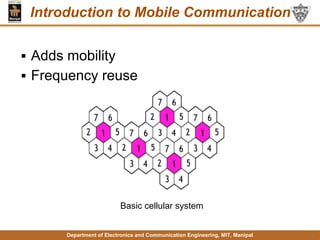
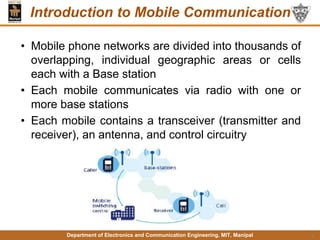
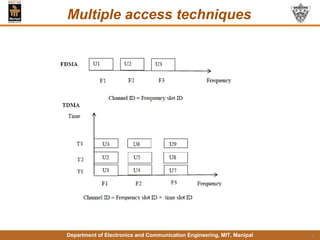
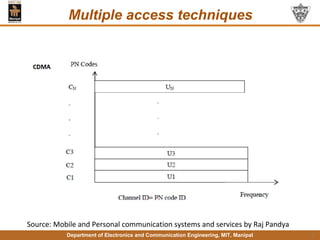
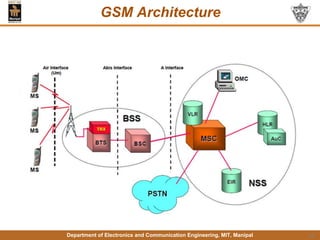
This document discusses principles of mobile communication. It introduces cellular systems and how they allow mobility and frequency reuse by dividing geographic areas into overlapping cells served by base stations. It describes uplink and downlink channels, handoffs, and roaming in cellular networks. The document also discusses multiple access techniques like FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA. Finally, it provides an overview of the GSM architecture including its base station subsystem, network subsystem components like HLR, VLR, AuC and EIR, and the mobile station elements of ME and SIM.