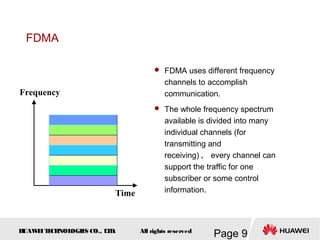
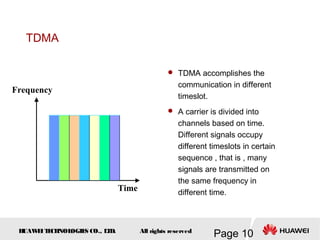
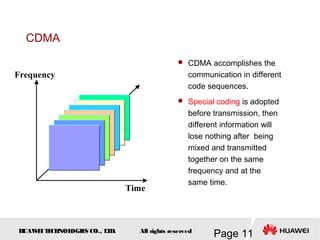
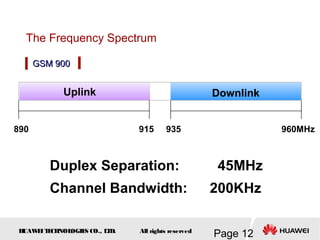
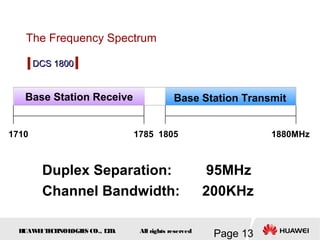
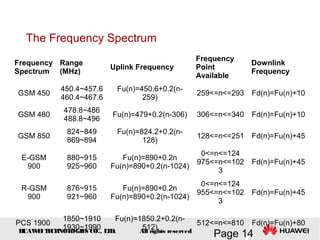
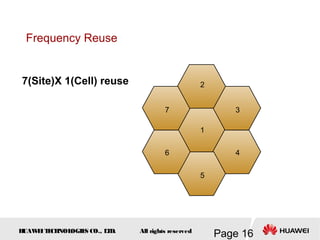
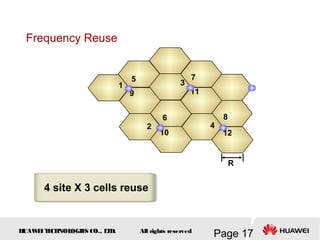
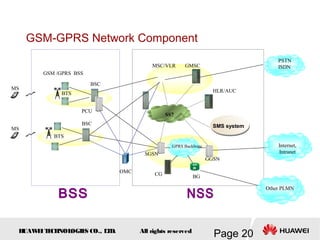
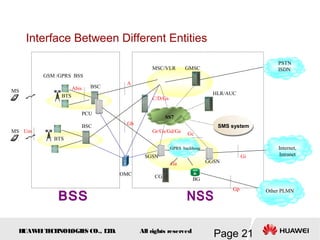
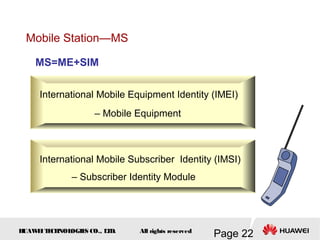
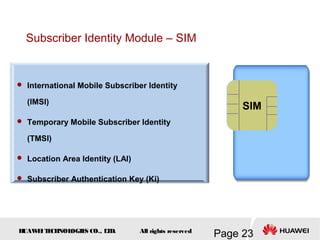
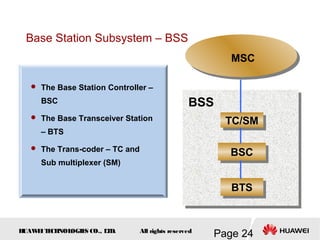
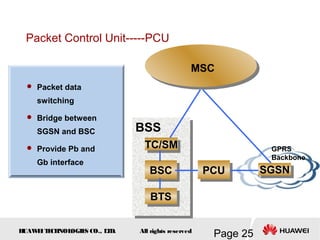
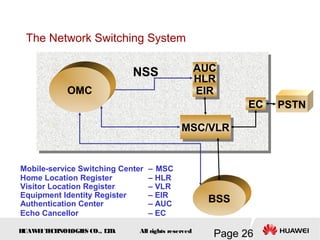
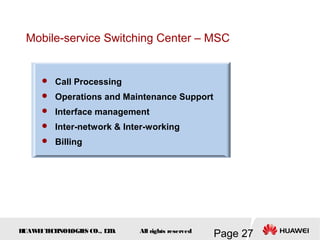
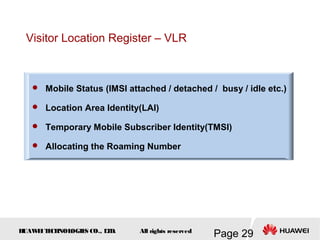
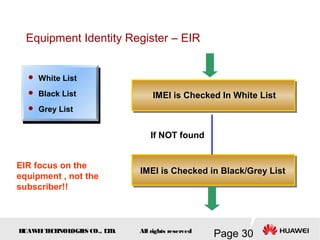
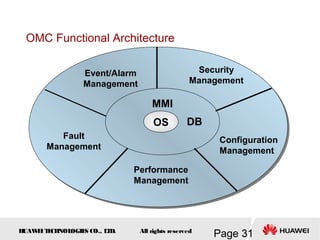
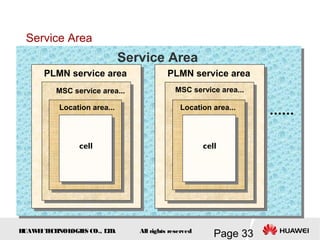
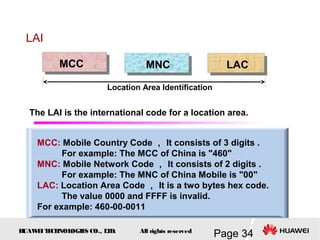
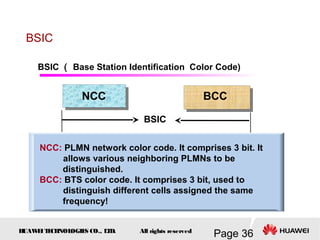
