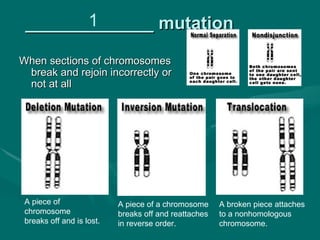
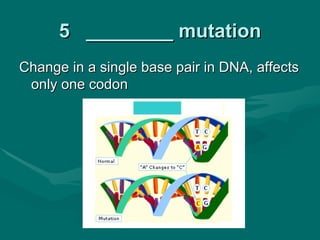
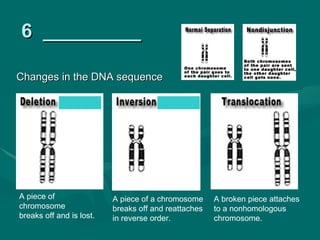
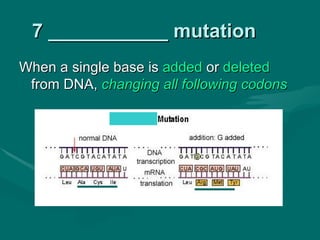
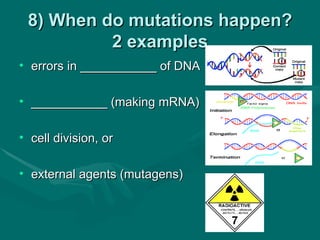
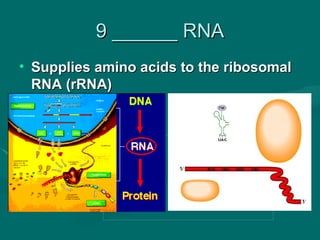
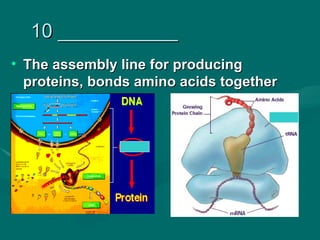
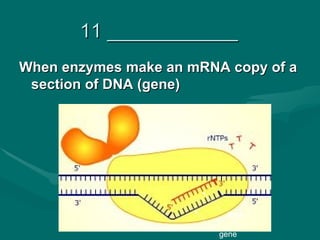
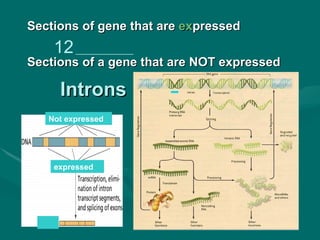
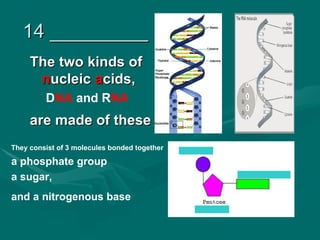
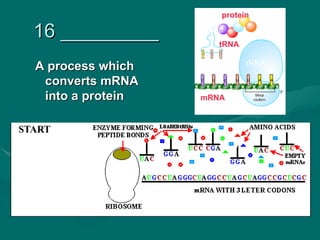
1. Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can occur due to errors in DNA replication, transcription, cell division, or exposure to mutagens.
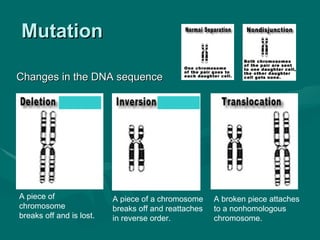
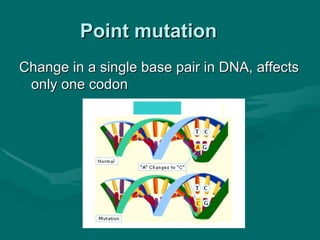
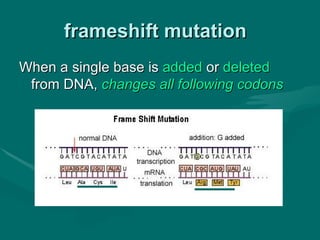
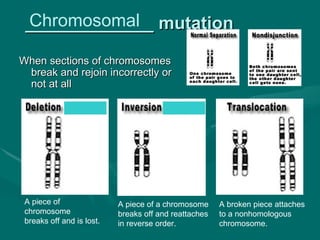
2. There are several types of mutations including point mutations, frameshift mutations, and chromosomal mutations.
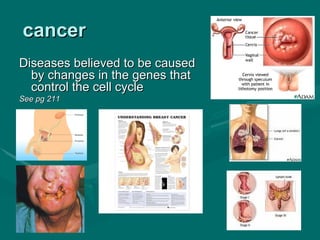
3. Cancer and other diseases can be caused by mutations that change genes controlling the cell cycle.