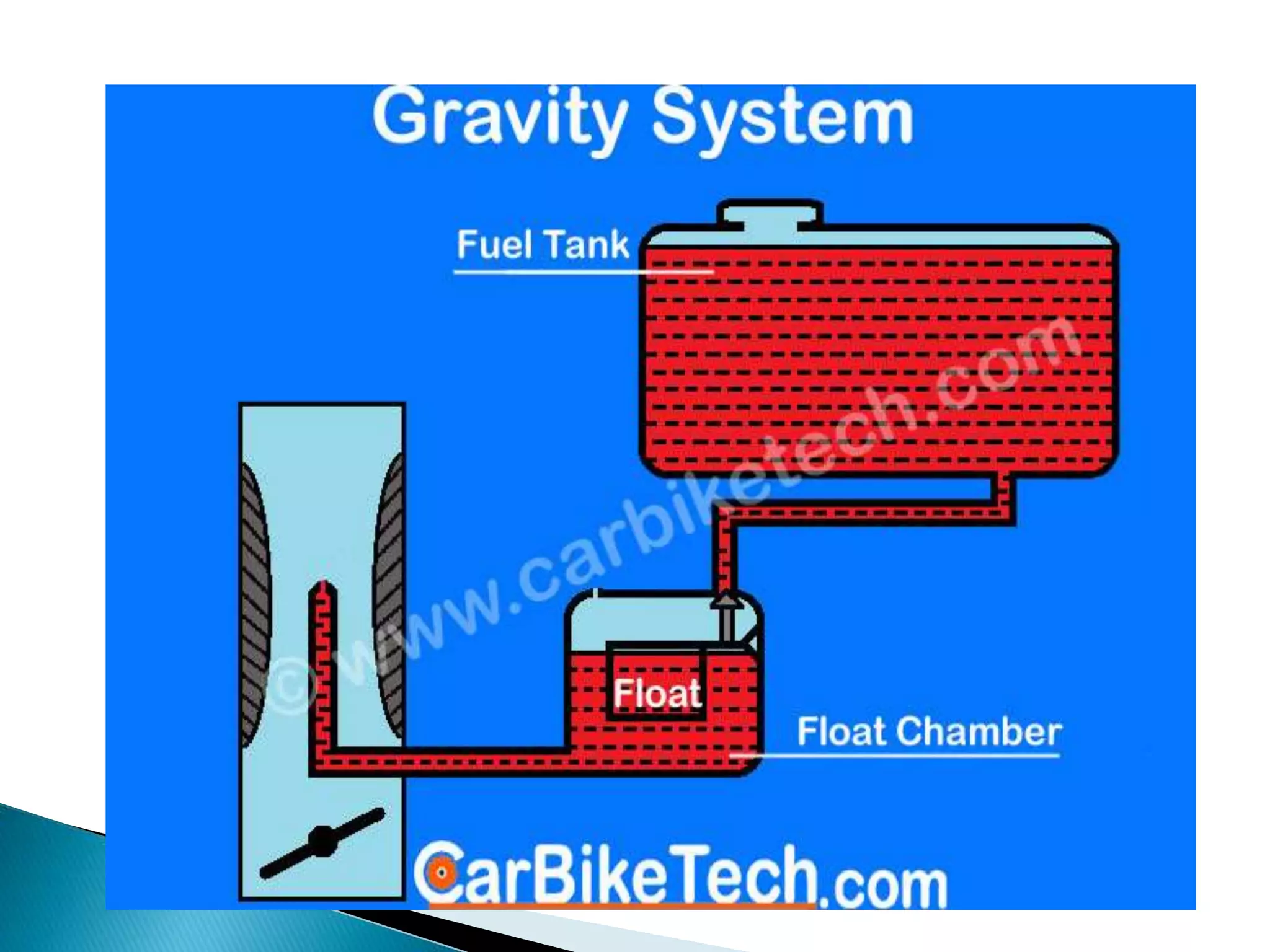
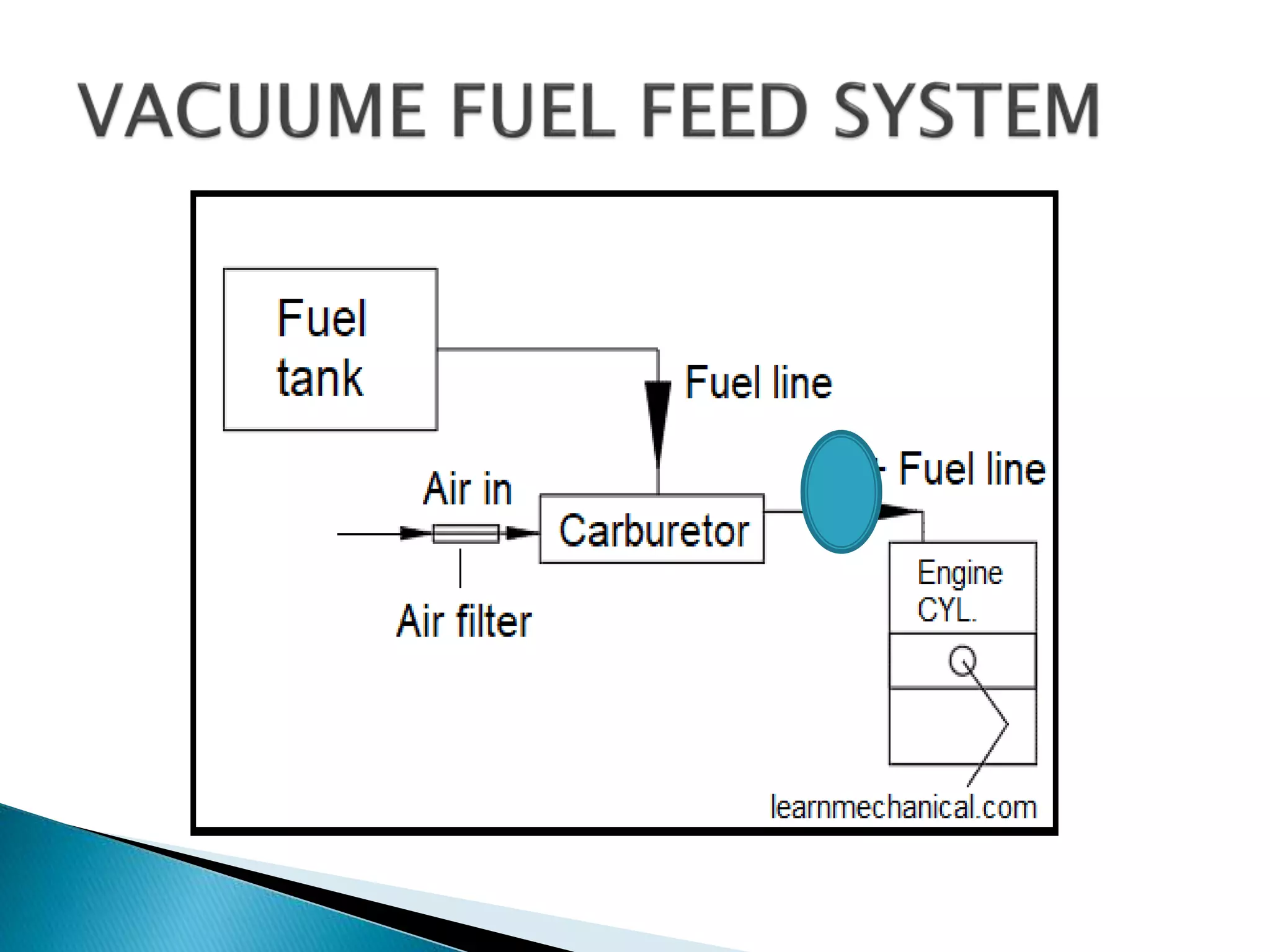
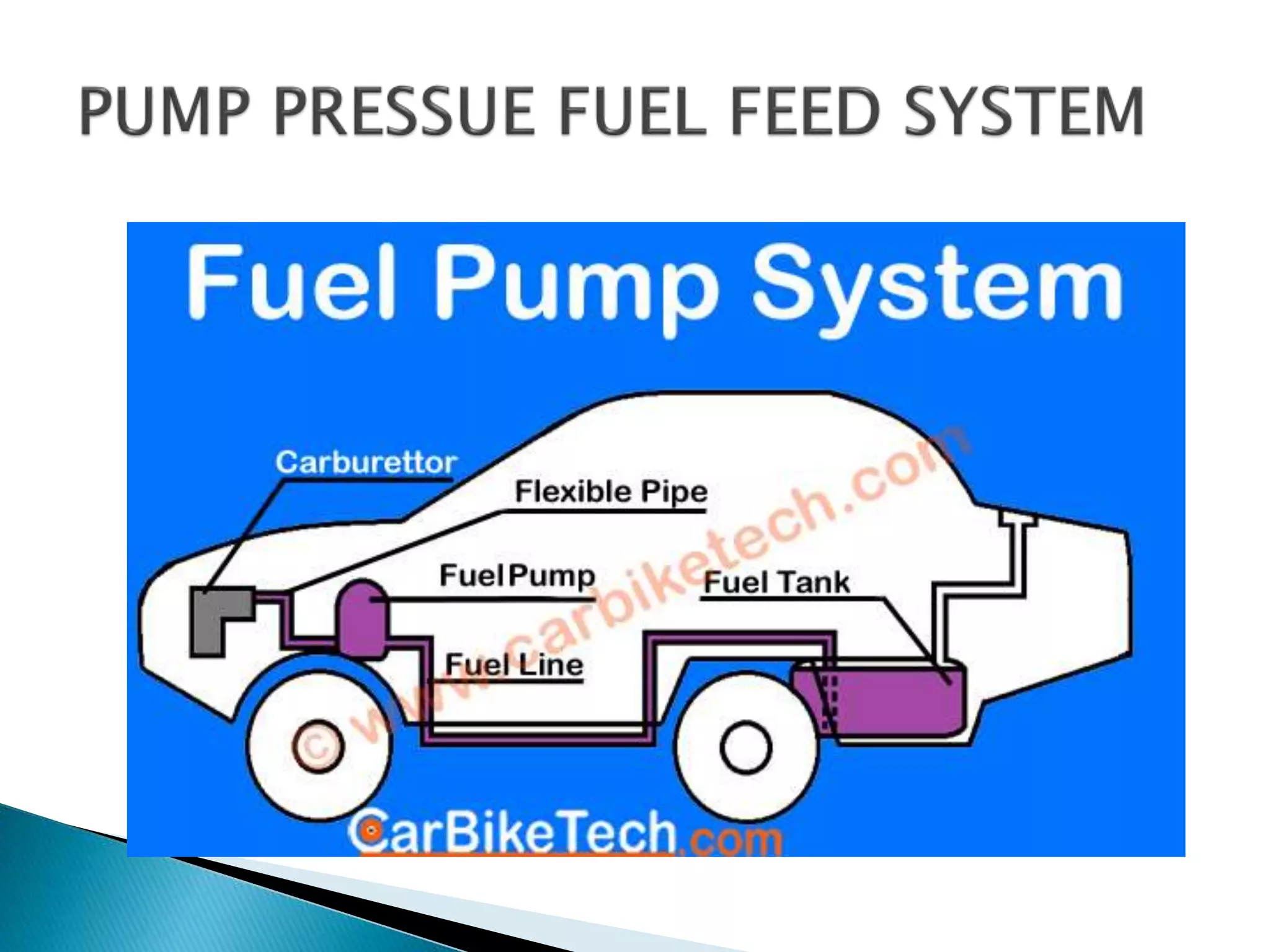
