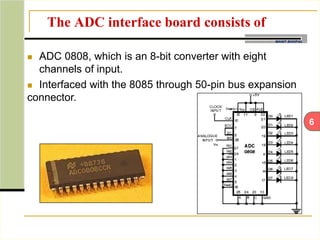
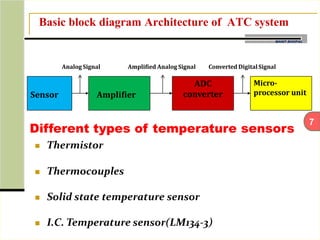
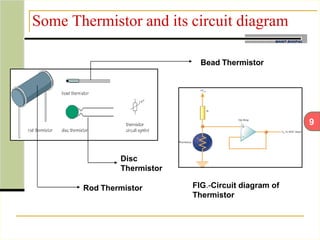
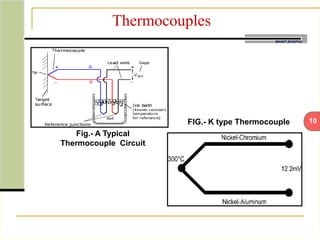
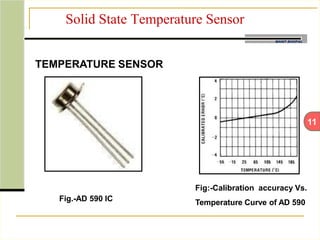
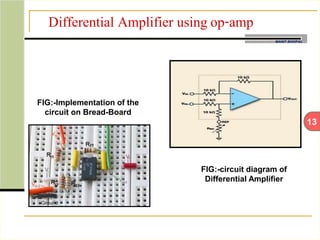
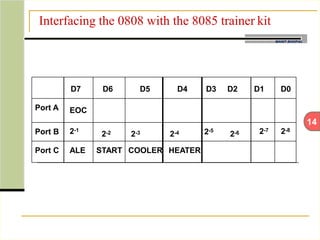
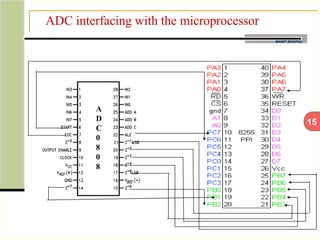
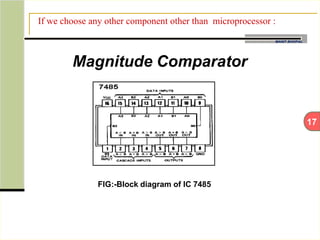
This document describes an automatic temperature control system using an 8085 microprocessor. The system uses an AD590 temperature sensor, differential amplifier, ADC0808 converter, and 8085 microprocessor to monitor and control the temperature. It aims to minimize manual intervention and control temperature in industrial plants. The system works by comparing the measured temperature to upper and lower setpoints and turning the heater or cooler on/off accordingly to maintain the temperature within the limits.