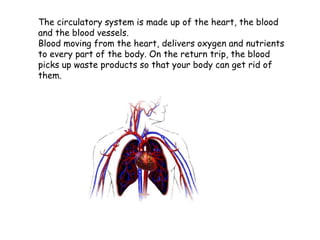
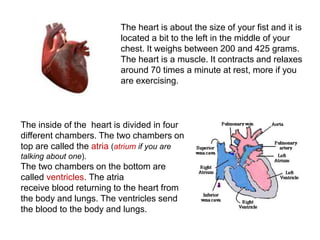
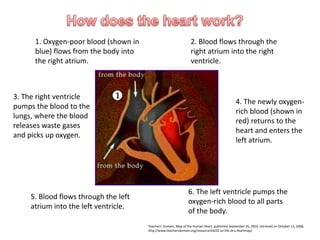
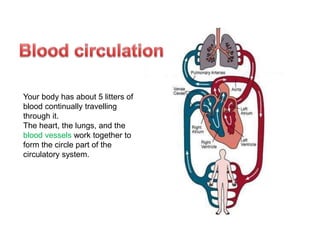
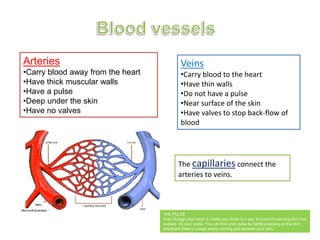
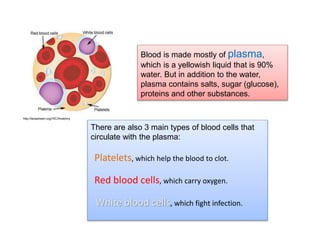
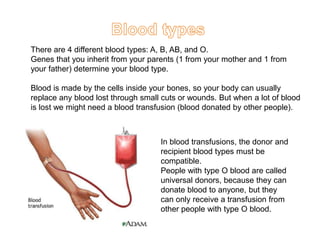
The circulatory system is made up of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. The heart pumps blood through the body via arteries and returns it via veins. The blood delivers oxygen and nutrients throughout the body and picks up waste. The heart has four chambers - two upper atria and two lower ventricles - that work together to pump blood through two circuits, one for the lungs and one for the body. Oxygen-poor blood enters the right side of the heart and is pumped to the lungs, where it receives oxygen and returns to the left side to be pumped throughout the body.