This document summarizes several bacterial diseases:
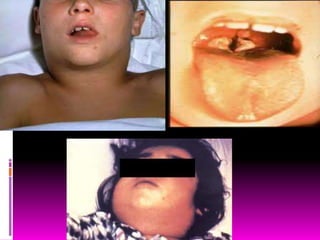
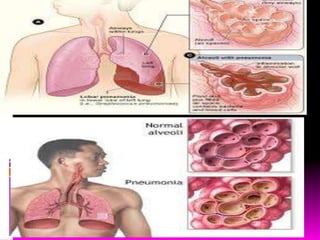
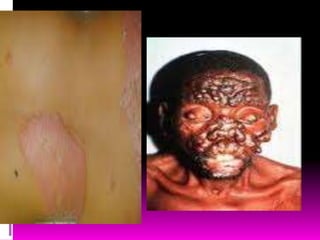
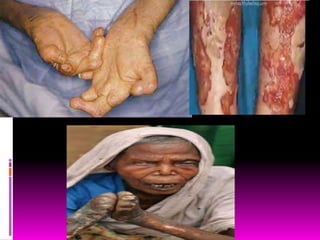
Tuberculosis is caused by two types of bacteria and spreads through coughing or sneezing. It is diagnosed using tuberculin tests and treated with long-term antibiotic therapy. Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae toxin and infects the respiratory tract, forming a membrane that can block breathing. It is prevented by the DTP vaccine. Pneumonia infects the lungs when bacteria are inhaled and is treated with antibiotics like penicillin. Leprosy is a chronic disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae that spreads through direct contact and is treated.