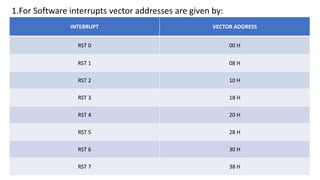
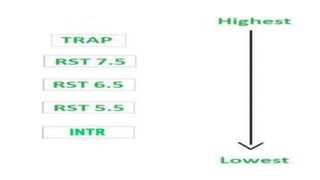
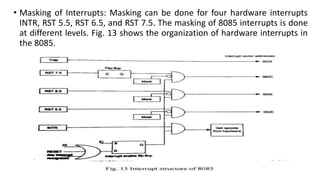
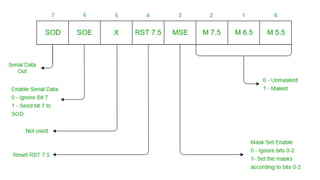
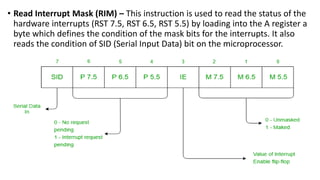
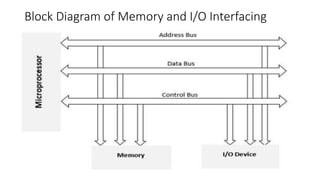
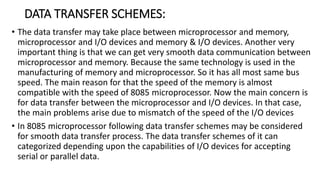
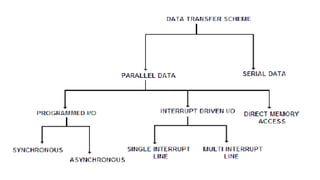
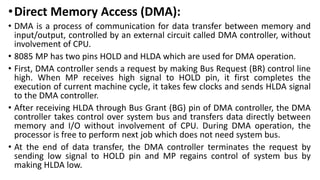
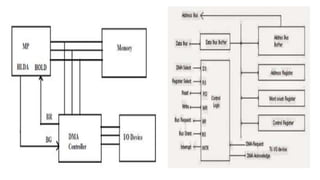
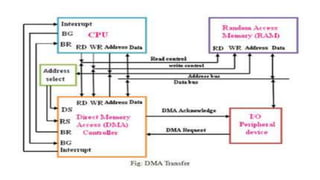
The document discusses different methods of data transfer between a microprocessor and input/output devices. It describes programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA) as common parallel data transfer schemes. For slower I/O devices, asynchronous or interrupt-driven methods are used to avoid wasted processor time waiting for the I/O device. Interrupt-driven I/O allows an I/O device to signal the processor when data is ready via an interrupt request, improving efficiency over programmed I/O.























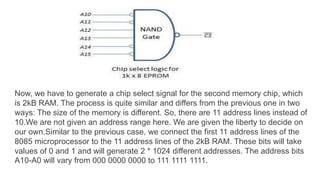







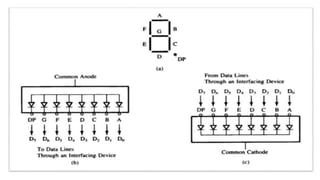

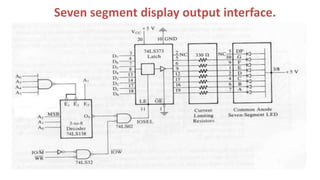
![Fig. 7 shows the example to interface seven segment display
and address decoder with an address of FDH. • The common
anode display is used therefore 0 logic is needed to activate
the segment. • Suppose to display number 4 at seven
segment display, therefore the segment F, G, B and C have to
be activated. • Follows are the instructions to execute it: –
MVI A, 66H [DISPLAY : 4 ]
OUT FDH
Data lines: D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Bits : X 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 = 66 H
Segments: NC G F E D C B A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsce5-210129073512/85/B-sc-e5-2-mp-unit-3-interfacing-69-320.jpg)