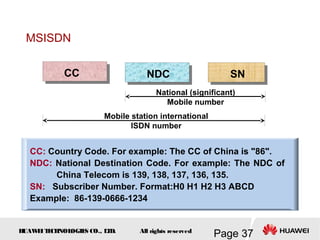
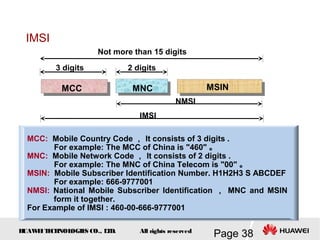
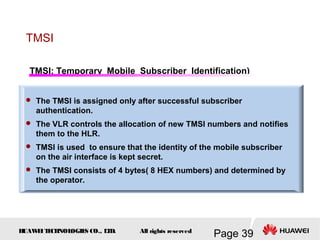
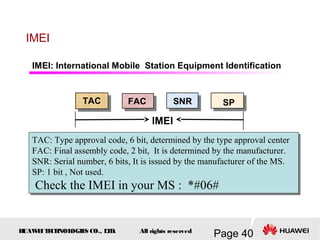
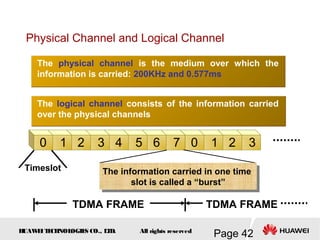
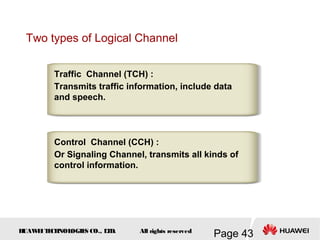
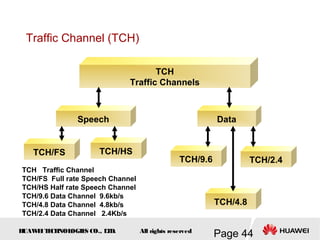
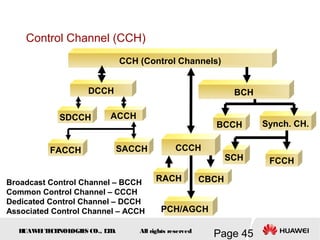
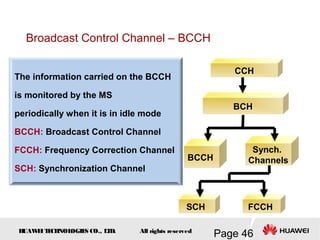
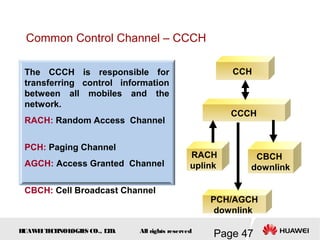
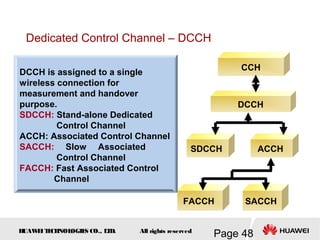
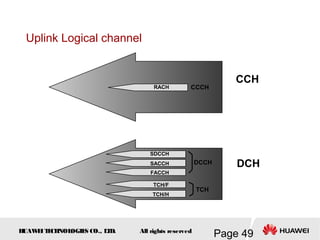
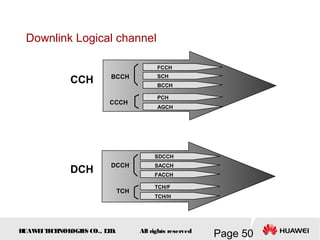
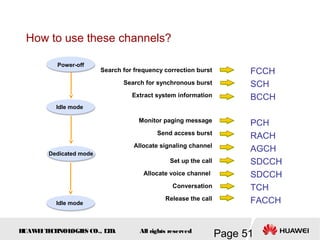
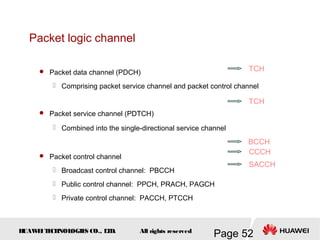
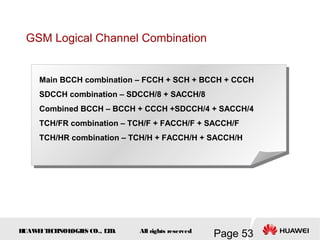
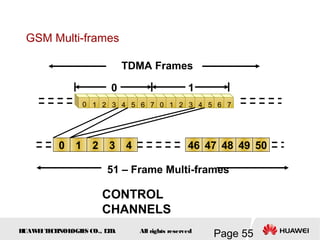
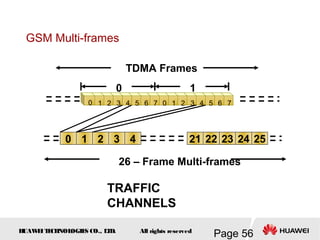
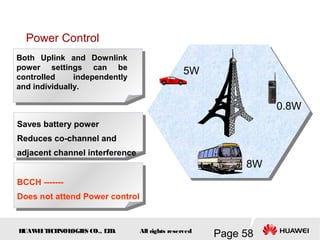
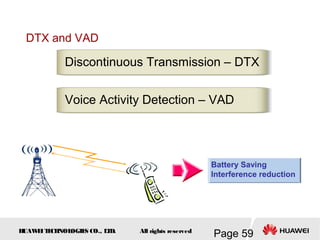
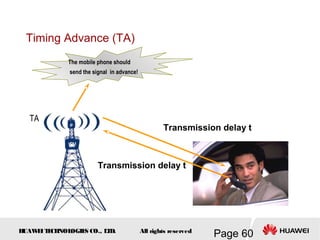
