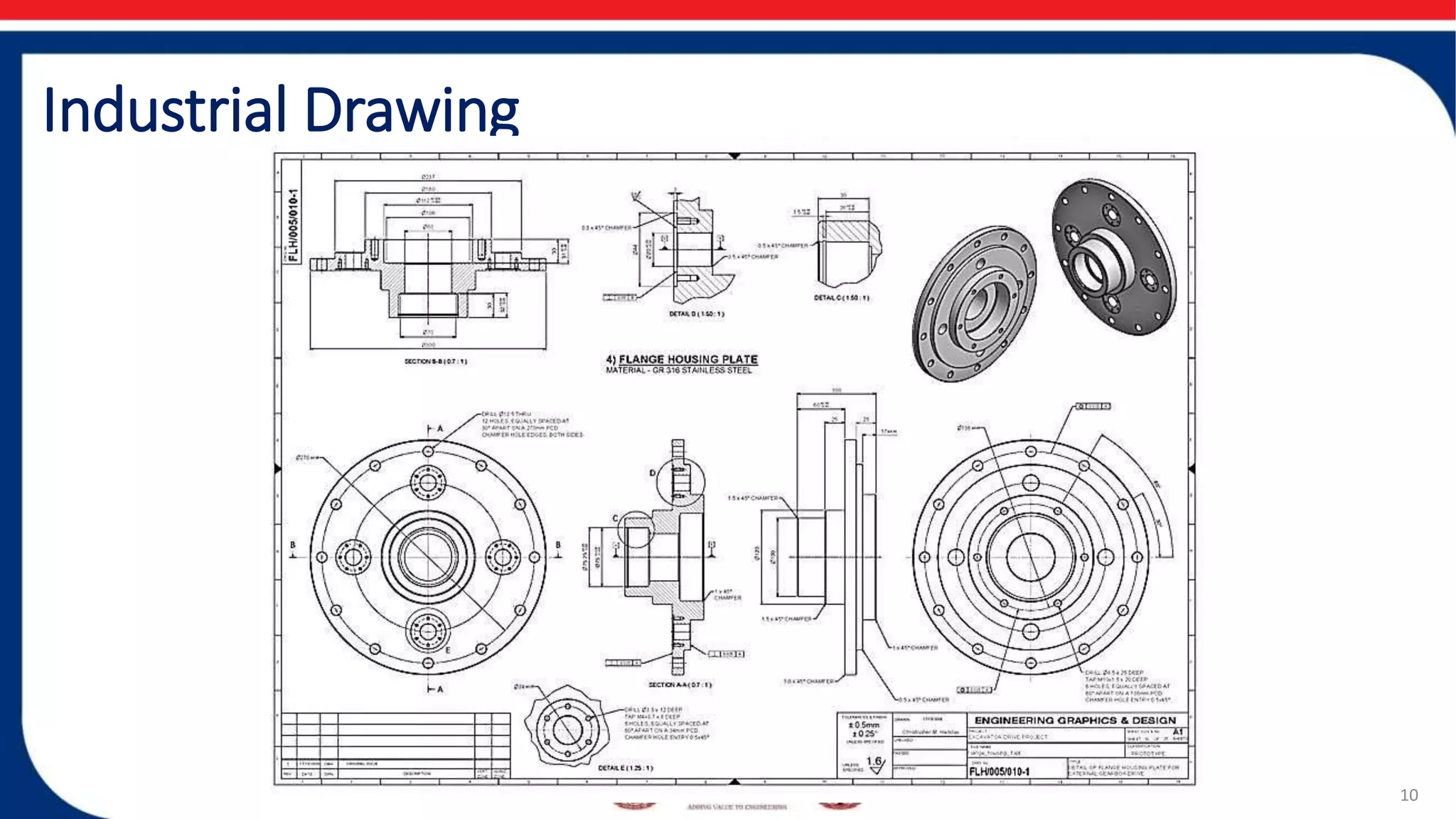
Engineering drawings are a graphical language used to clearly define and communicate designs to interested parties involved in design collaboration, manufacturing, and construction. There are two main types of drawings - artistic drawings and technical drawings, with technical drawings being the preferred method used in engineering fields. The purpose of engineering drawing is to develop the ability to read, produce, and abstract information from drawings and diagrams used in different industries. Main types of engineering drawings include mechanical, electrical, electronics, and civil drawings used in various applications such as manufacturing, construction, aerospace, and more.