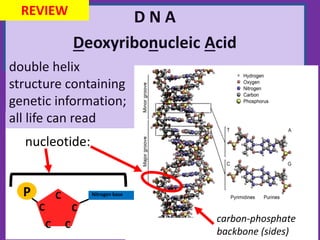
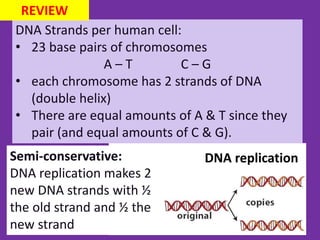
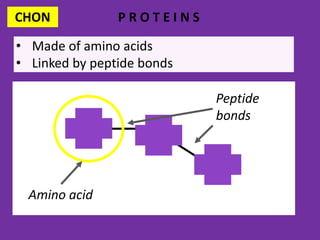
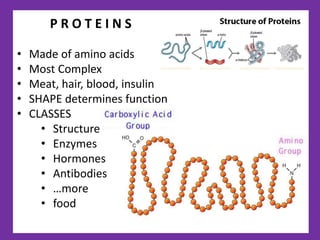
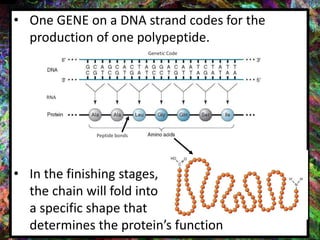
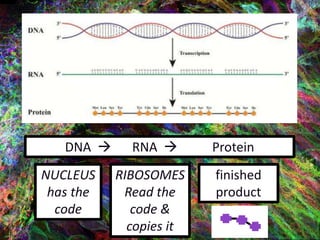
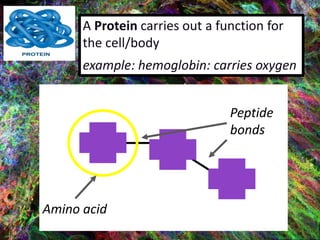
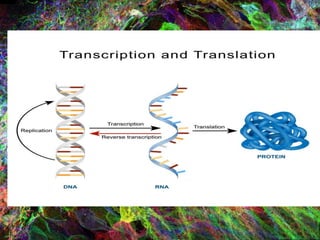
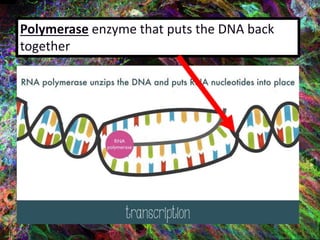
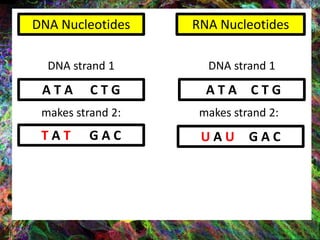
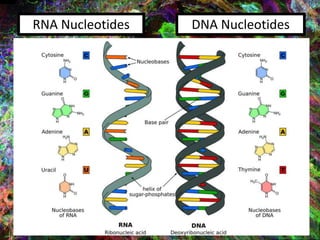
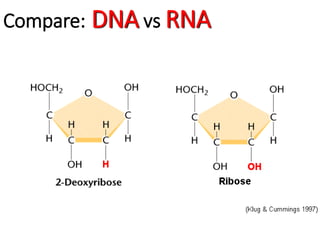
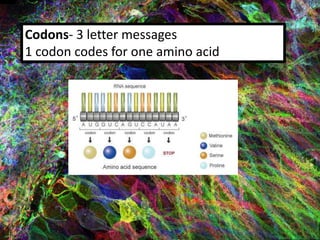
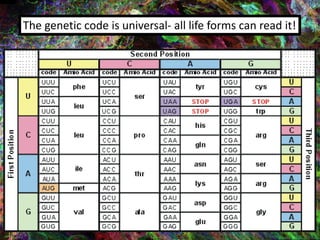
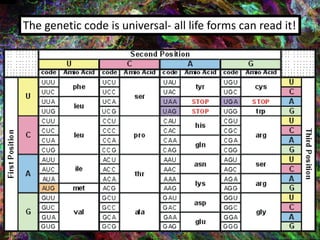
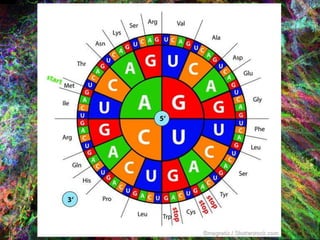
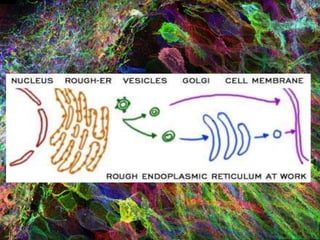
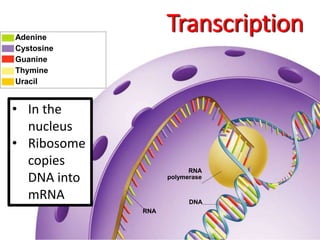
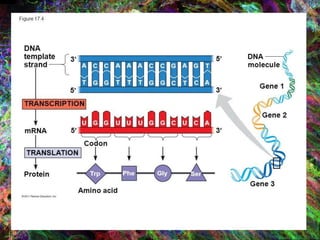
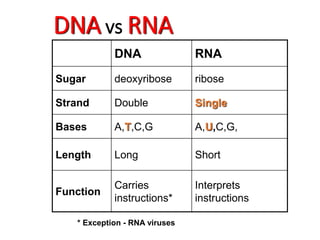
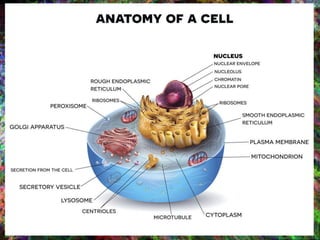