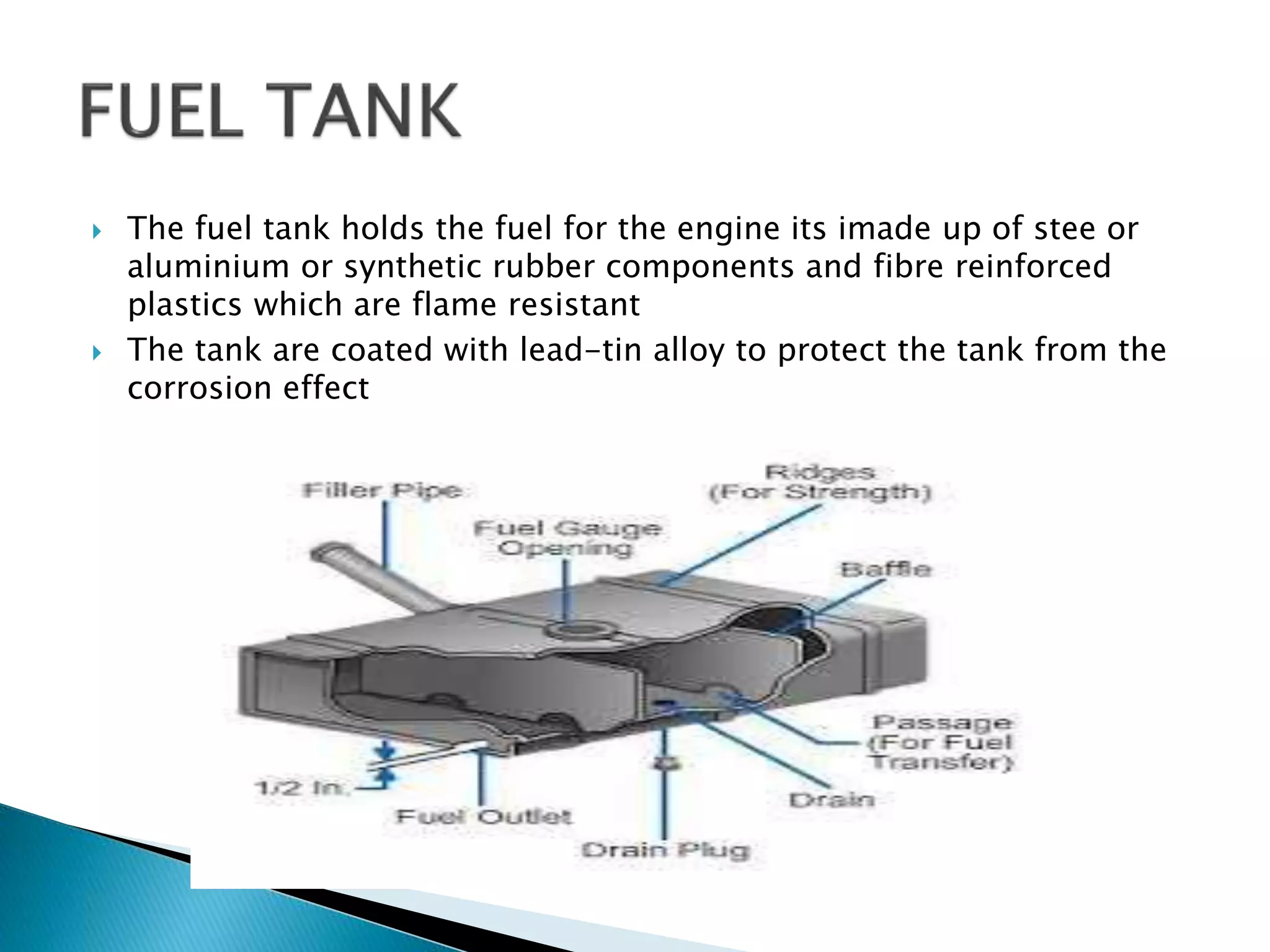
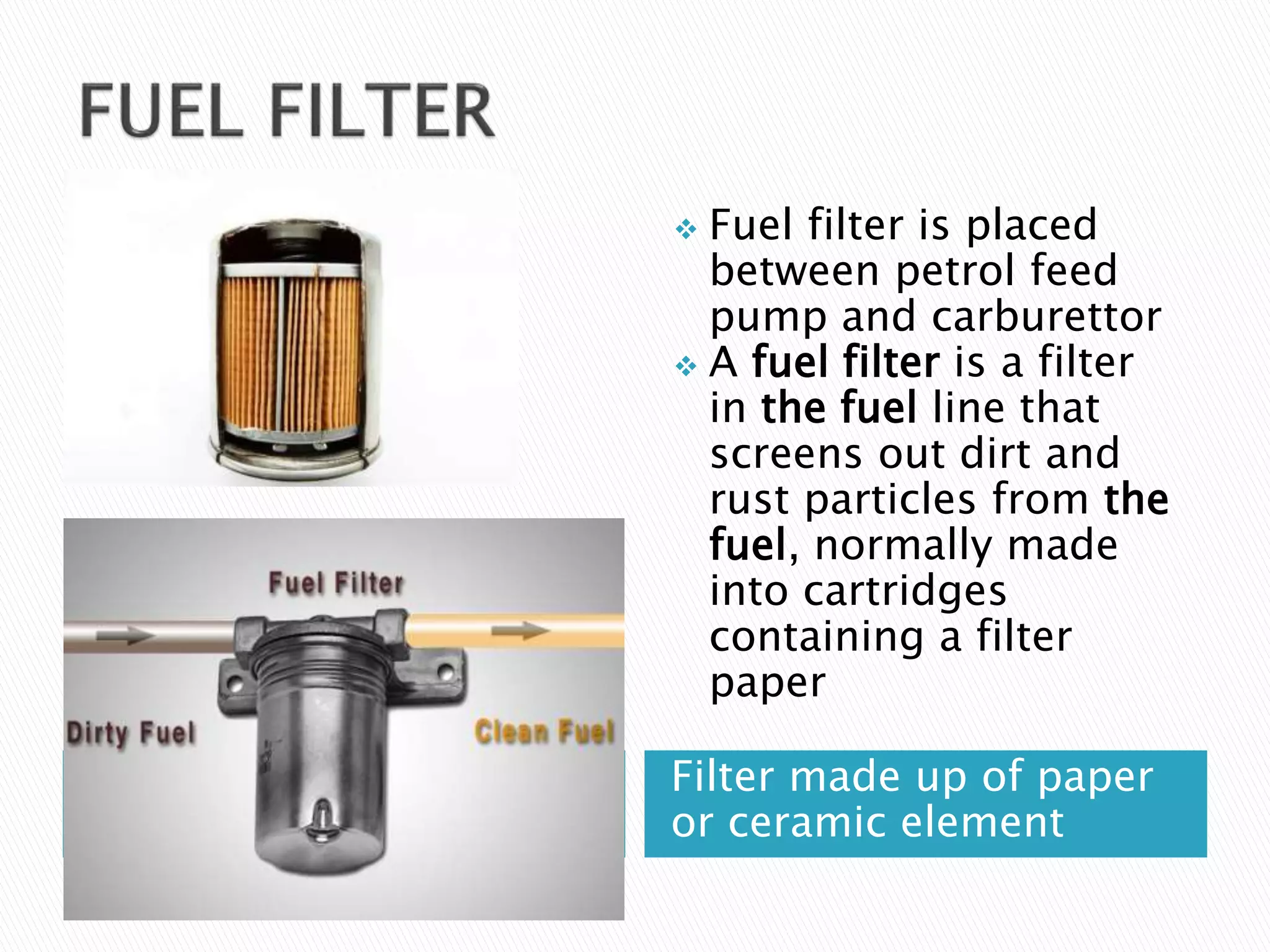
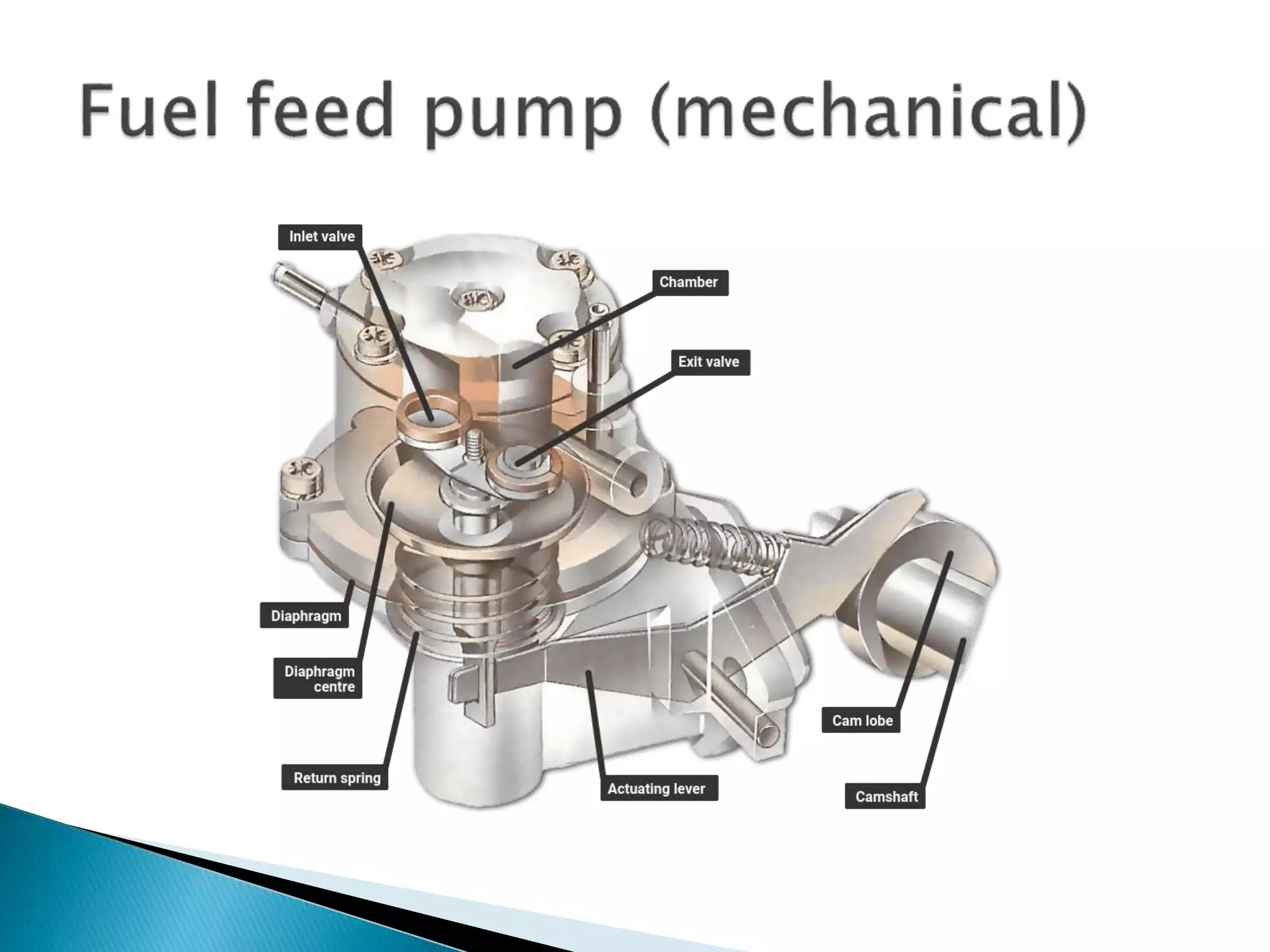
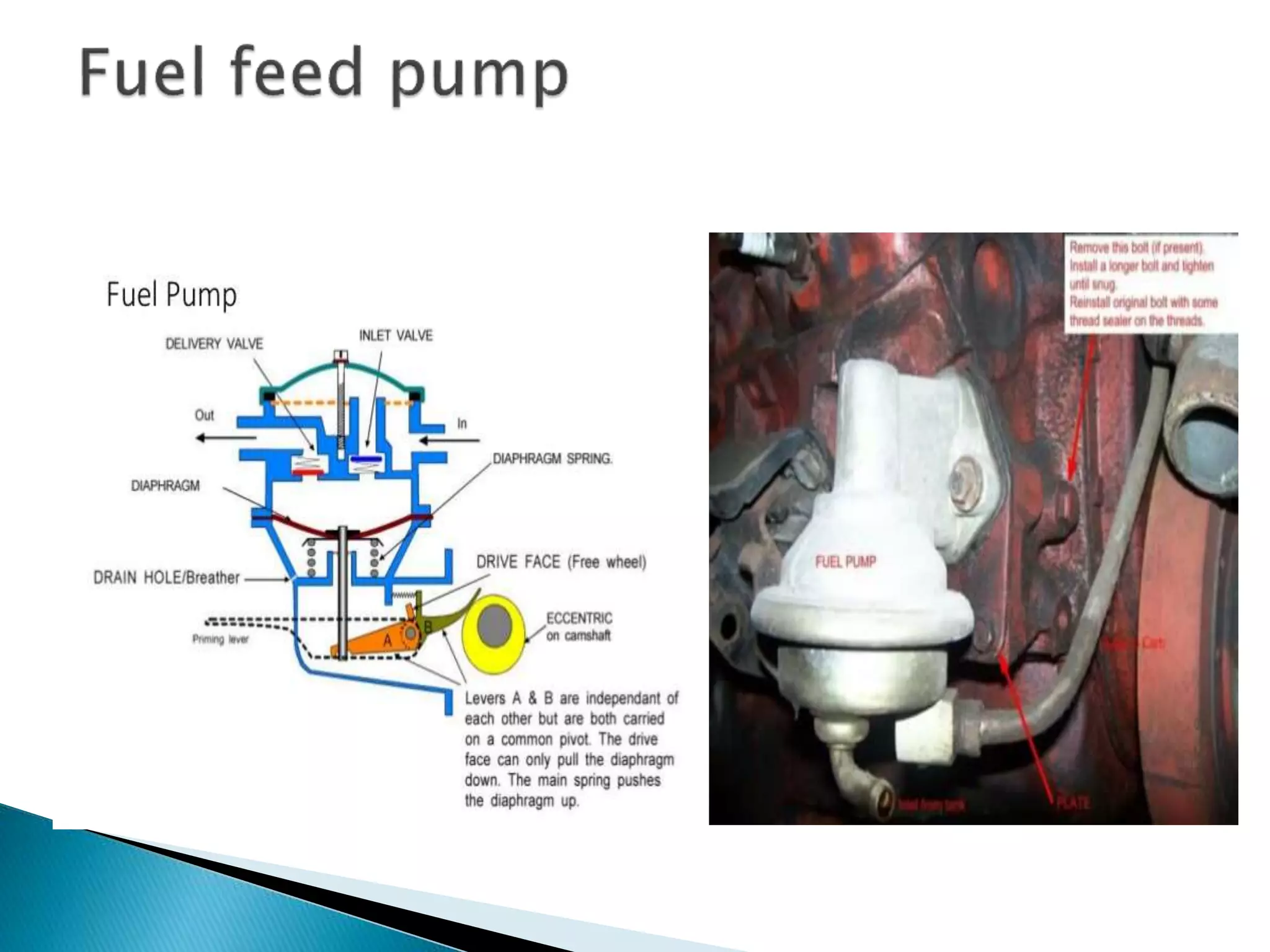
