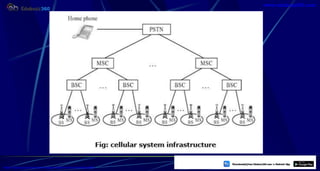
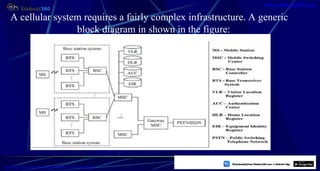
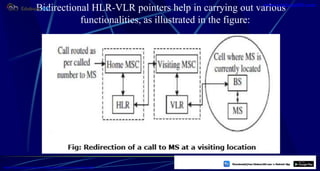
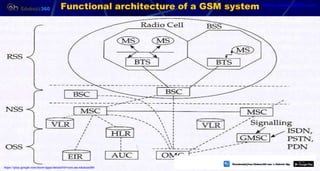
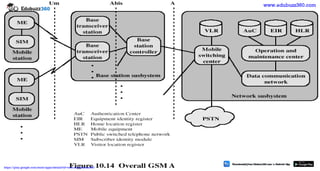
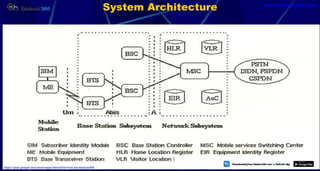
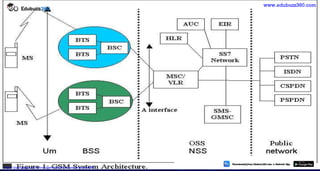
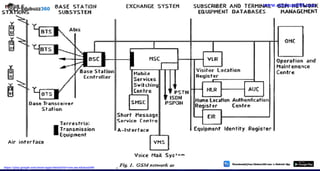
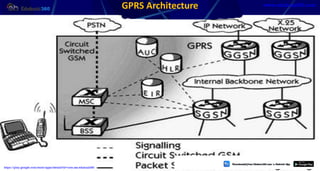
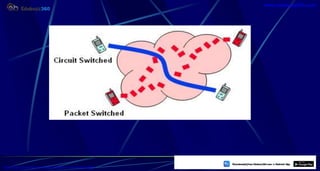
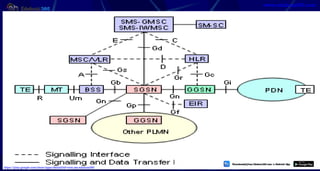
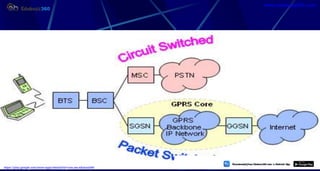
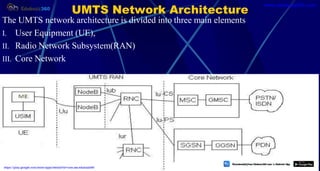
This document provides information about mobile computing and mobile telecommunication systems. It discusses cellular systems and how they implement space division multiplexing using base stations and cells. It describes the advantages and disadvantages of cellular systems. It also provides details on cellular infrastructure including base stations, base station controllers, mobile switching centers, home location registers, visitor location registers, and authentication centers. Finally, it discusses global system for mobile communication (GSM) including its services, architecture, security features, and advantages over other mobile standards.