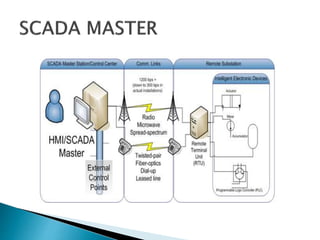
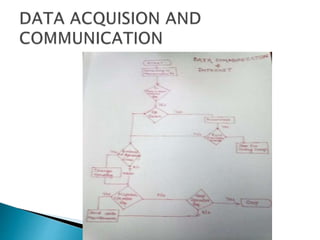
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes. The document discusses the history and components of SCADA, including how it collects data from sensors using RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and sends control signals. It also describes how SCADA is important for maintaining efficiency at power plants by remotely monitoring operations and automating processes to reduce costs. SCADA plays a key role in hydroelectric power plants by integrating maintenance systems and enabling remote monitoring and control to optimize maintenance scheduling.