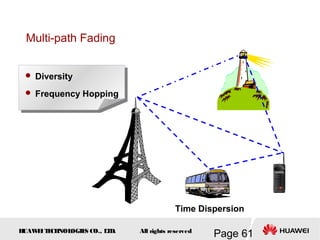
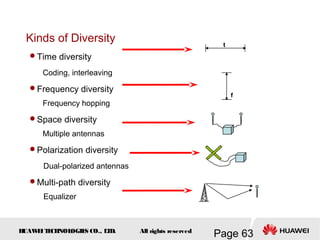
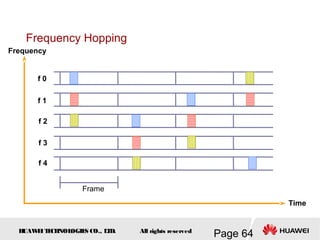
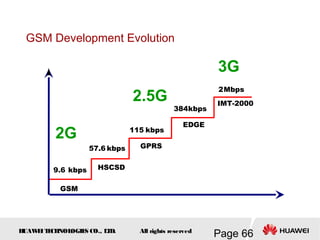
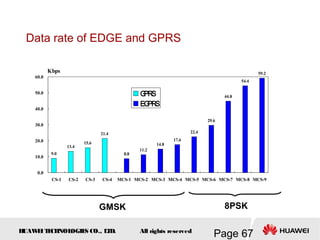
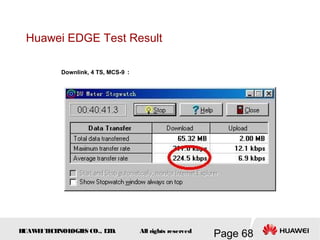
This document provides an overview of the fundamentals of GSM systems. It begins with learning objectives and outlines 6 chapters that will cover topics like GSM network structure, service area and number planning, channels on the wireless interface, radio techniques, and GPRS and EDGE introduction. The document then goes into details on concepts like GSM system overview describing frequency-division duplex and time-division multiple access techniques, frequency reuse, cell types, and multiple access techniques used in GSM. Network components of GSM like the mobile station, base station subsystem, and network switching system are also summarized.