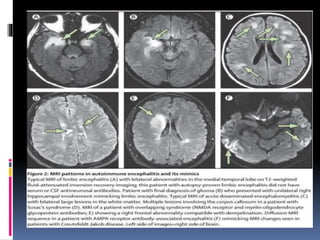
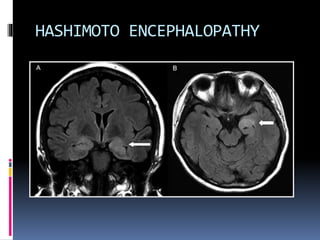
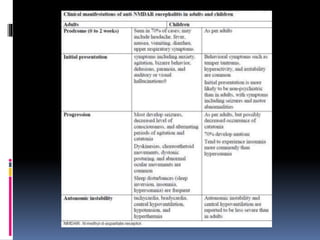
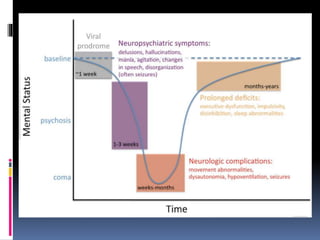
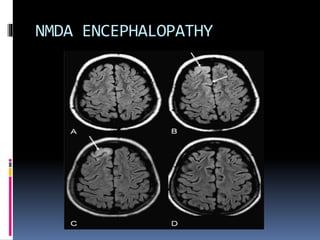
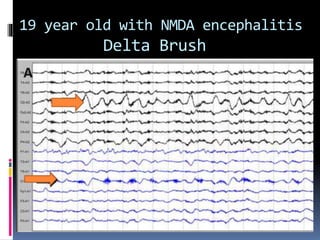
This document discusses several types of autoimmune encephalitis, including Hashimoto's encephalopathy, NMDA encephalitis, and limbic encephalitis. Hashimoto's encephalopathy is defined by the presence of thyroid peroxidase antibodies in patients with encephalitis that responds to steroids. It can cause non-specific neurological symptoms. NMDA encephalitis commonly affects young women and can cause psychiatric issues, decreased consciousness, and movement disorders. Diagnosis involves detecting NMDA receptor antibodies in CSF or serum. Limbic encephalitis involves inflammation of limbic structures and is associated with antibodies against proteins like LGI1; it typically causes memory loss, behavioral changes and seizures in older patients.






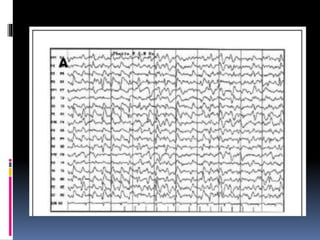







![ In 1968 , as Para neoplastic syndrome
median age of patients is 60 years
Severe short term memory loss
hyponatremia and myoclonic-like
movements, described as faciobrachial
dystonic seizures
Other antibodies associated- antibodies
against intracellular antigens (eg, Hu, CRMP5,
Ma2) or against cell surface or synaptic
proteins (eg (AMPA) [GABA(B)] [mGluR5])
Ophelia syndrome (- association with
Hodgkin’s lymphoma)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autoimmuneencephalitis-180320183251/85/Autoimmune-encephalitis-21-320.jpg)