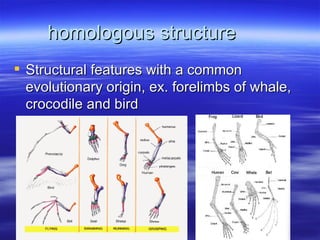
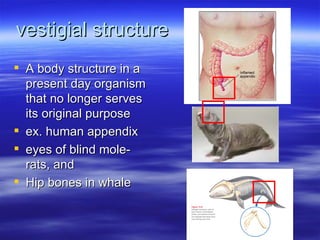
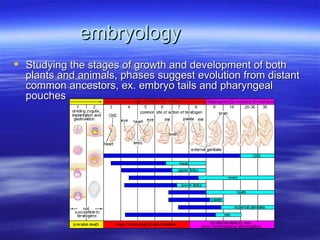
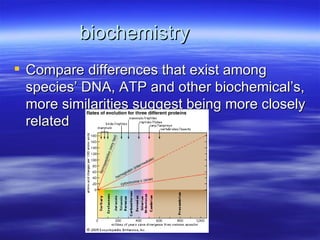
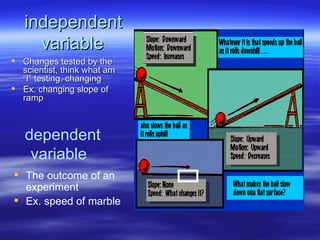
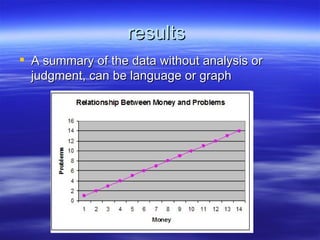
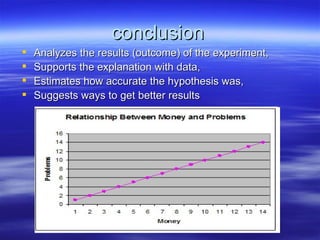
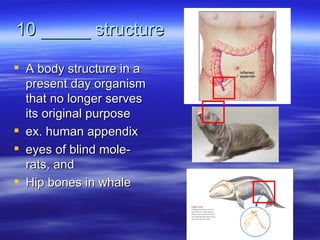
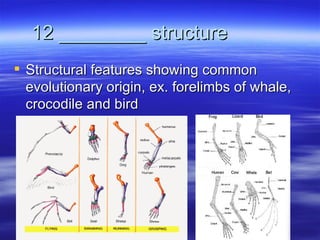
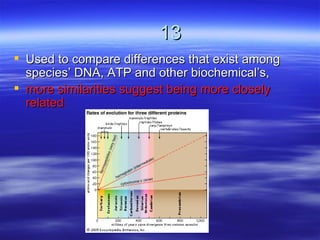
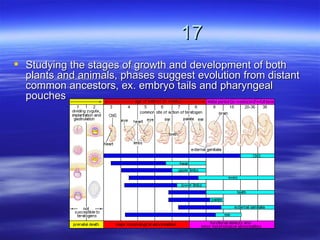
The document discusses key concepts relating to evolution over time, including that all living things have a common ancestor, and that humans and apes evolved from a common ancestor rather than humans evolving from apes. It also discusses various evolutionary mechanisms and adaptations, such as artificial selection, natural selection, adaptations, homologous and analogous structures, vestigial structures, and more. The document contains examples and definitions for many important evolutionary terms.