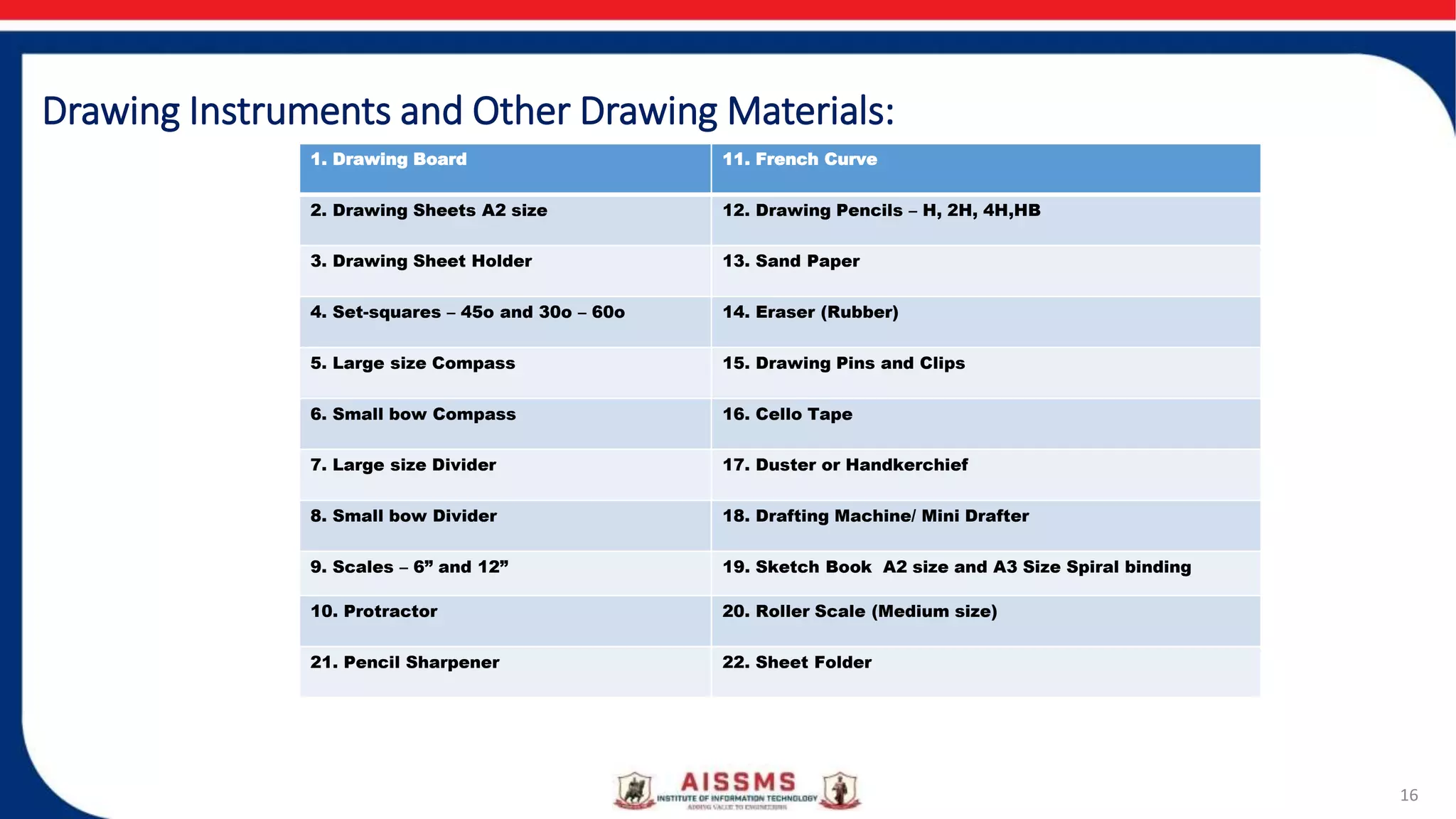
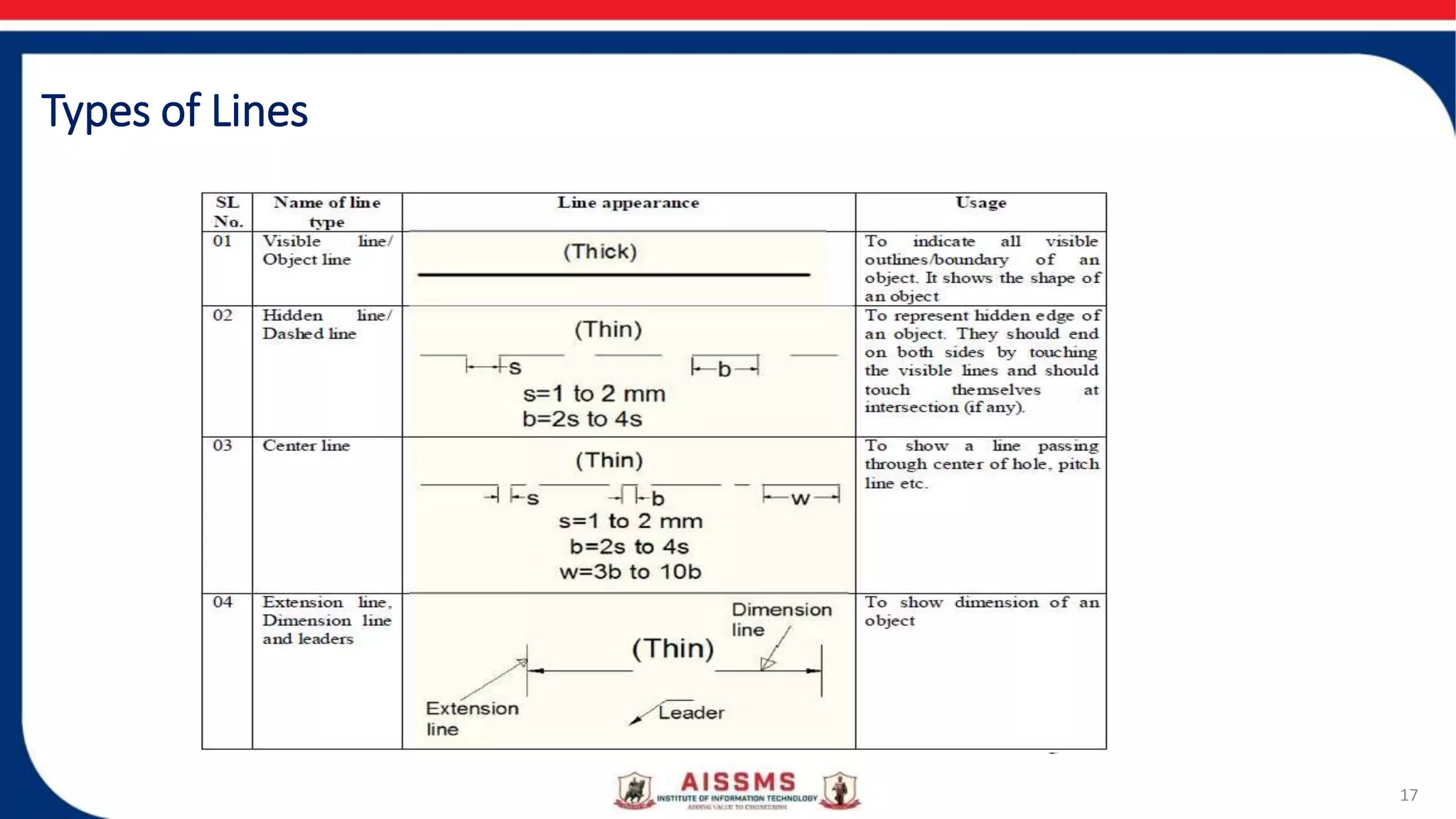
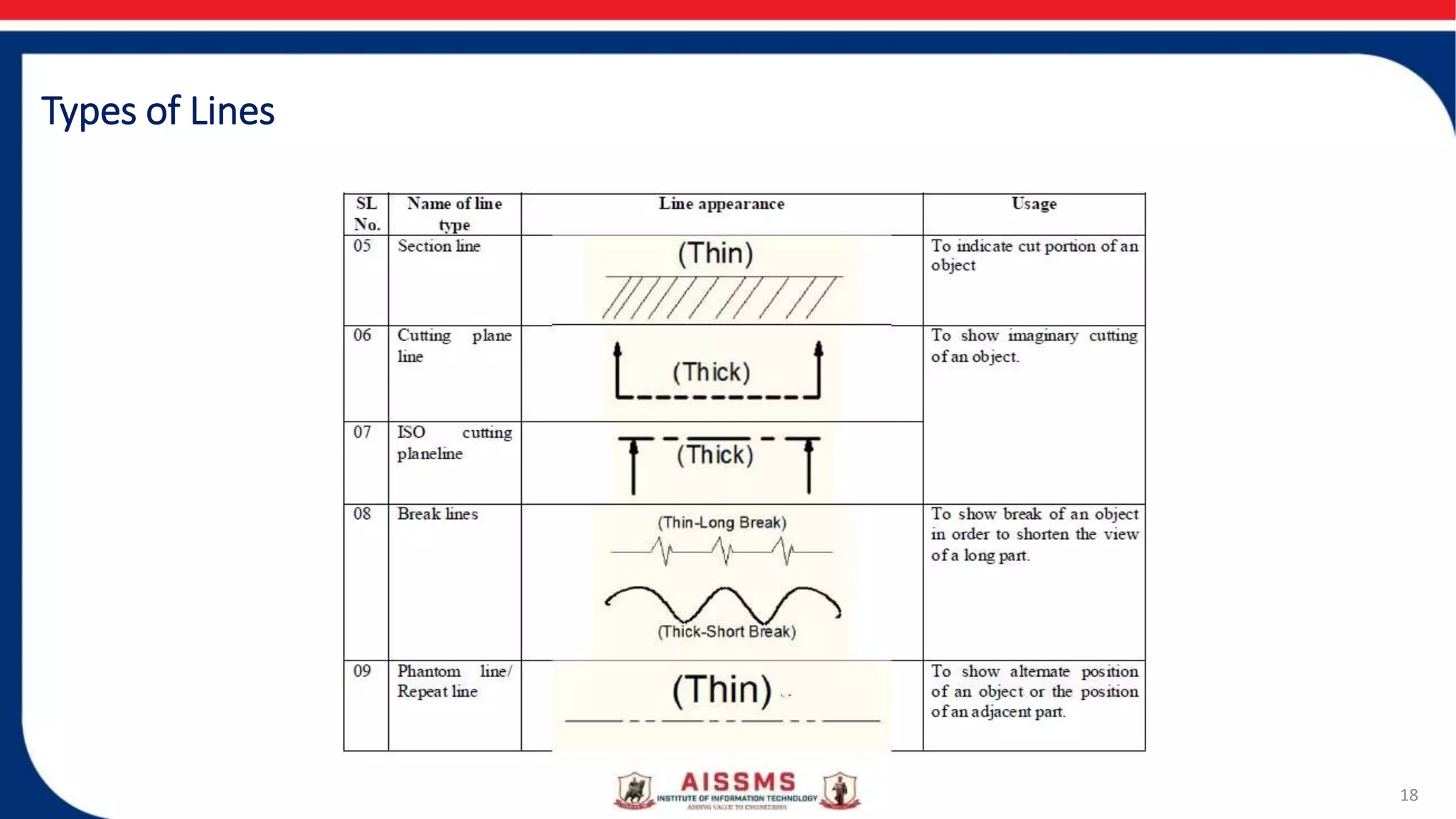
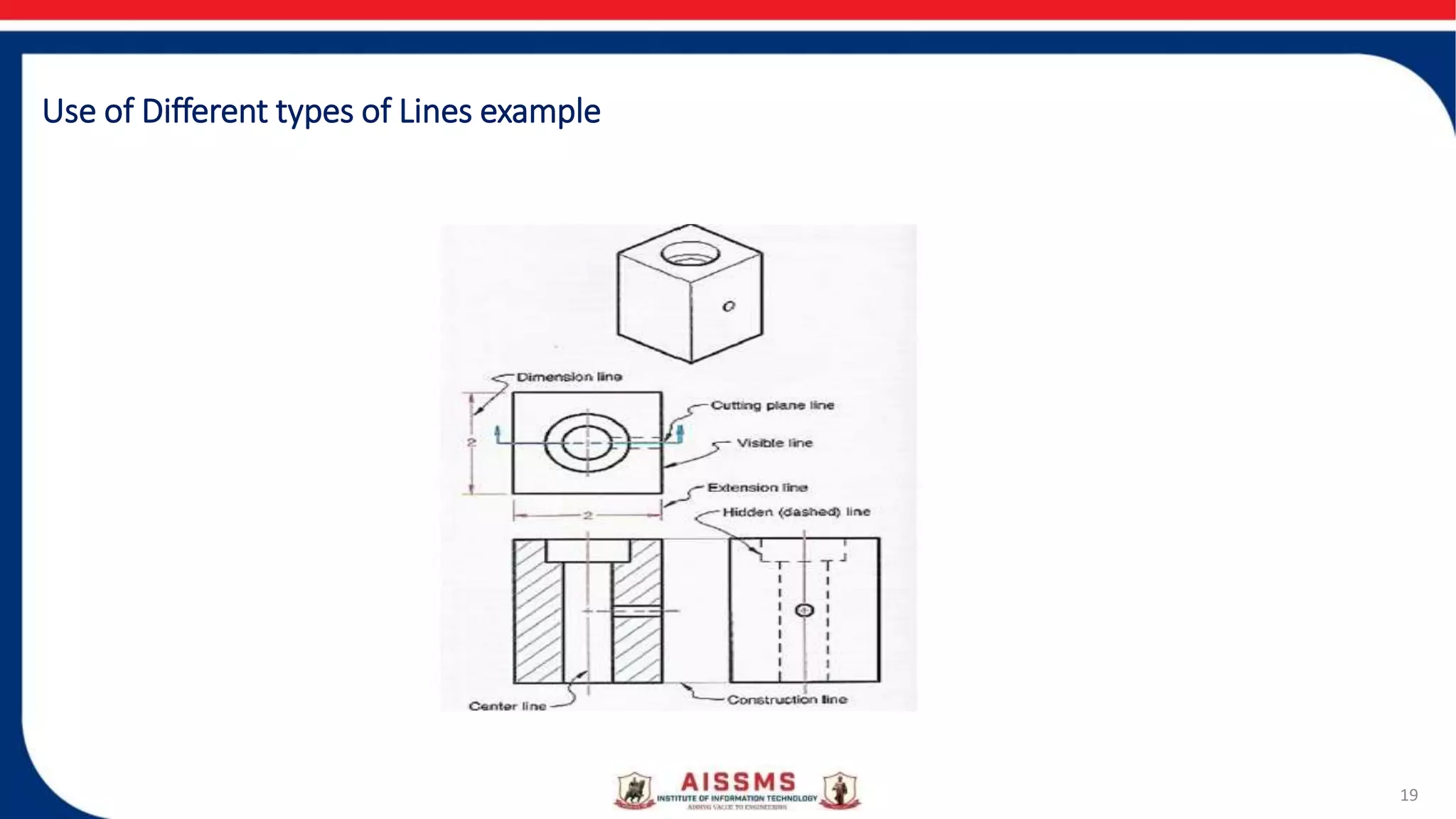
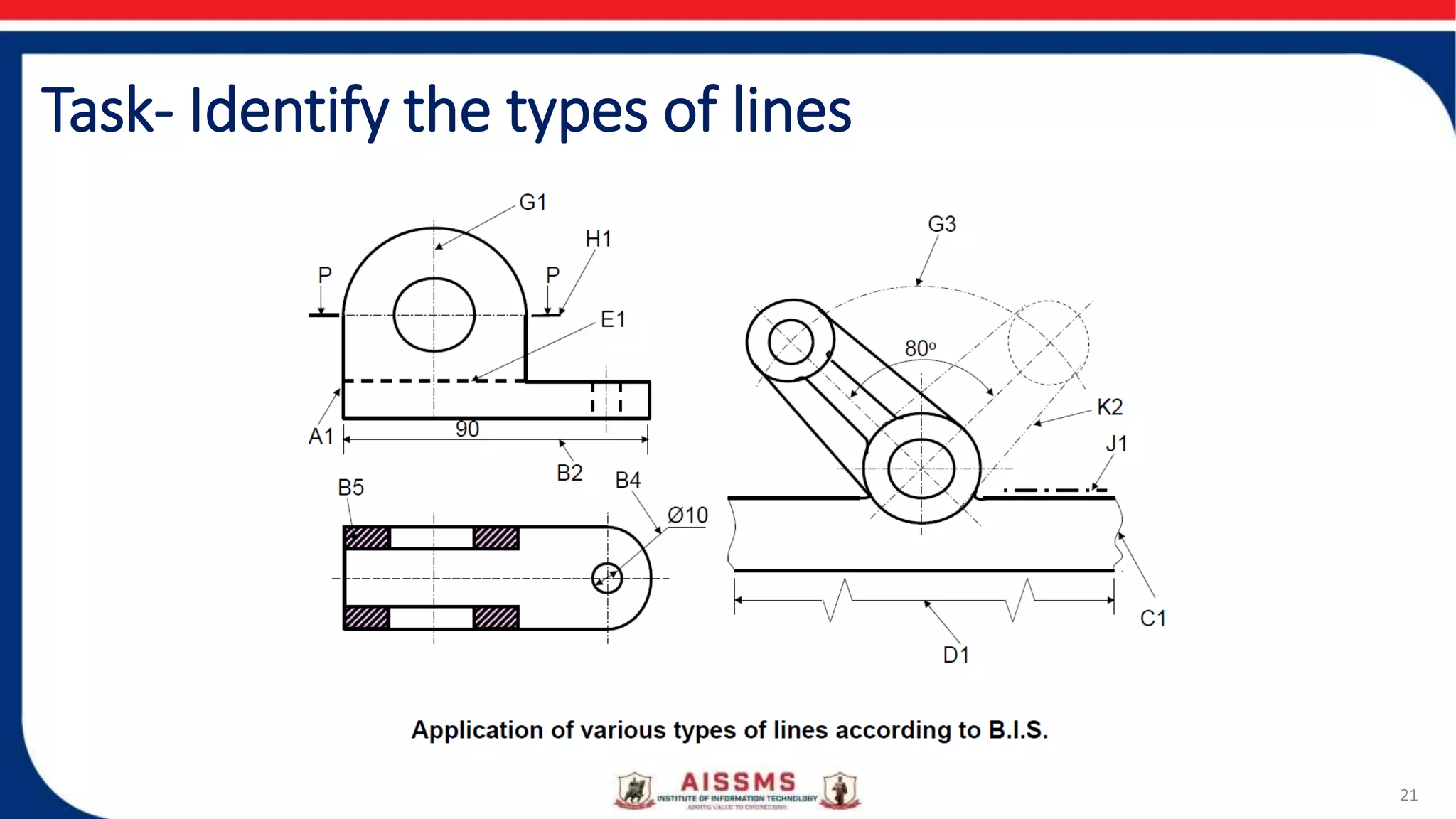
This document provides an overview of engineering drawing and graphics. It discusses the concept and need for engineering drawing, as well as its applications. Engineering drawing is defined as a graphical language used by engineers to fully and clearly define engineered items. It involves representing real or imaginary objects precisely using graphics, symbols, letters, and numbers. Engineering drawing is classified into artistic drawing and technical drawing. Technical drawing, also called instrument drawing, is used to represent engineering objects like machines, buildings, and roads. The document also covers the different types of lines used in engineering drawings and the instruments used to create them.