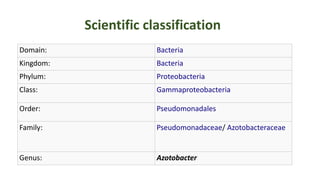
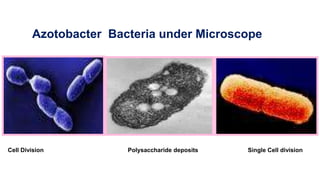
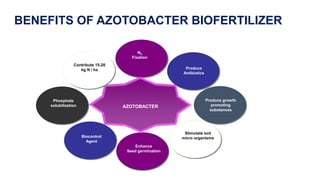
Azotobacter is a genus of nitrogen-fixing bacteria that was discovered in 1901. It plays an important role in the nitrogen cycle by fixing atmospheric nitrogen and making it available to plants. Azotobacter species are used in biofertilizers to increase soil fertility and stimulate plant growth. They produce auxins and other substances that promote plant development. Recent research has shown that Azotobacter isolates can produce the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) when supplied with tryptophan, and that different concentrations of tryptophan and IAA can both stimulate and inhibit plant root growth.