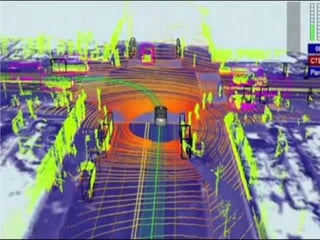
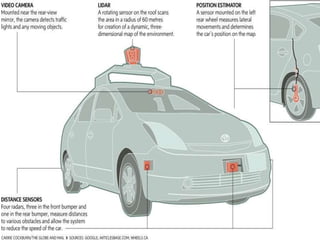
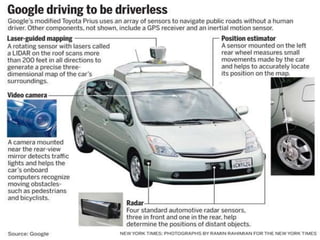
An autonomous vehicle uses sensors like radar, LIDAR, GPS and computer vision to navigate without human input. Radar uses radio waves to determine distance, speed and track objects. LIDAR uses lasers to precisely map physical features. GPS provides maps, directions and real-time traffic data. Computer vision allows the vehicle to analyze images of the road and environment. Together these technologies allow autonomous vehicles to drive itself, potentially reducing accidents.