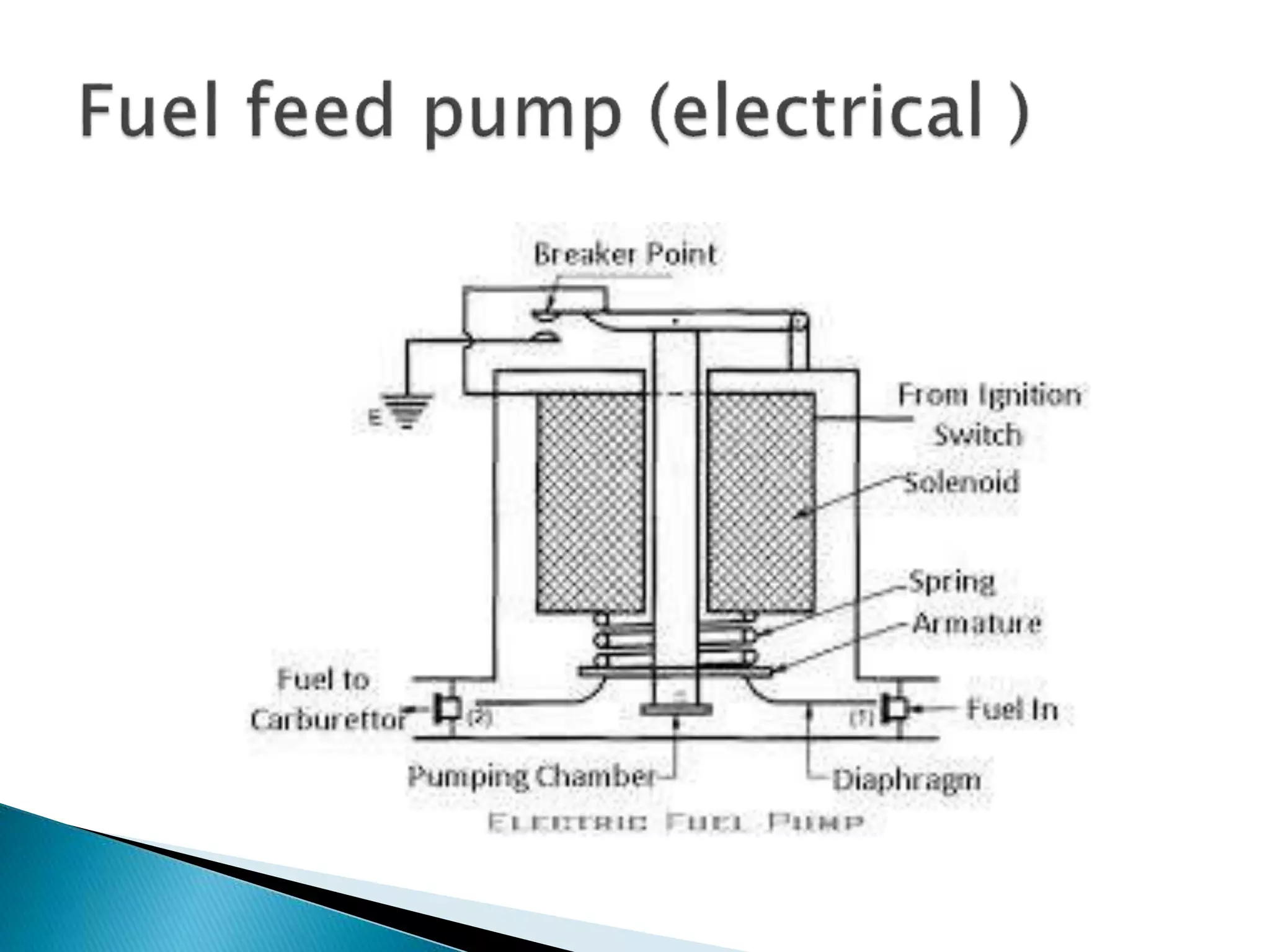
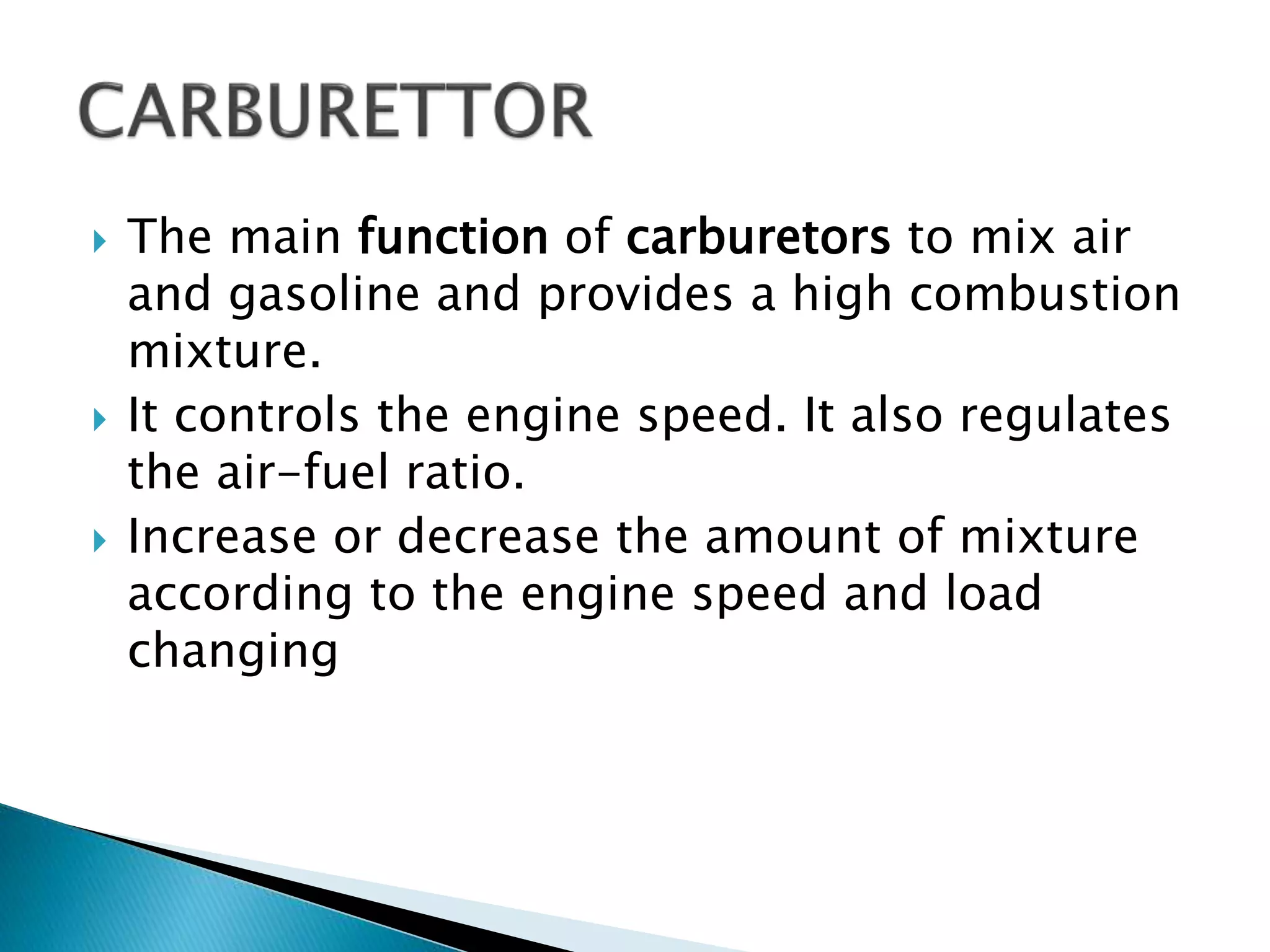
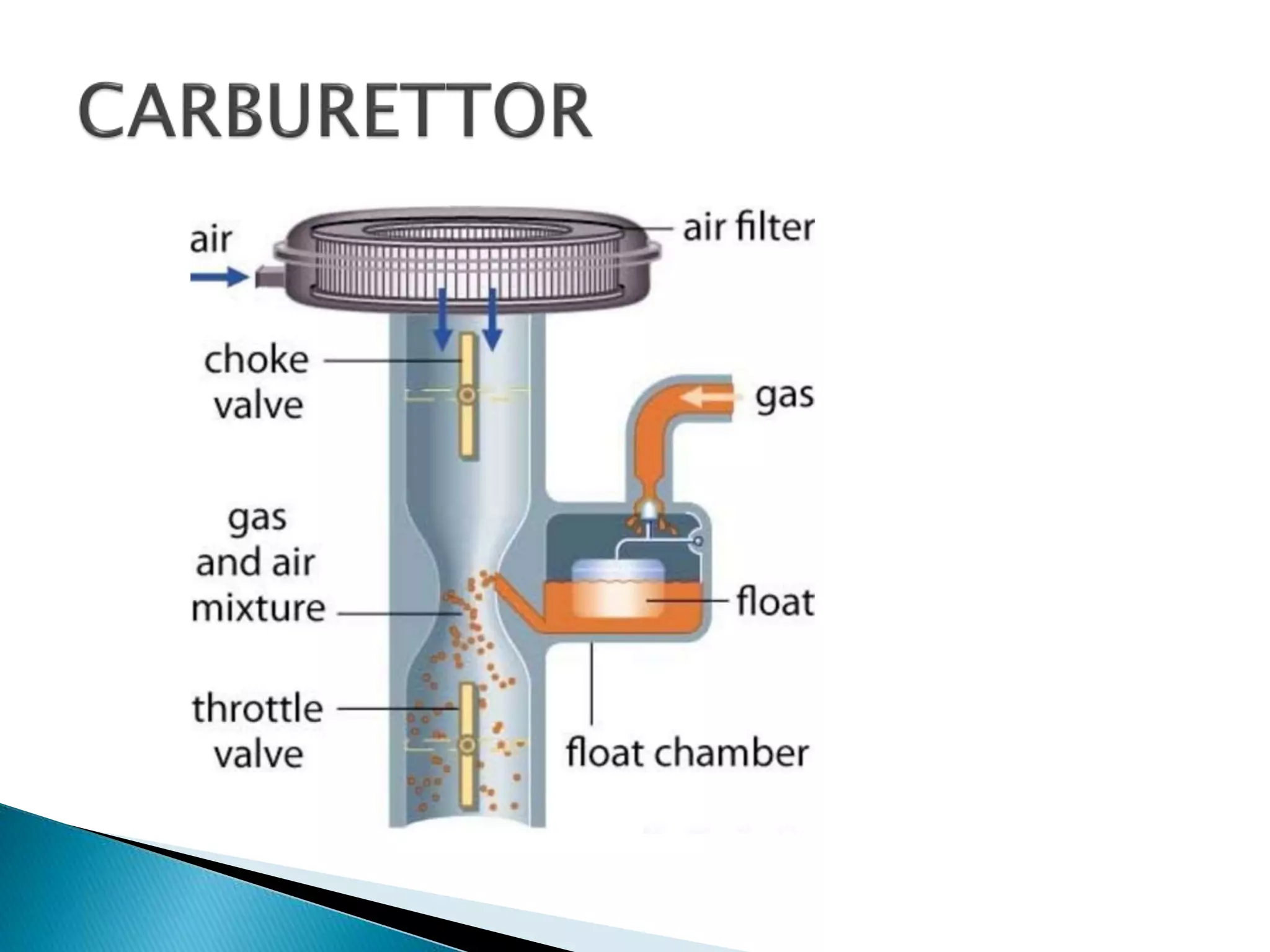
