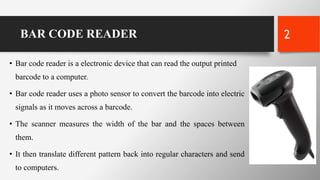
The document provides a comprehensive overview of barcode readers, explaining how they work, their components, and their significance in various industries. It details the process of converting barcodes into digital signals, the structure of barcodes including start and end codes, and the role of check digits in ensuring accuracy. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using barcode systems across applications such as retail, libraries, and healthcare.