This document provides an overview of basic electricity principles including:
- Electricity is a form of energy generated by friction, induction, or chemical change that has magnetic, chemical, and radiant effects.
- There are two types of electricity: static electricity caused by friction and current electricity produced by moving electrons.
- Key concepts include voltage, current, resistance, circuits, and Ohm's Law. Circuits can be connected in series or parallel.
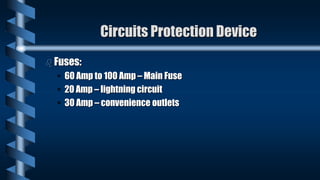
- Proper wire sizing and circuit protection devices like fuses or circuit breakers are important for standard home wiring specifications.