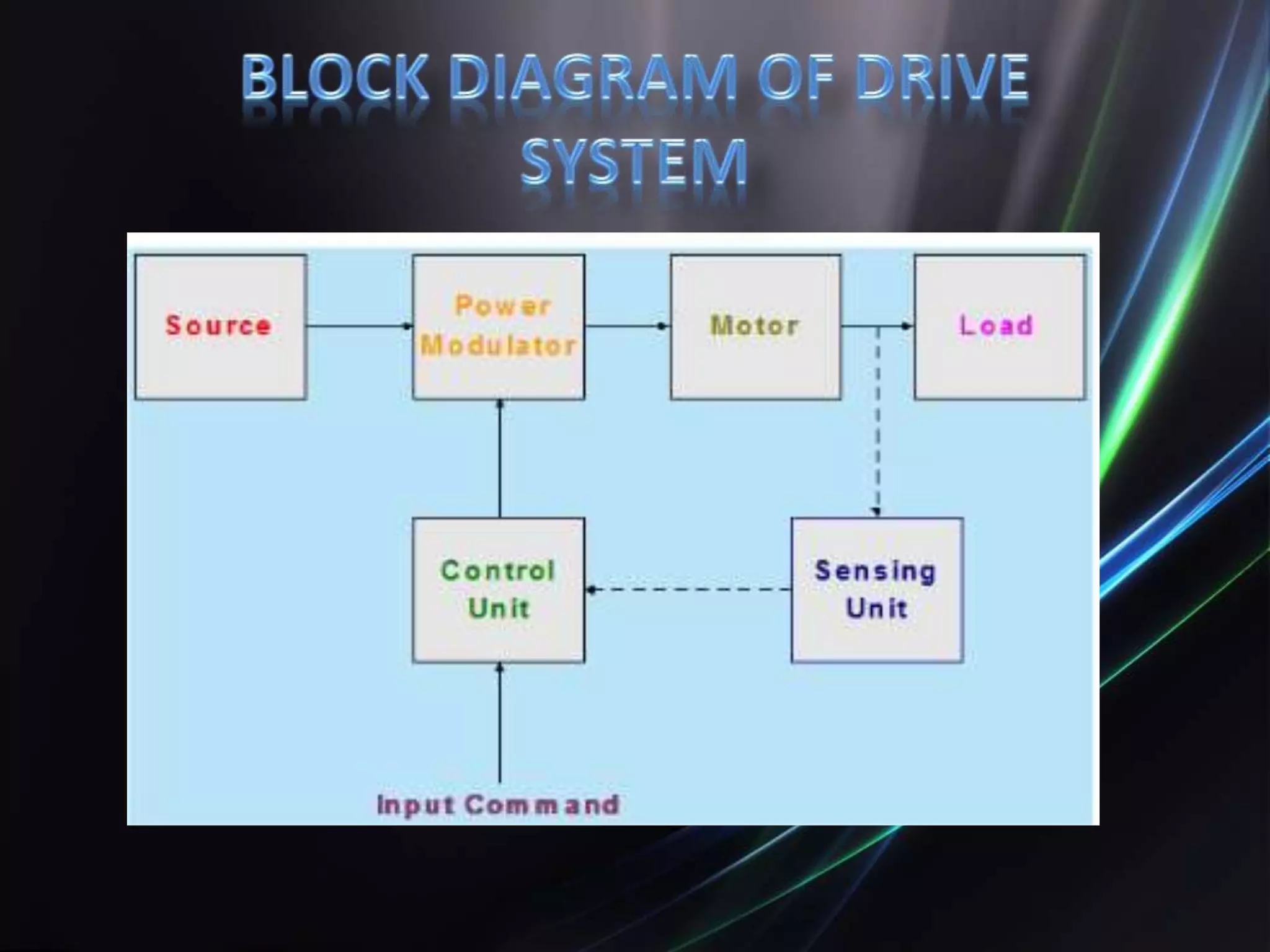
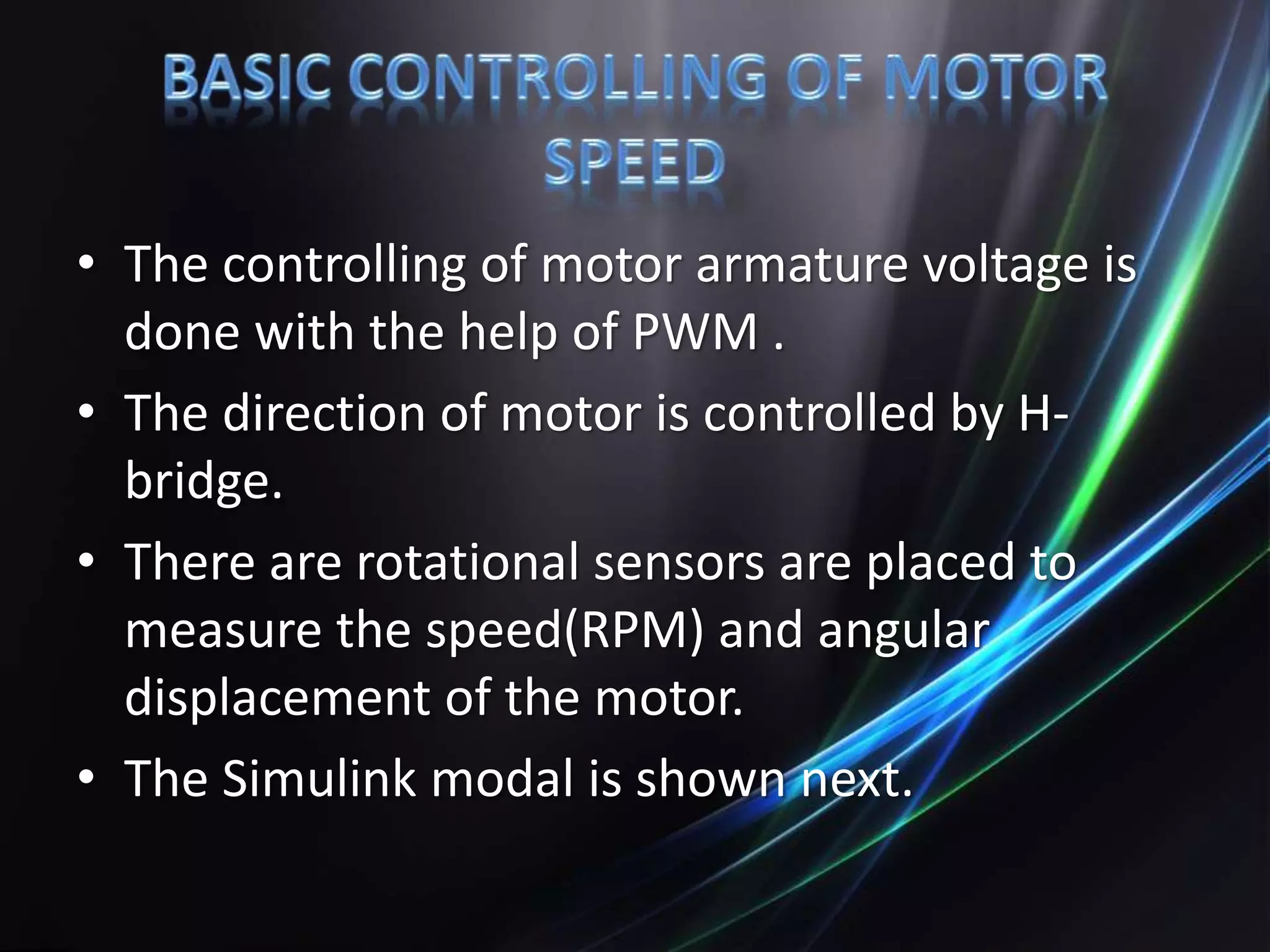
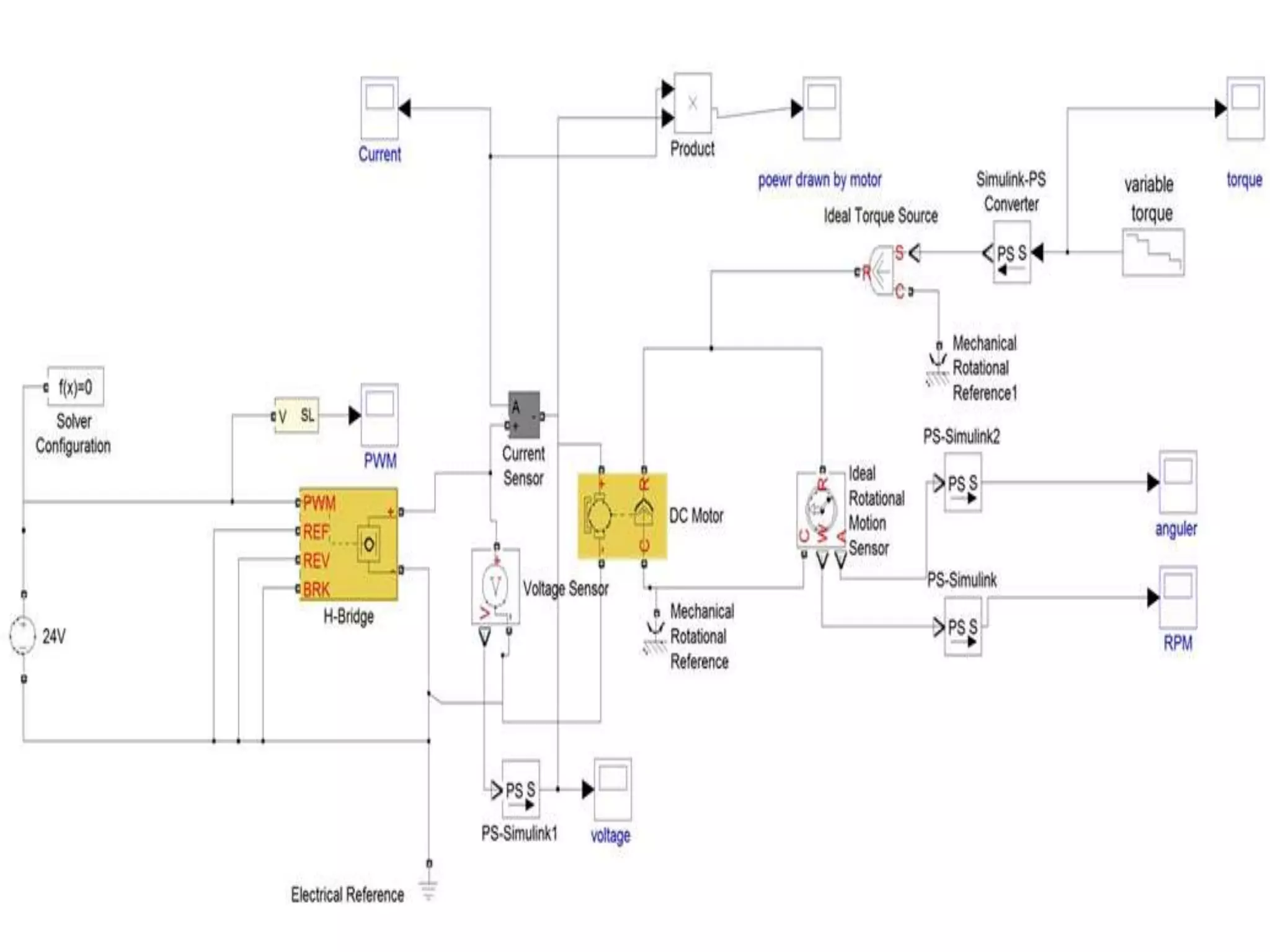
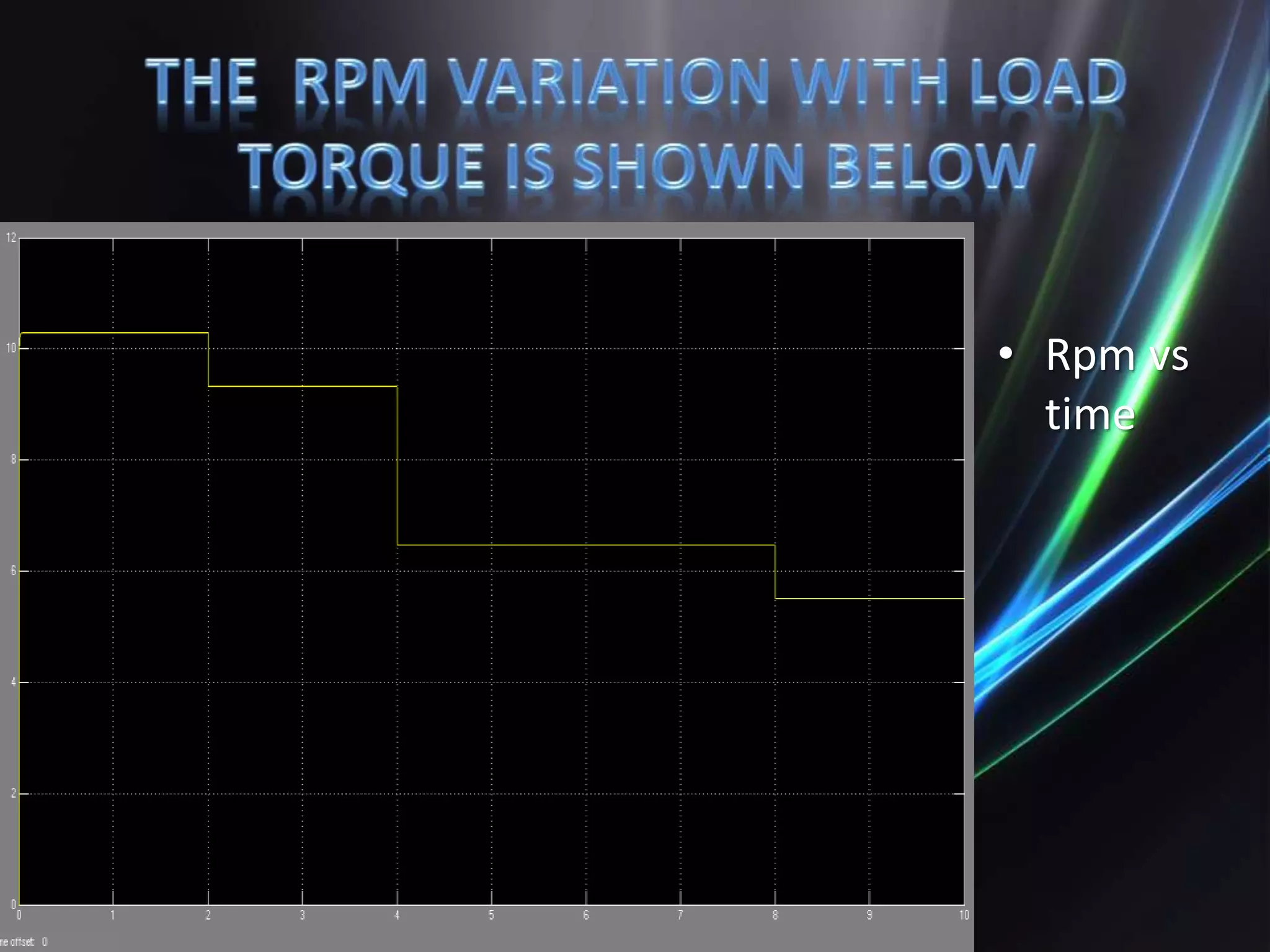