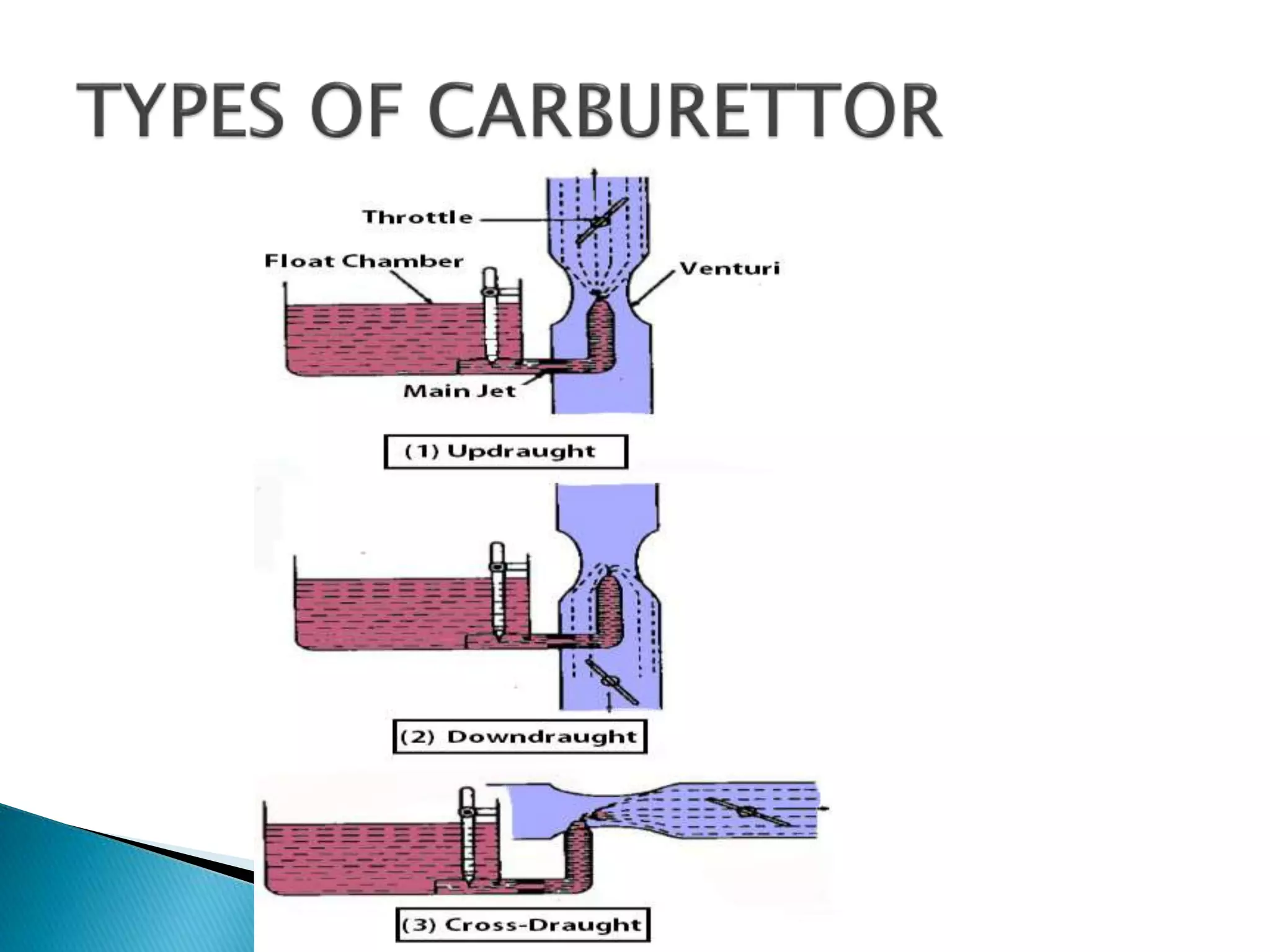
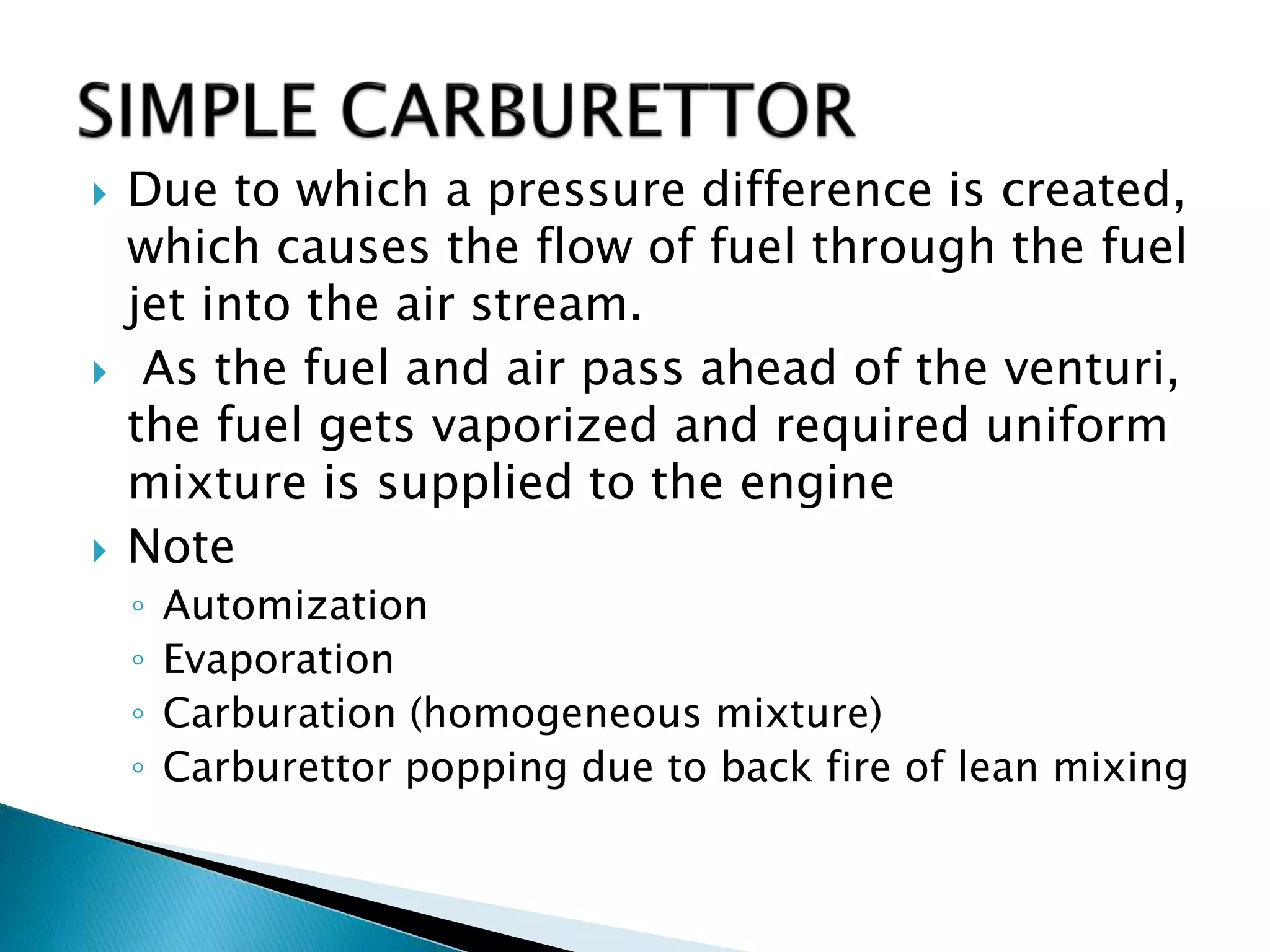
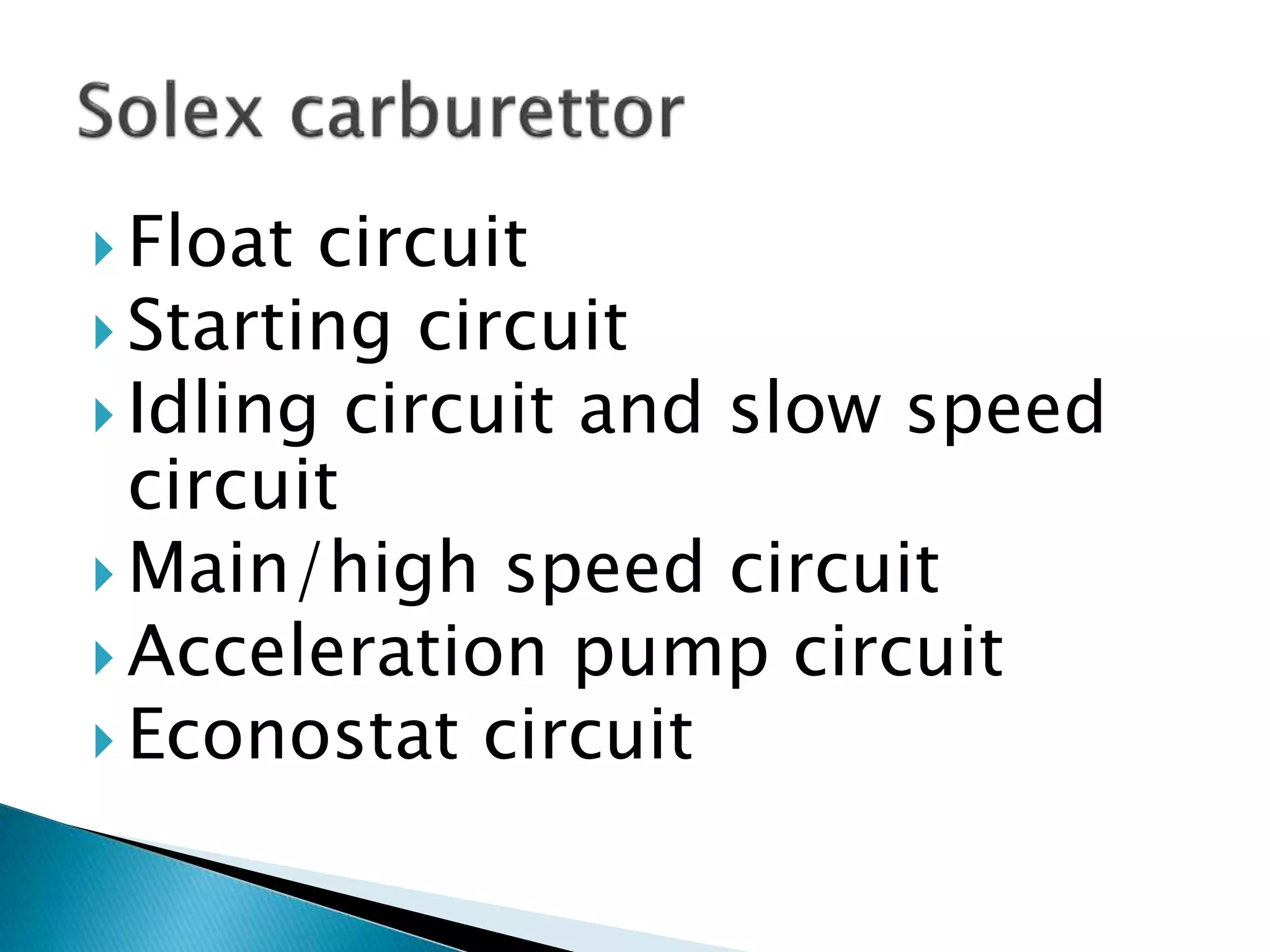
