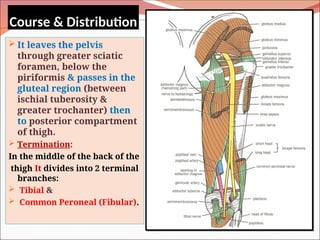
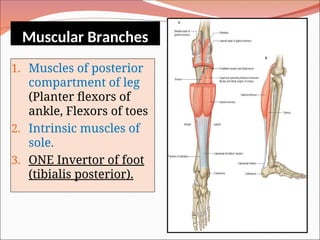
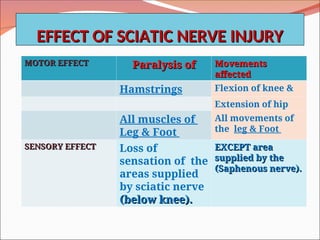
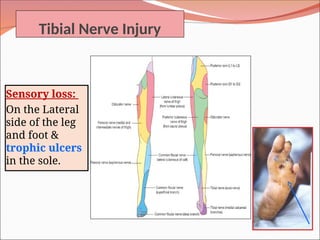
The document outlines the anatomy, functions, and potential injuries of the sciatic nerve, including its origin from the sacral plexus and branches. It details the manifestations of sciatic nerve injuries, such as motor and sensory effects, as well as specific conditions like sciatica and common peroneal nerve injury. Both tibial and common peroneal nerve injuries are discussed, highlighting their clinical features and the implications of such injuries on movement and sensation.