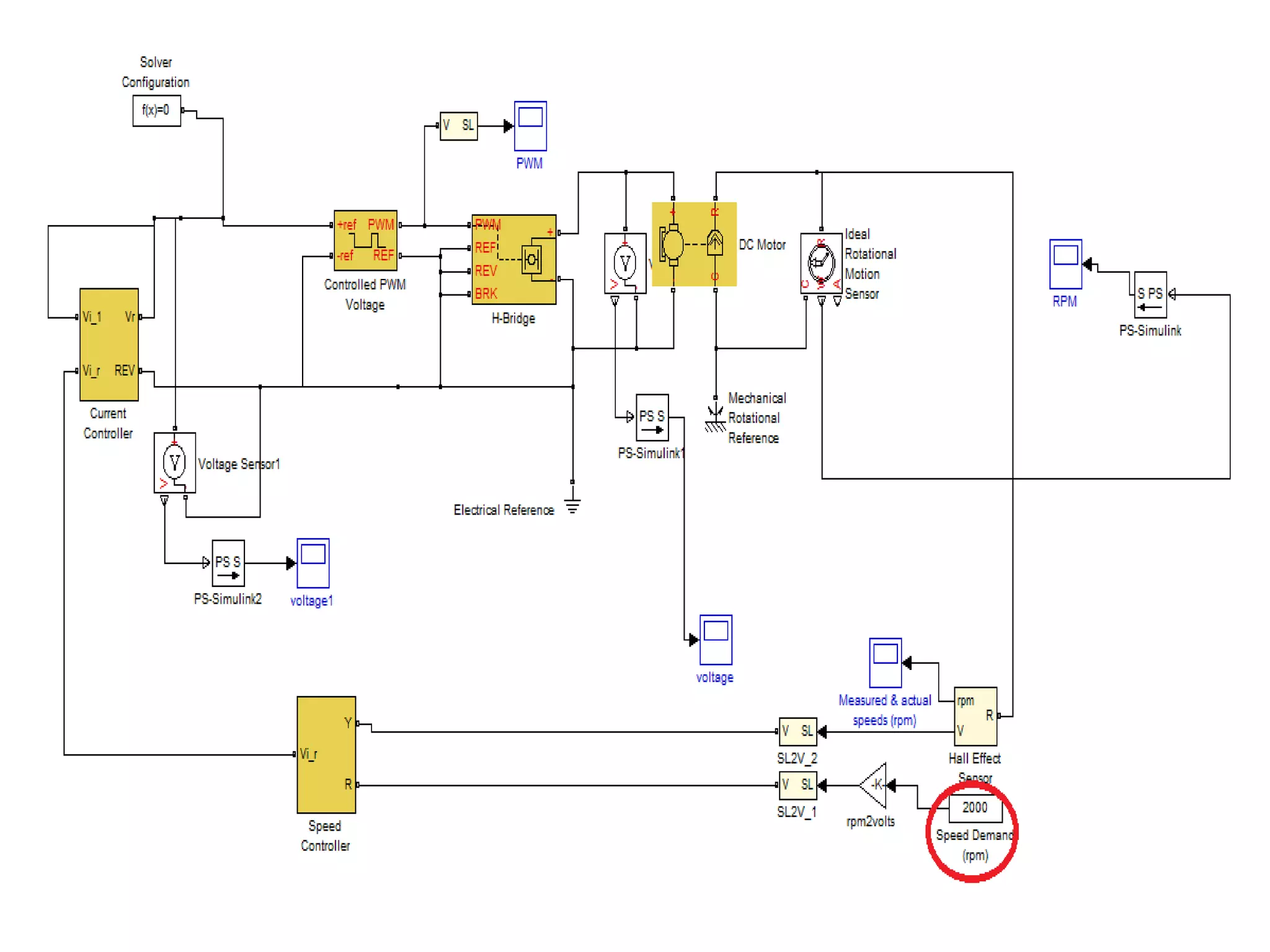
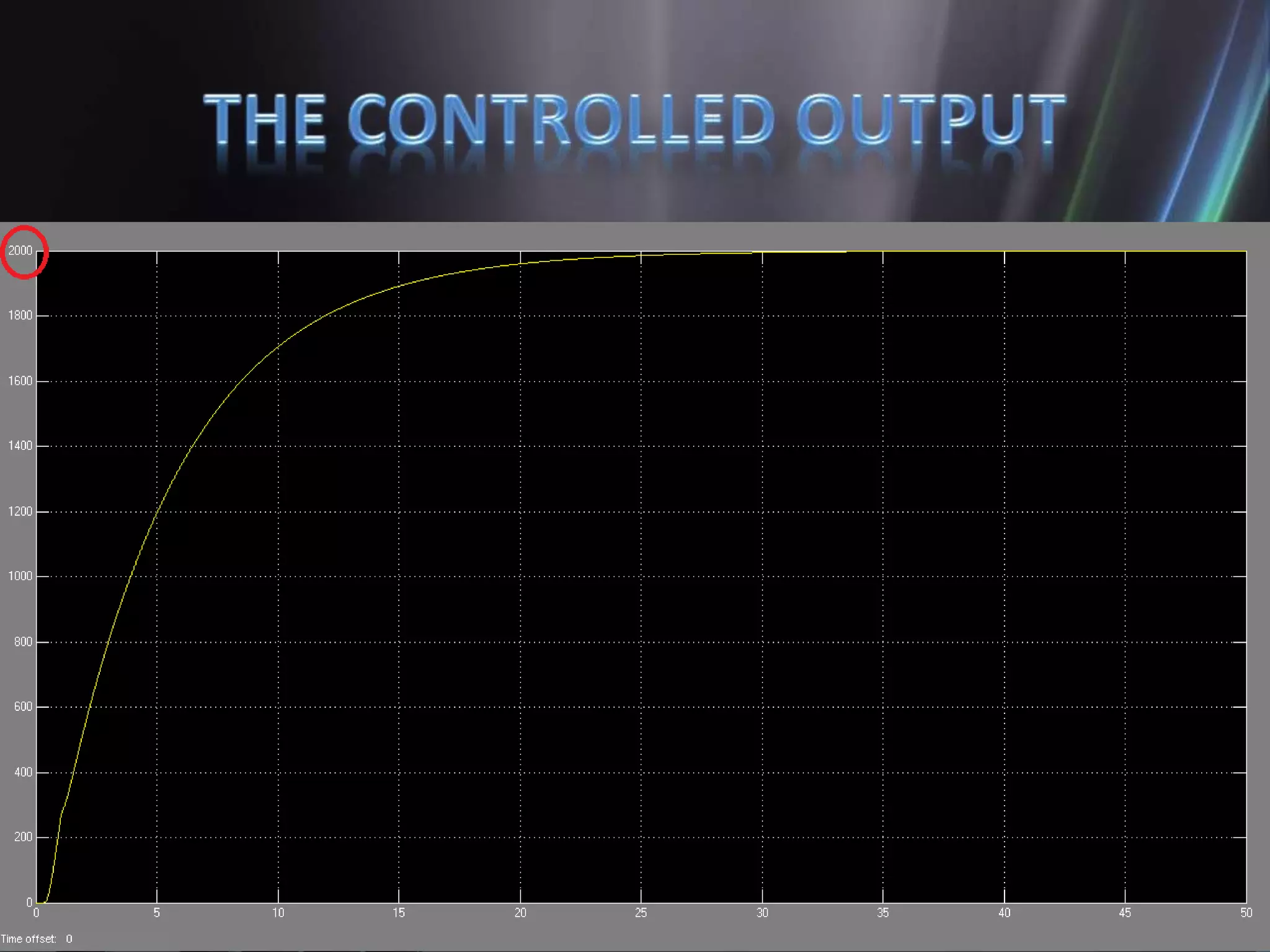
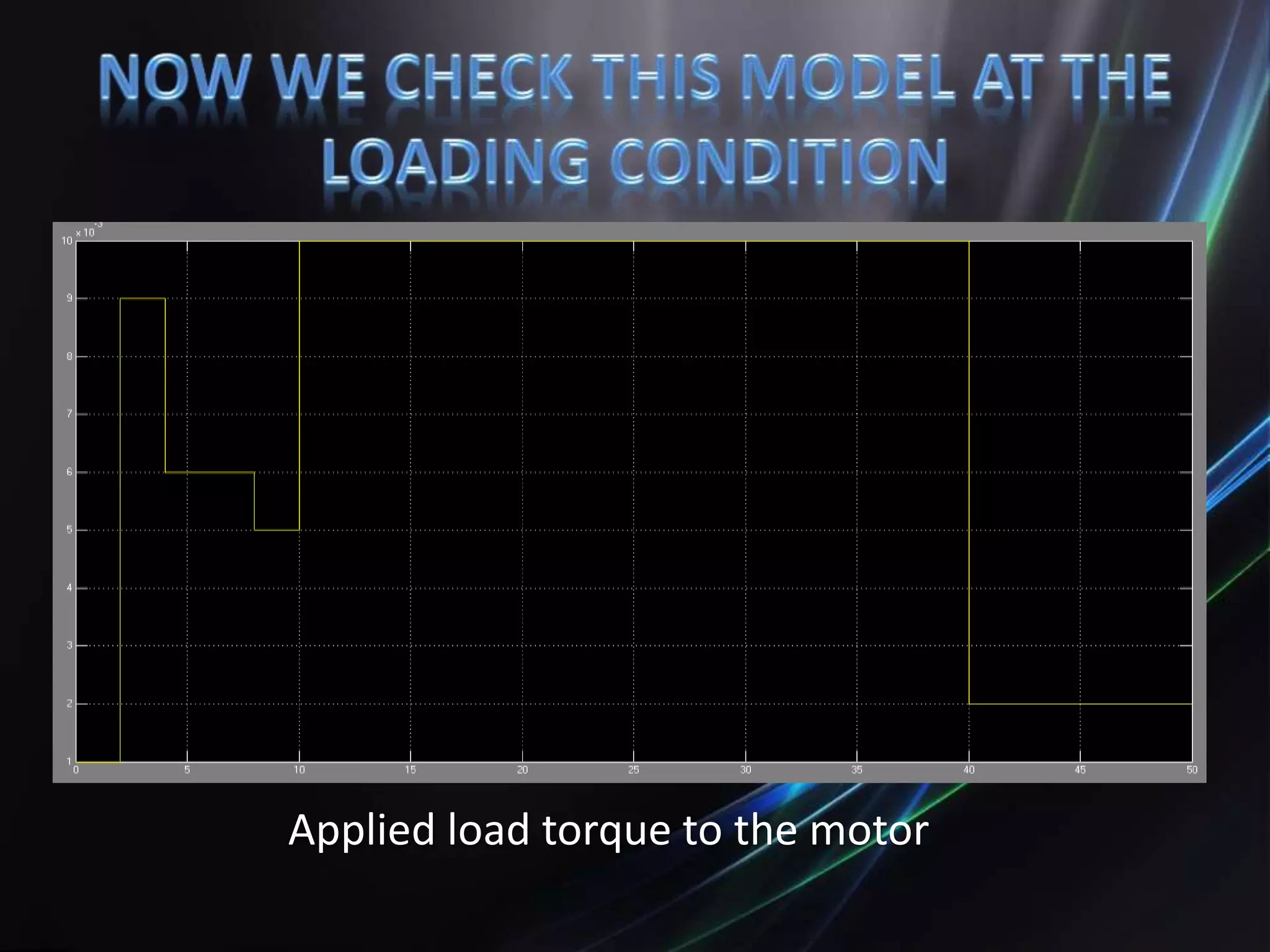
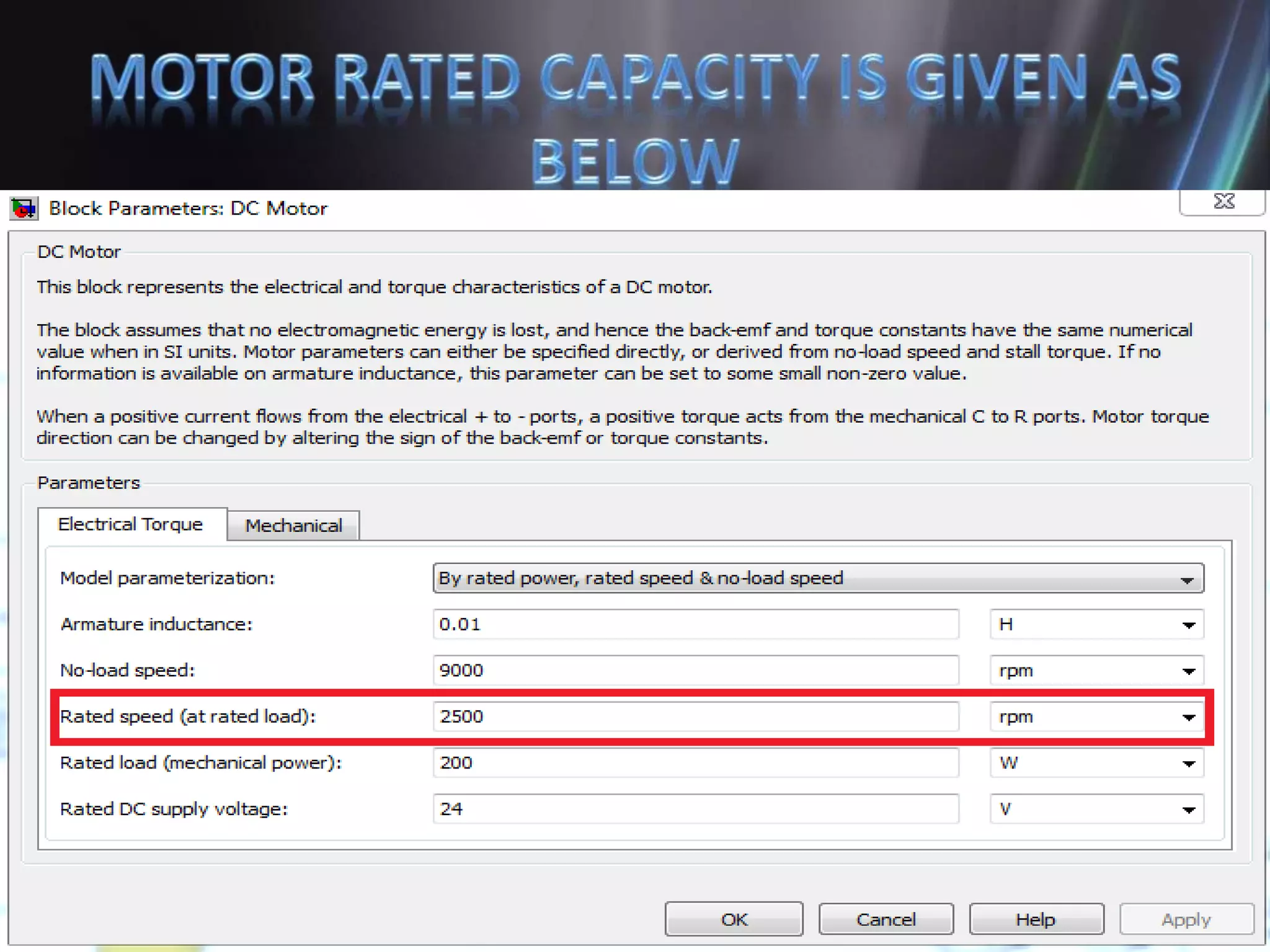
