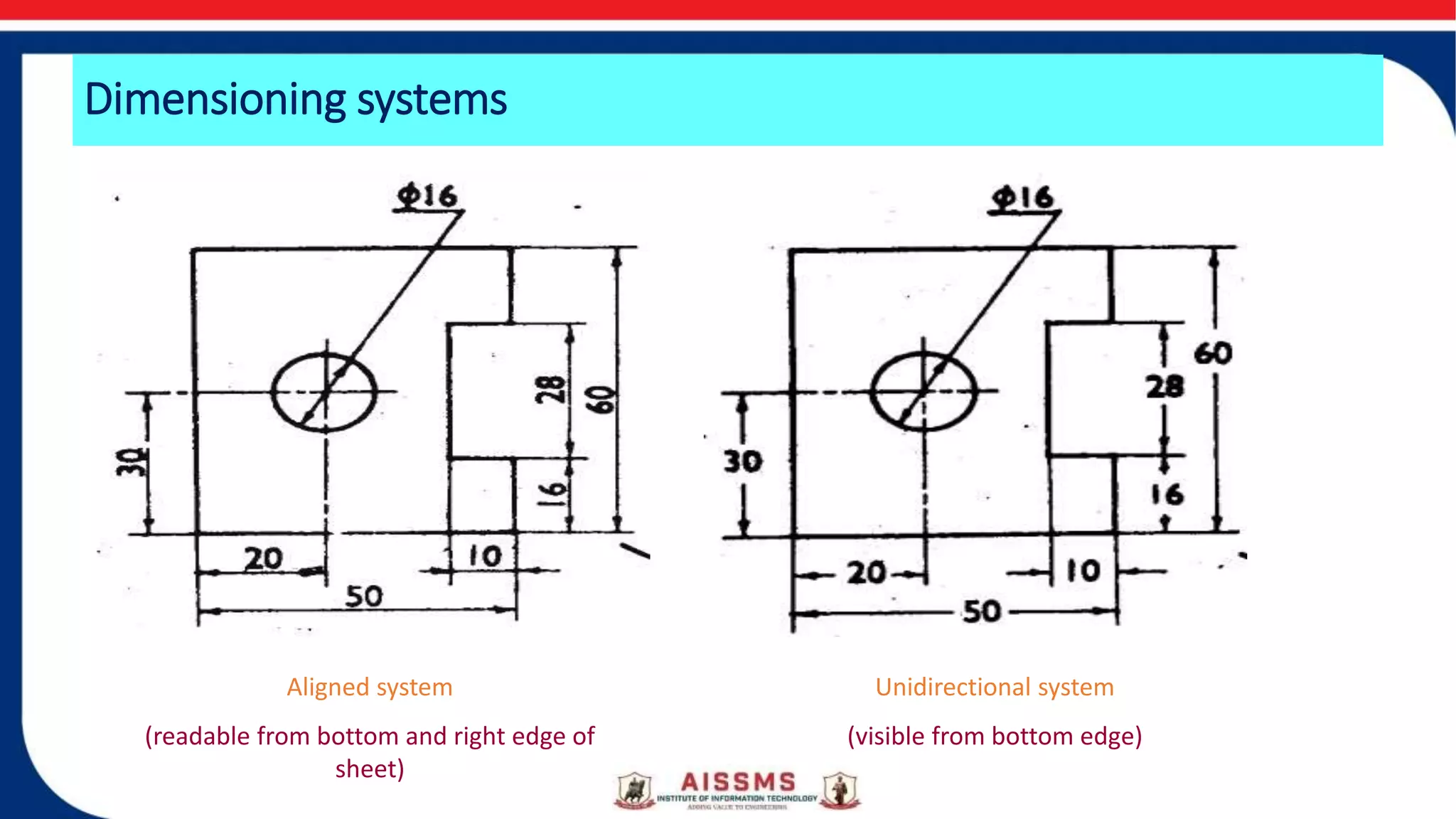
This document provides an overview of dimensioning rules for engineering drawings. It defines dimensions as numerical values that define the size, location, and other geometric characteristics of a part. There are different types of dimensions, including linear, angular, radius/diameter, and reference dimensions. Dimensioning systems include the aligned system, where dimensions are perpendicular to dimension lines and readable from the bottom or side, and the unidirectional system, where dimensions are placed to be readable from the bottom and dimension lines are broken in the middle. Guidelines are provided for dimension units in inches or millimeters and specifying the unit of measurement.