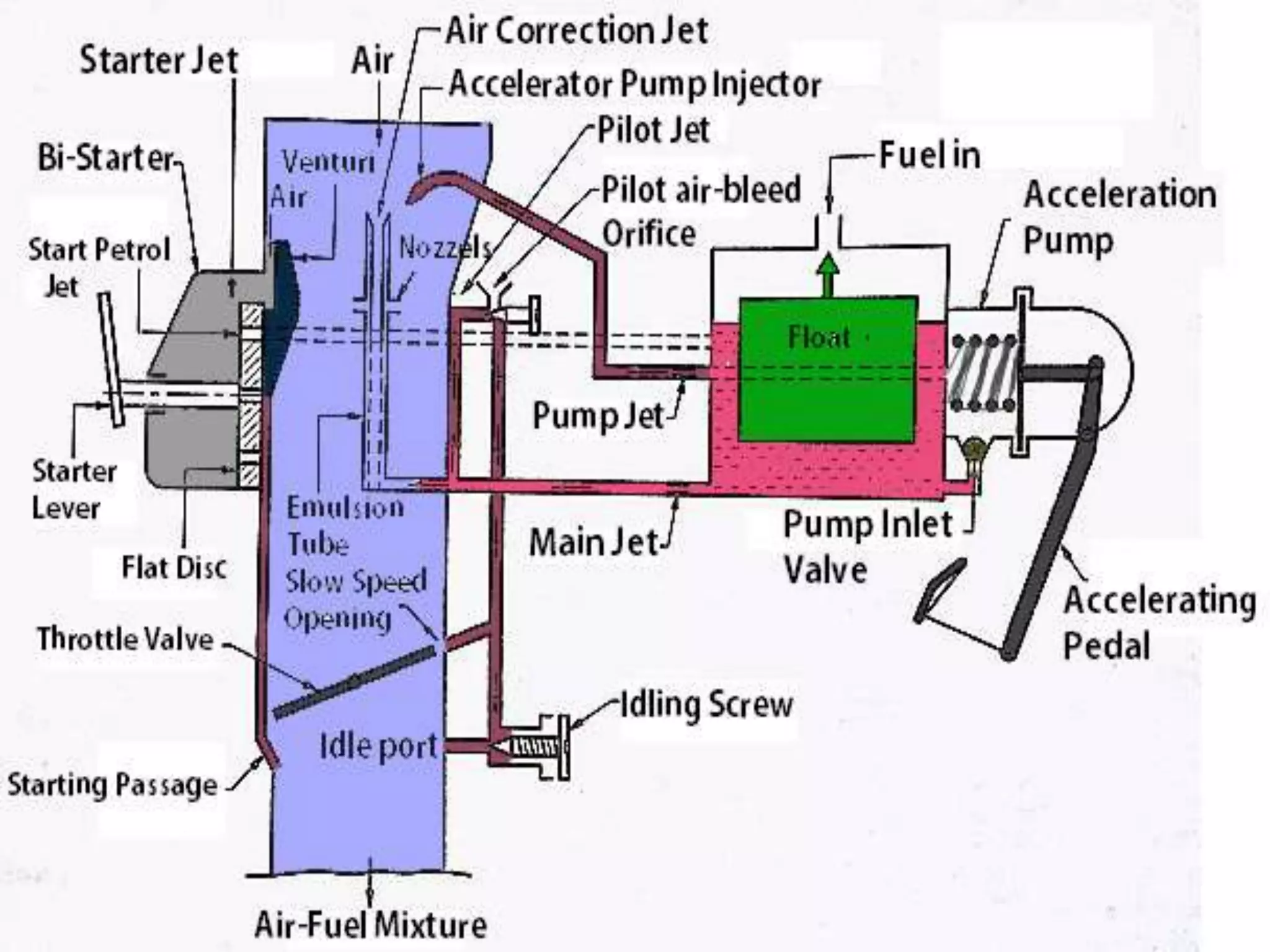
The document discusses various fuel feed systems for petrol engines. It describes gravity, air pressurized, vacuum, pump, and fuel injection systems. It explains that modern vehicles primarily use fuel injection systems with separate injectors for each cylinder. The fuel injection system provides more accurate control of the air-fuel mixture than earlier carburetor systems. Key components of fuel systems are also outlined, including the fuel tank, filters, fuel lines, carburetor or injectors, and engine management systems.