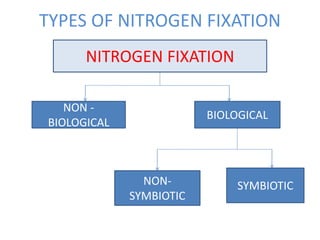
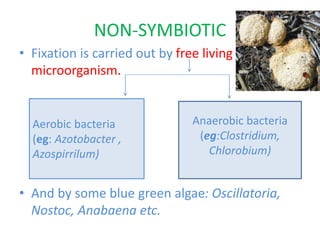
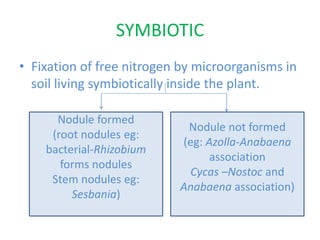
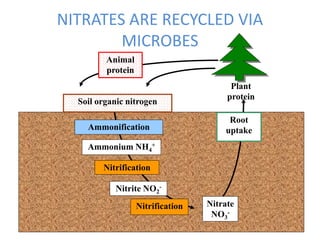
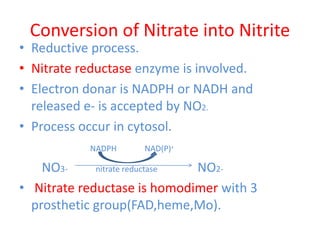
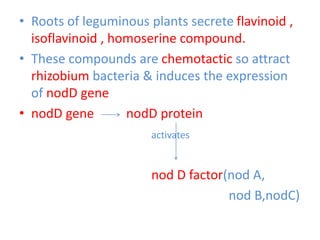
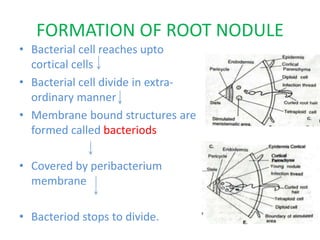
This document discusses nitrogen fixation in plants, specifically alfalfa. It describes how nitrogen exists in the atmosphere, mostly as N2, which plants cannot use directly. It then discusses how nitrogen is essential for plant growth and metabolism. The document outlines two types of nitrogen fixation - biological and non-biological. Biological fixation is further divided into symbiotic and non-symbiotic types. Much of the document focuses on symbiotic nitrogen fixation between leguminous plants and rhizobia bacteria, including the formation of root nodules and nodulation factors.