1. DNA contains the genetic instructions and is located in the nucleus.
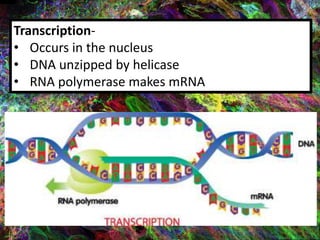
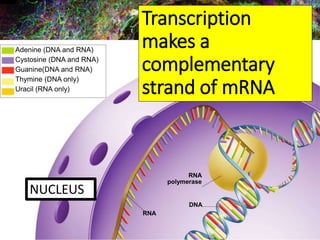
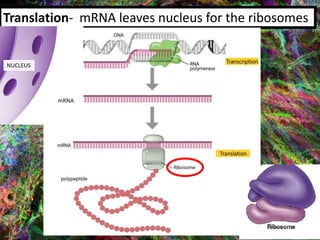
2. During transcription, DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase.
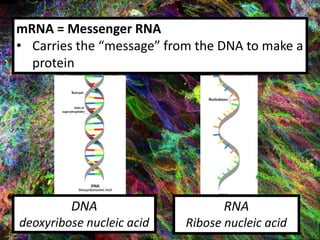
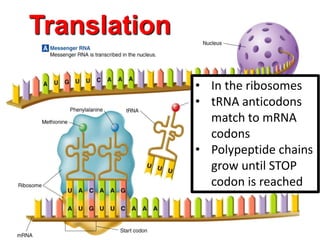
3. The mRNA carries the genetic message to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs through translation.
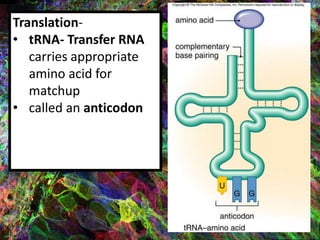
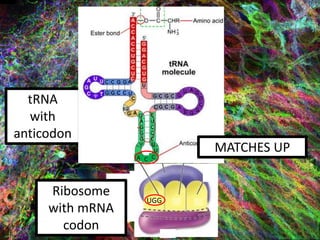
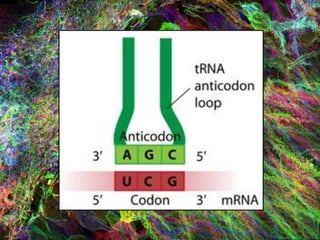
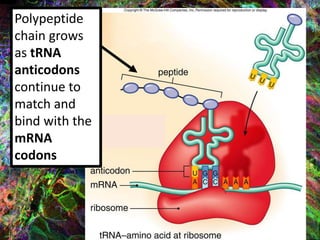
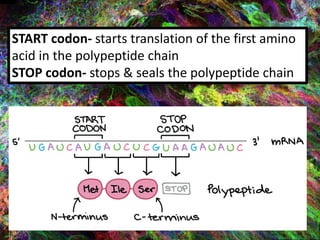
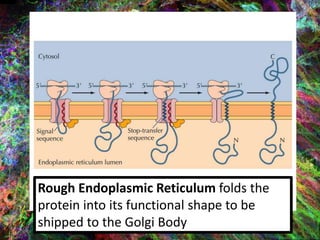
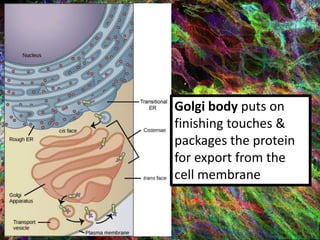
4. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes in the cytoplasm work together to assemble amino acids into proteins based on the mRNA instructions.