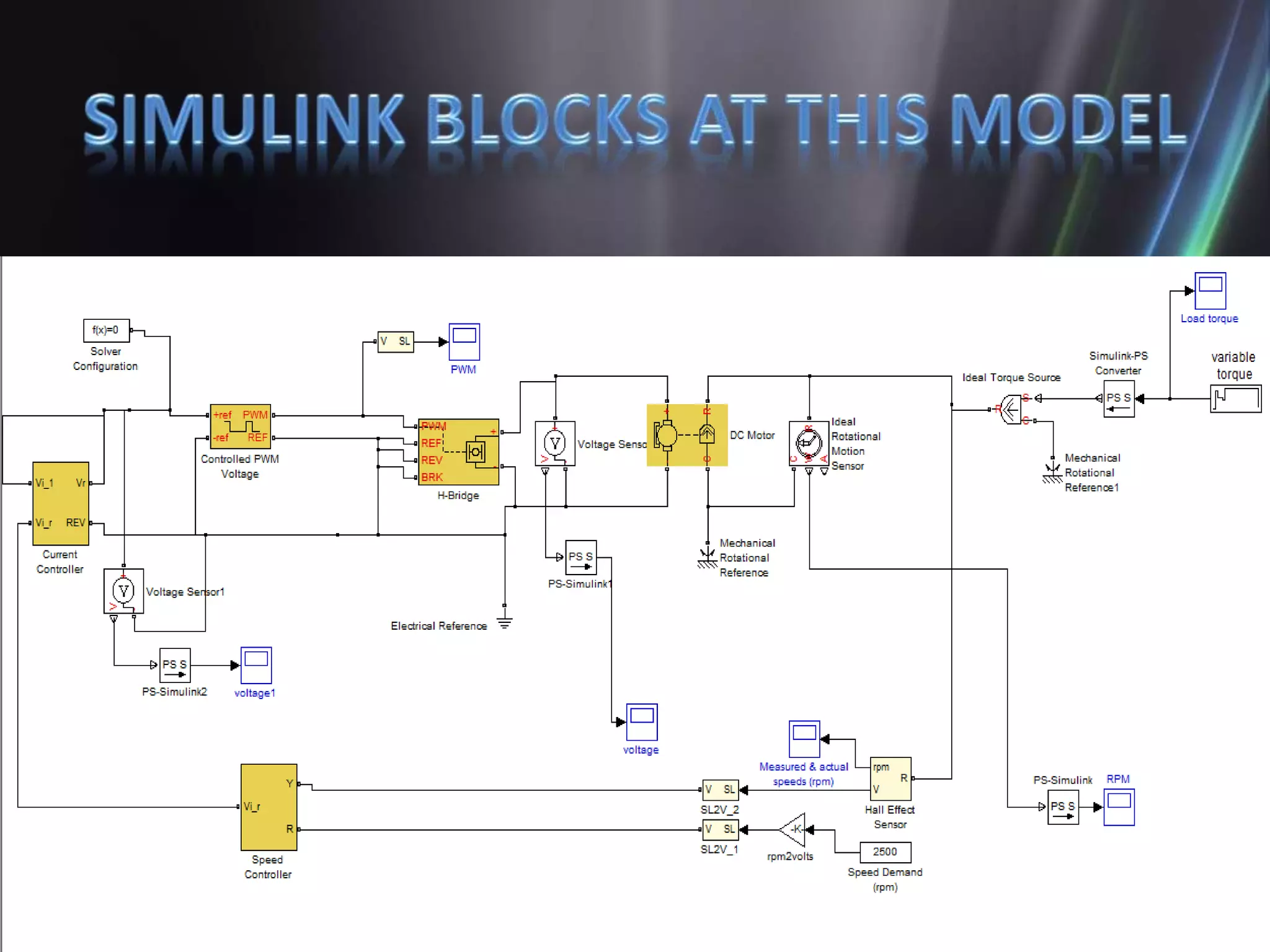
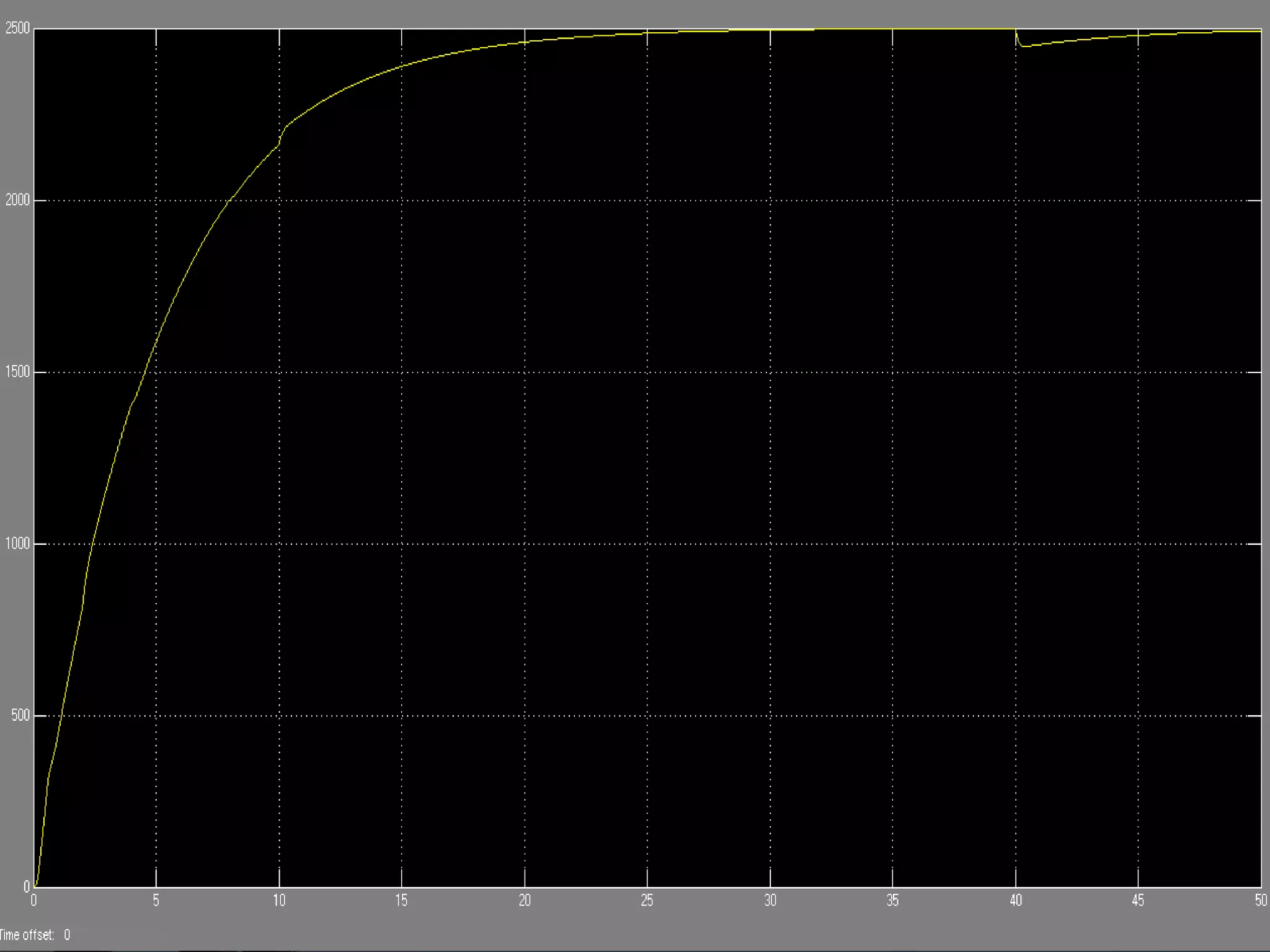
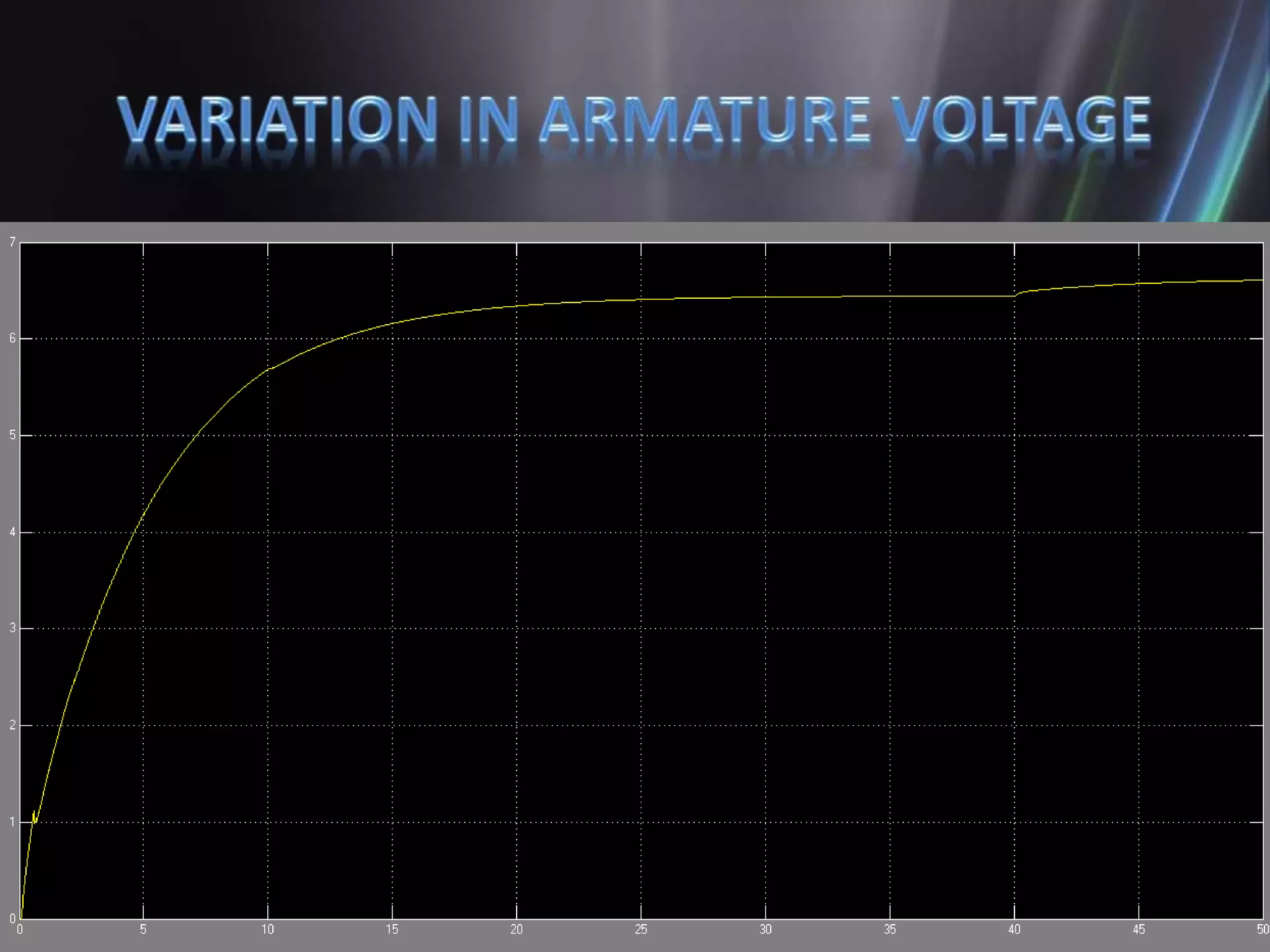
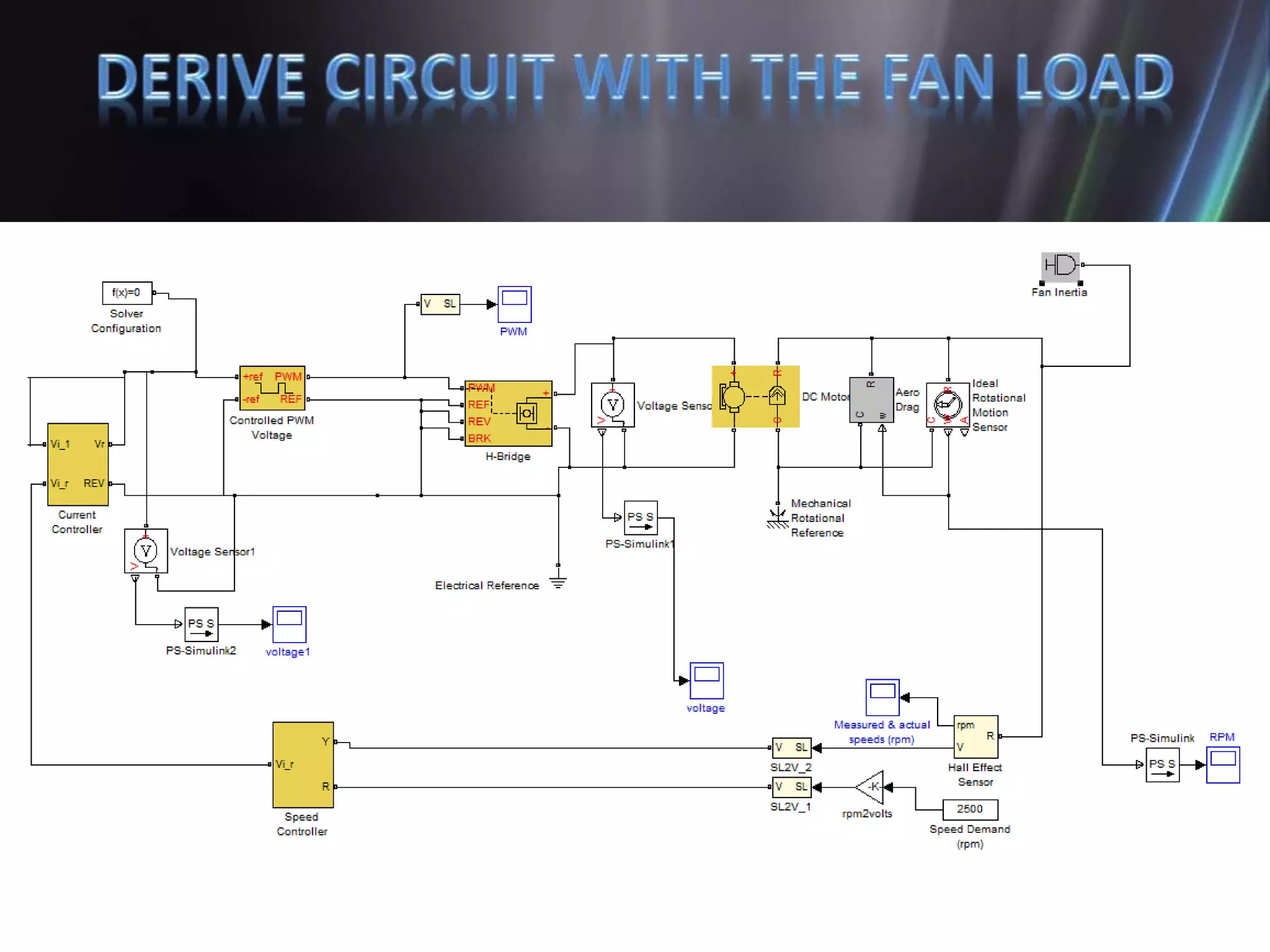