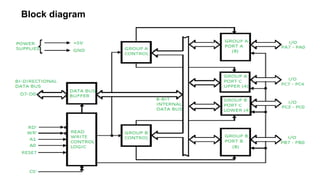

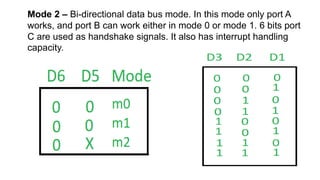


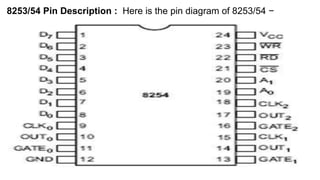
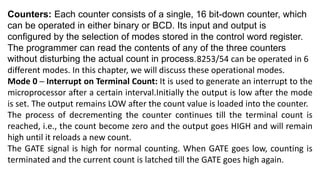
![The timer has three counters, numbered 0 to 2.[5] Each channel can be programmed
to operate in one of six modes. Once programmed, the channels operate
independently.[1] Each counter has two input pins – "CLK" (clock input) and "GATE" –
and one pin, "OUT", for data output. The three counters are 16-bit down counters
independent of each other, and can be easily read by the CPU.[6]
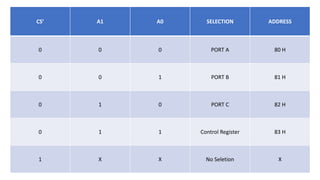
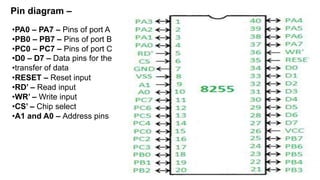
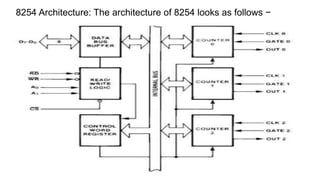
•Data bus buffer contains the logic to buffer the data bus between the microprocessor
and the internal registers. It has 8 input pins, usually labelled as D7..D0, where D7 is
the MSB.Read/write logic has 5 pins, which are listed below. The "X" denotes X is an
active low signal.
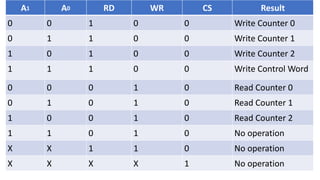
•RD: read signal
• WR: write signal
• CS: chip select signal * A0, A1: address lines
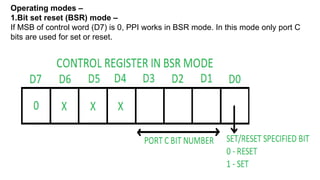
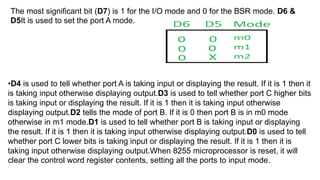
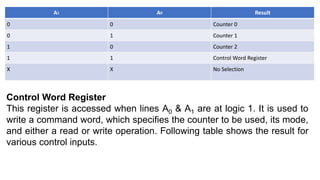
Operation mode of the PIT is changed by setting the above hardware signals. For
example, to write to the Control Word Register, one needs to
set CS=0, RD=1, WR=0, A1=A0=1. The control word register contains the
programmed information which will be sent (by the microprocessor) to the device. It
defines how each channel of the PIT logically works. Each access to these ports
takes about 1 µs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsce5-210129073512/85/B-sc-e5-2-mp-unit-3-interfacing-83-320.jpg)






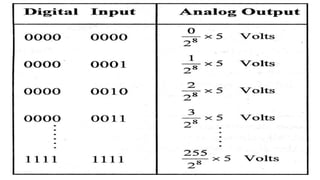

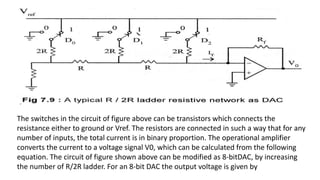

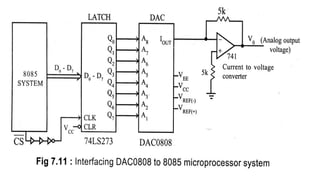
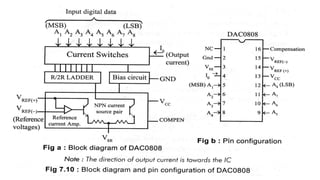
![bus and it requires only two control signals: Chip Select (CS) and
Chip Enable (CE). [No handshake signals are necessary for interfacing
a DAC. The time between loading two digital data to DAC is
controlled by software time delay]. The DAC0808 of National
Semiconductor Corporation is an example of 8-bit DAC without
internal latch and I to V converting amplifier. The internal block
diagram and the pin configuration of DAC0808 are shown in figure
below.The DAC0800 can be interfaced to 8085 system through an 8-
bit latch as shown in figure below. The chip select (CS) signal from
the decoder of the microprocessor system is delayed and inverted to
clock the latch. If the DAC is memory mapped then the CS is from
memory decoder. If the DAC is I/O mapped then CS is from I/O
decoder.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsce5-210129073512/85/B-sc-e5-2-mp-unit-3-interfacing-98-320.jpg)