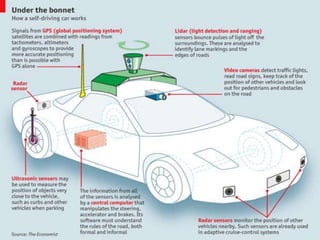
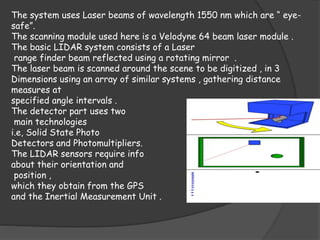
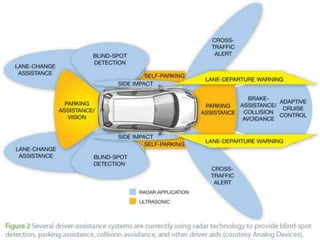
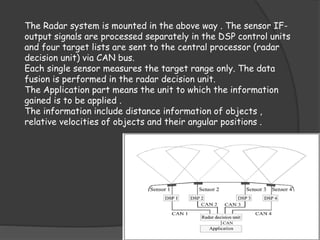
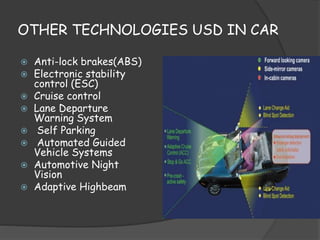
The document discusses autonomous or self-driving cars. It describes how autonomous cars use sensors like LIDAR, radar, cameras and ultrasonic sensors along with GPS and an inertial measurement unit to navigate without human intervention. The central computer combines data from these sensors to construct a 3D map of the vehicle's surroundings and control systems like steering and braking. Major companies developing autonomous vehicle technology include Google, Audi, BMW, Ford and General Motors.