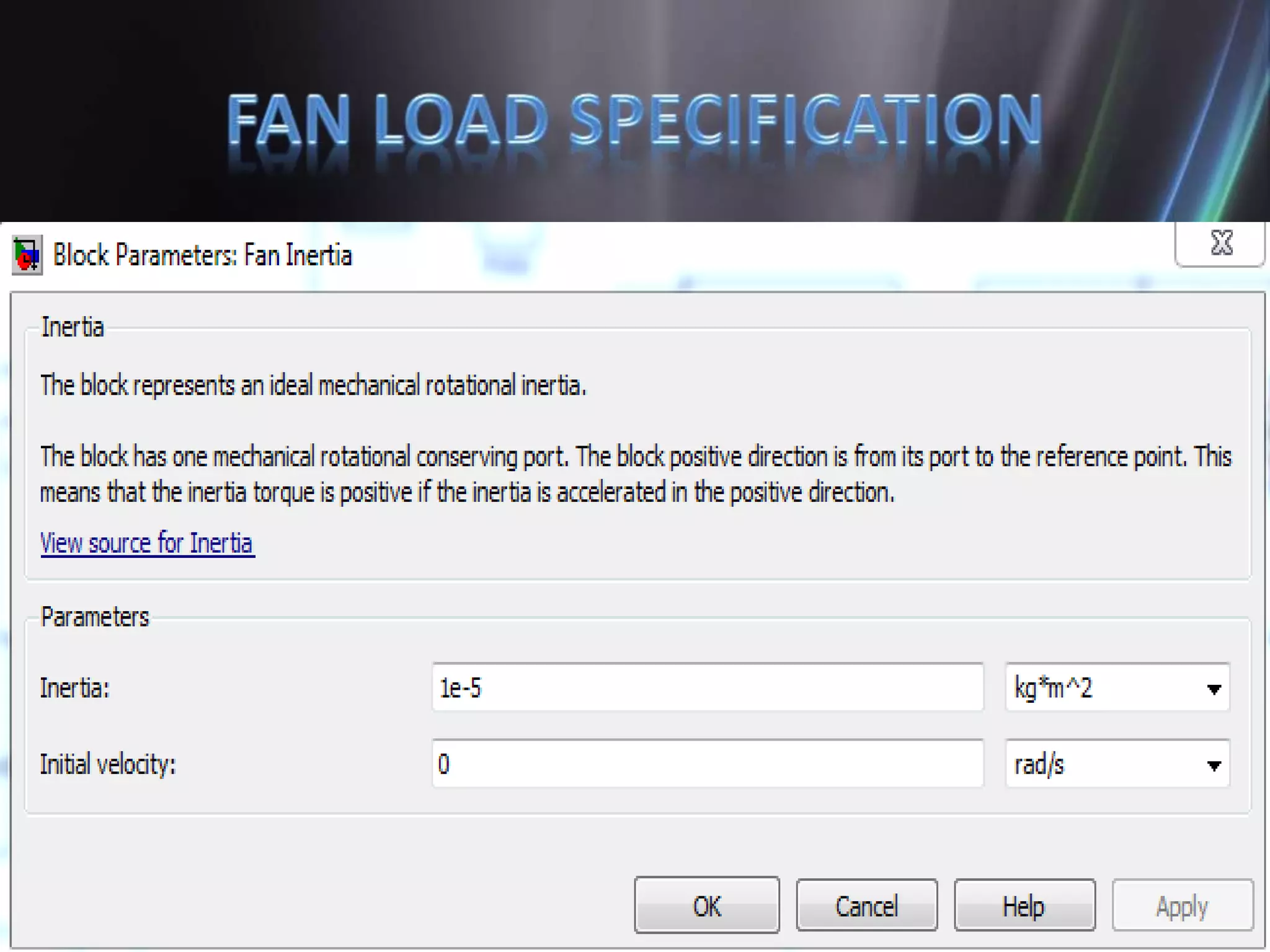
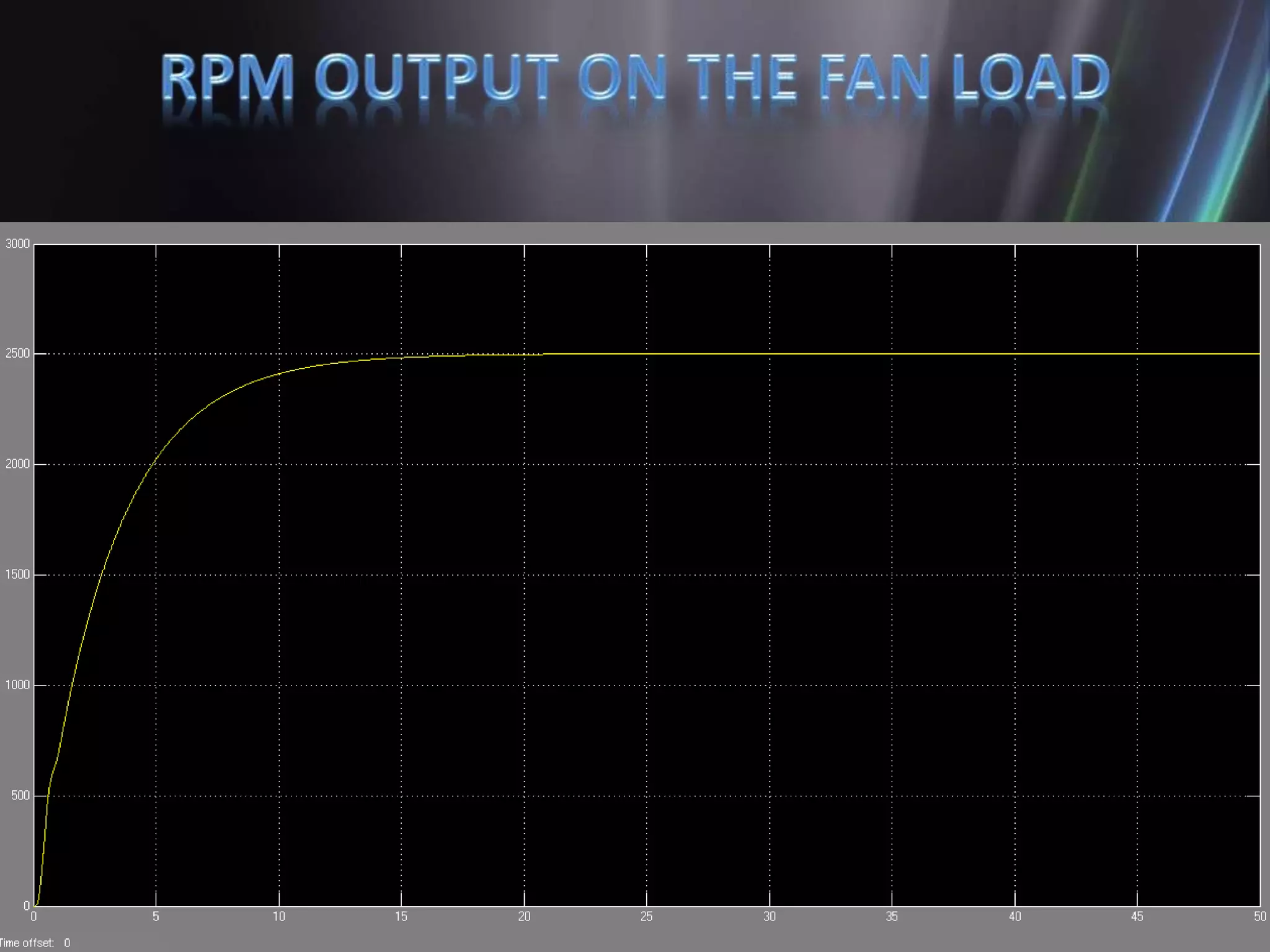
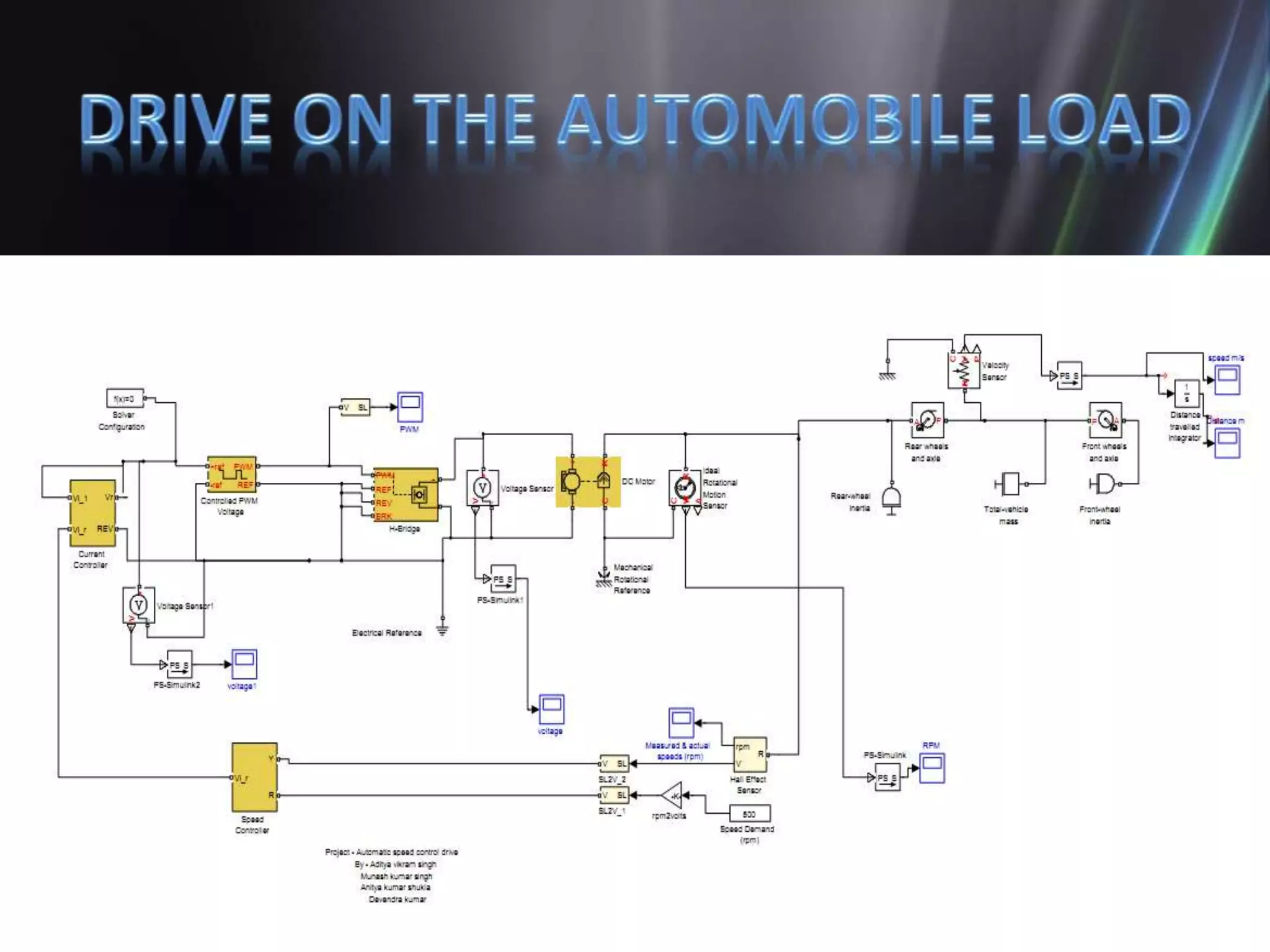
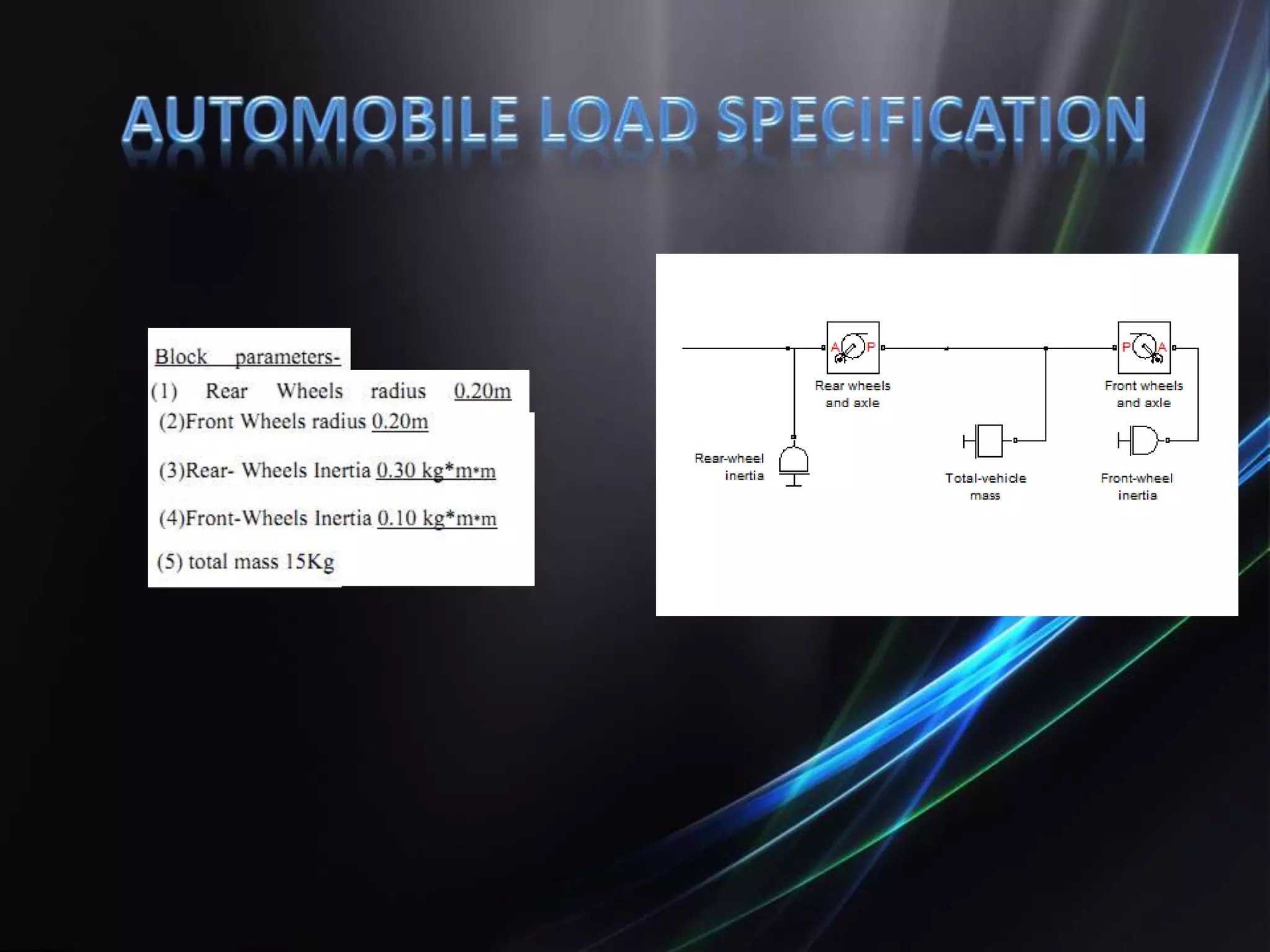
