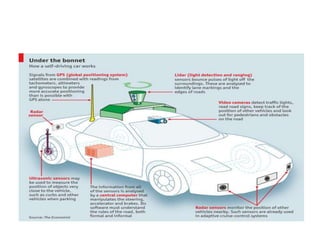
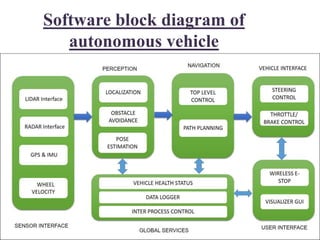
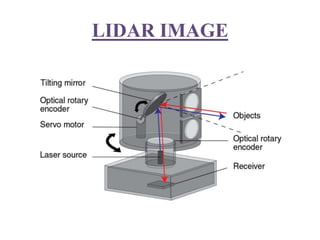
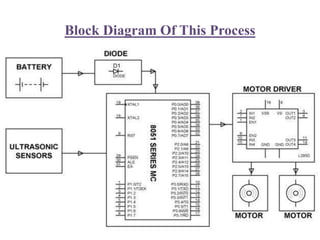
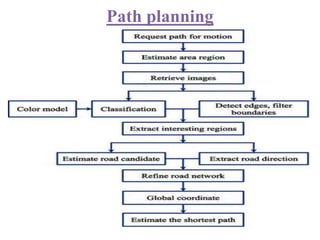
The document presents an overview of the technology and principles behind autonomous vehicles, focusing on Google's self-driving car project and its components, such as sensors (lidar, radar, GPS) and software architecture. It discusses advantages like reduced accidents and efficient highway use, as well as challenges such as data noise and testing difficulties. The conclusion highlights the need for rigorous safety standards and the limitations of current machine learning systems in ensuring reliability.