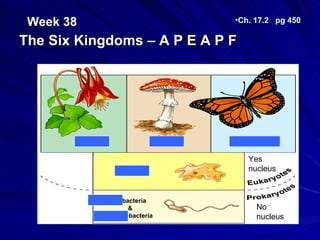
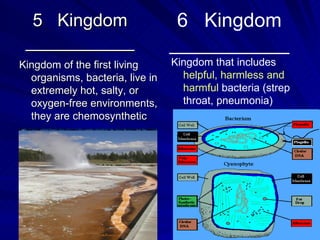
1. The document discusses the six kingdoms of life: Bacteria, Archaebacteria, Protist, Fungi, Plant, and Animal. It describes key characteristics of each kingdom.
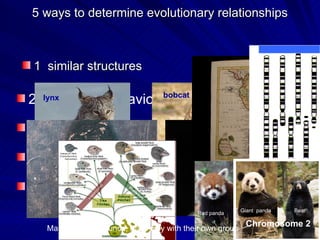
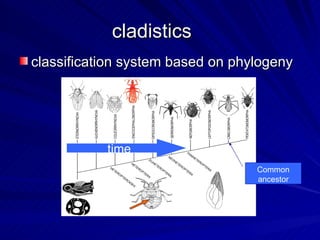
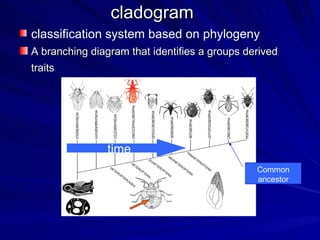
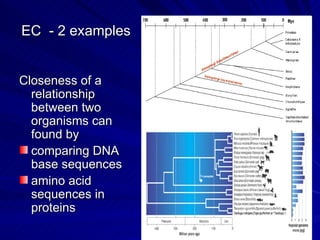
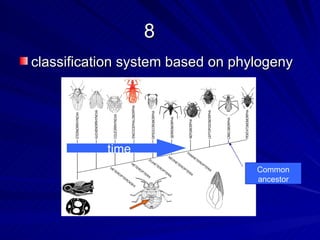
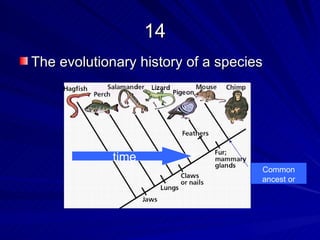
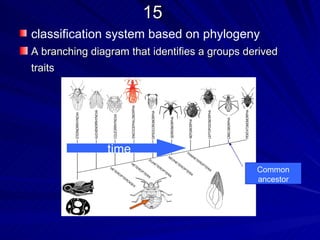
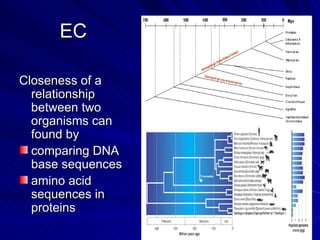
2. Five methods for determining evolutionary relationships are discussed: similar structures, breeding behavior, geographic distribution, chromosome comparisons, and biochemistry. Cladistics is the classification system based on evolutionary history/phylogeny.
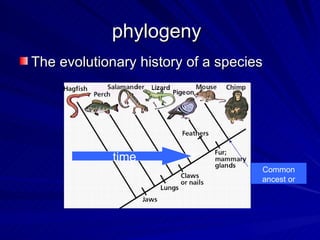
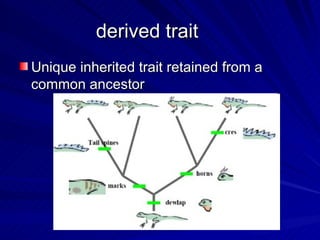
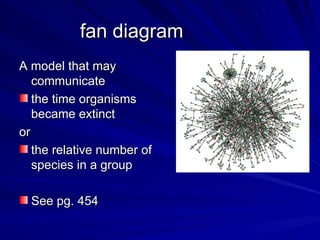
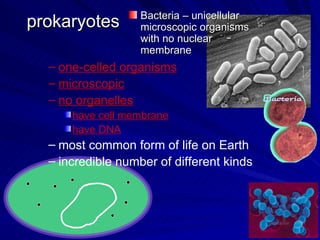
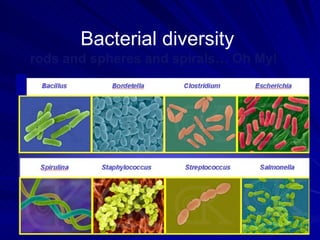
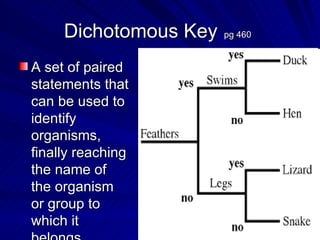
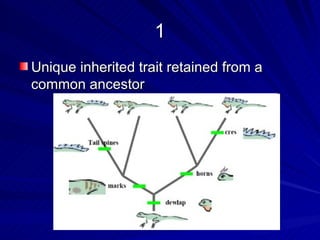
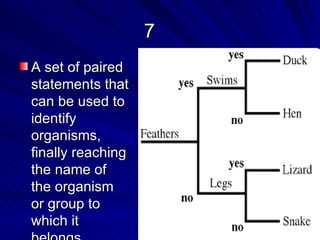
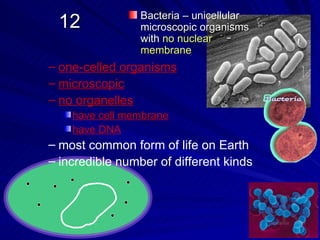
3. Key terms discussed include: derived trait, fan diagram, heterotroph, autotroph, chemosynthetic, photosynthetic, dichotomous key, and phylogeny. Bacteria are described as unicellular, microscopic organisms without nuclei.