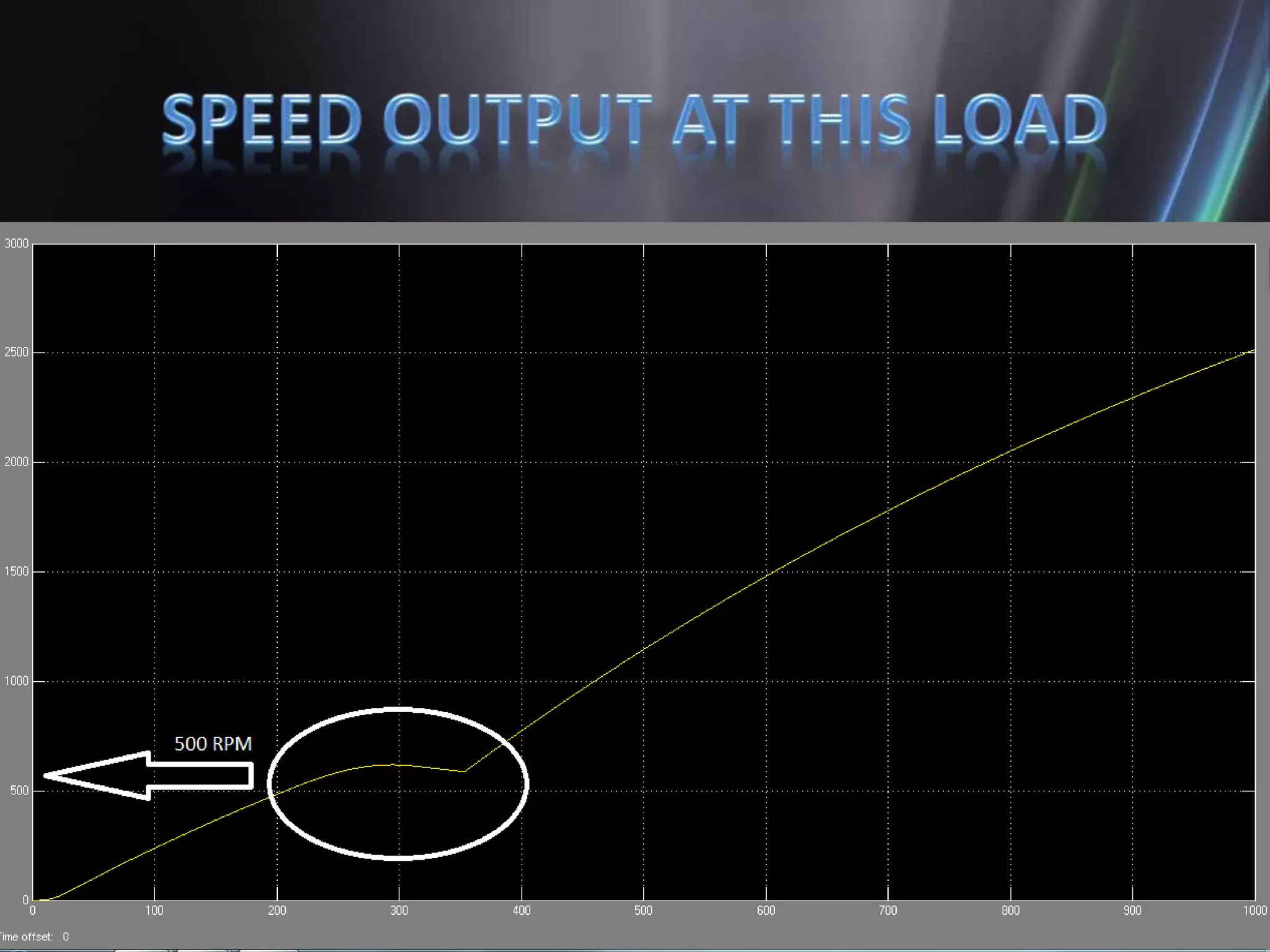
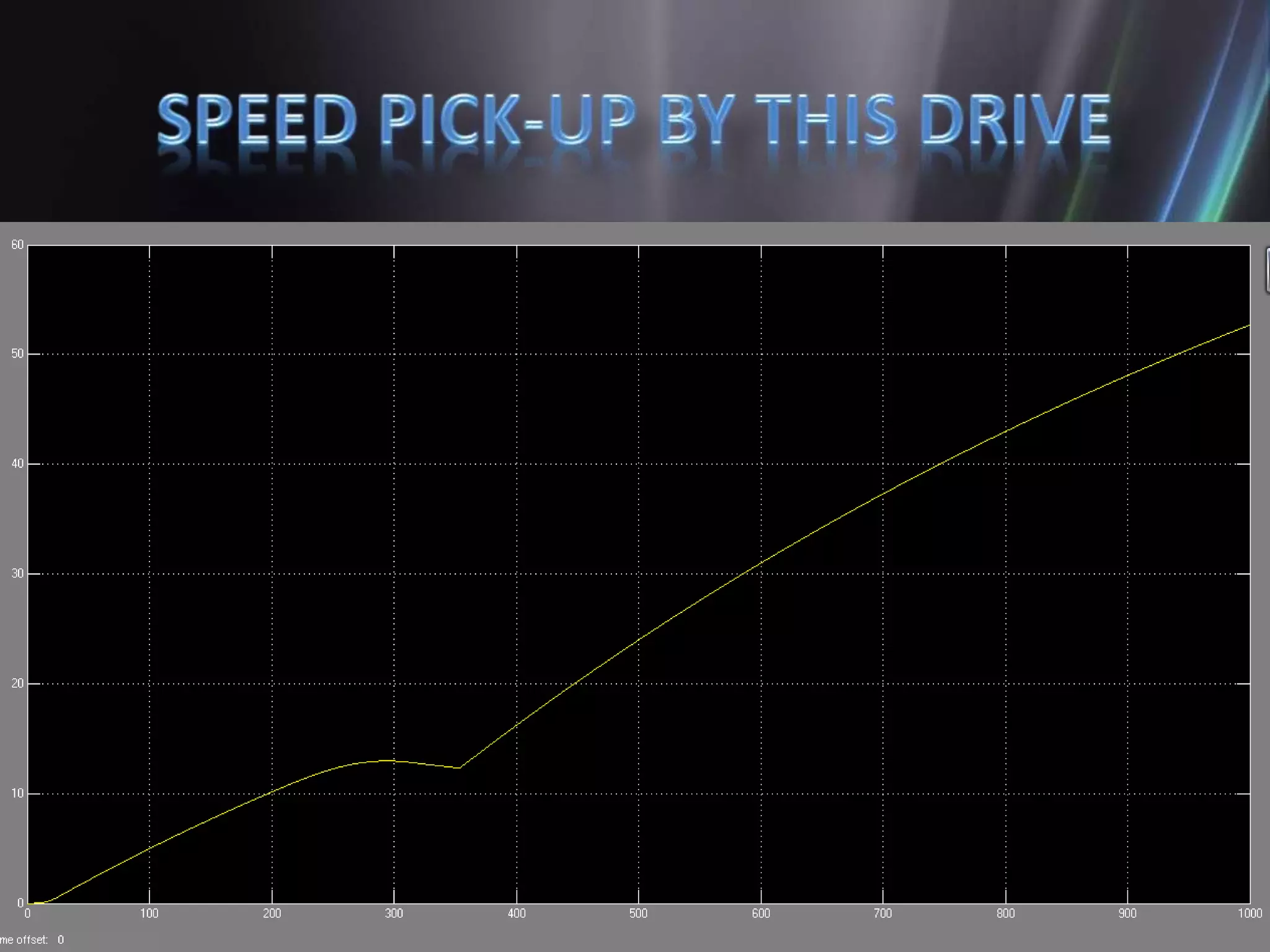
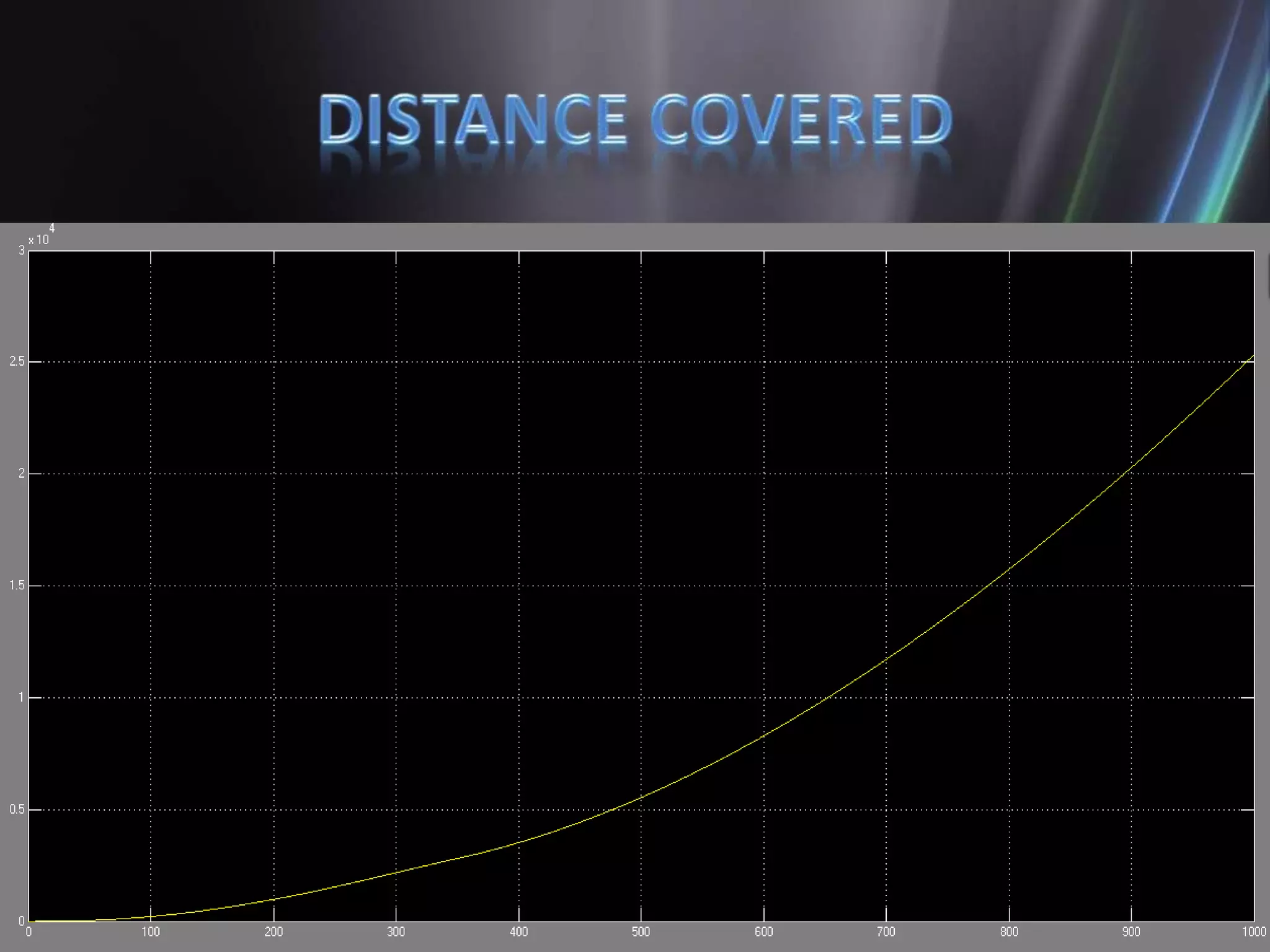
This document discusses the design and implementation of an adjustable speed drive (ASD) to control the speed of DC motors using PWM and an H-bridge. It highlights the challenges faced in maintaining constant motor speed under varying load conditions using feedback from rotational sensors, specifically Hall effect sensors. The findings indicate that while the drive works well for fan loads, it struggles to maintain control under automobile loads, suggesting potential improvements through automatic control mechanisms like rotational detectors.