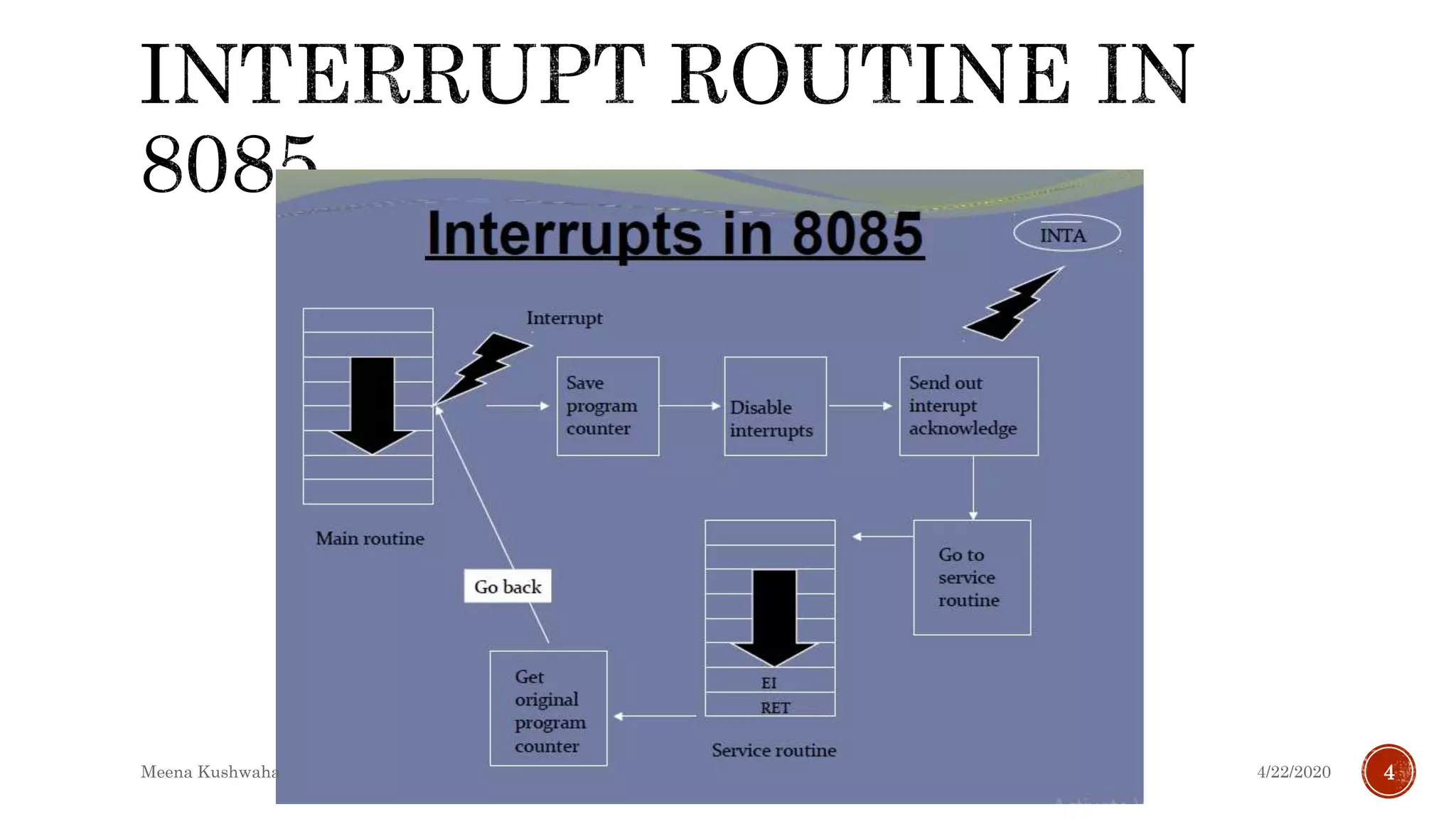
The document discusses interrupts in microprocessors. It defines interrupts as signals initiated by external devices to get the processor's attention. When an interrupt occurs, the processor suspends the current program and jumps to an interrupt service routine (ISR) before returning to the main program. Interrupts can be classified as maskable, non-maskable, vectored, non-vectored, hardware, or software. The 8085 microprocessor has specific interrupt pins and instructions to manage interrupts.



![Interrupts can be classified into two types:
Maskable Interrupts (Can be delayed or Rejected)
Non-Maskable Interrupts (Can not be delayed or Rejected)
Interrupts can also be classified into:
Vectored : The address of the subroutine is already known to the
Microprocessor
Non-vectored (the address of the service routine needs to be
supplied externally by the device)
Interrupts can also be classified into:
Hardware Interrupt [TRAP, RST7.5, RST6.5, RST5.5,INTR]
Software Interrupt [RST n]
4/22/2020Meena Kushwaha 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8085interrupts-200426050323/75/8085-interrupts-5-2048.jpg)













